C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 à 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + 36 ATP
advertisement

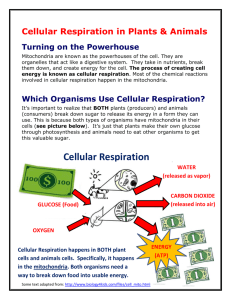
Name: ______________________________________ Unit 5: Photosynthesis & Respiration Per. _______ respiration photosynthesis autotroph o ex: heterotroph o ex: ATP Photosynthesis summary equation: parts of visible spectrum used/ reflected chromatography light reactions (photophase) o grana o photolysis o oxygen released dark reactions o carbon fixation o stroma o PGA PGAL glucose starch alternative pathways o guard cells o stoma(ta) rate of photosynthesis affected by: Aerobic Respiration summary equation: two phases o glycolysis (anaerobic) in cytoplasm does not require oxygen produces pyruvic acid + 2 ATP (net) o aerobic phase in mitochondria carbon dioxide produced oxygen accepts hydrogen to make water produces 34 ATP (total= 36) Anaerobic Respiration summary equations does not use oxygen alcoholic fermentation (yeasts) lactic acid fermentation (muscle cells) produces 2 ATP for each glucose 1 Photosynthesis I. Capturing the Energy in Light Energy Relationships 1. Photosynthesis: CHLOROPLAST: energy from sun converts inorganic to organic compounds 2. Respiration: MITOCHONDRIA: convert energy from organic compounds to form compounds more easily used by cells. Biochemical pathways: a series of reactions, in which the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. ex. photosynthesis ***all life depends on the sun*** autotrophs use CO2 and H2O to make glucose giving off O2 heterotrophs use O2 and C6H 12O6 giving off CO2 and H2O materials are constantly recycling energy not recycled; must be supplied constantly Autotrophs vs. Heterotrphs make own food from inorganic cannot make their own compounds organic compounds ex. green plants, algae, blue-green bacteria ex. animals, fungi, some bacteria, protists some prokaryotes Energy is the ability to do work Work for a cell includes growth & repair, active transport across cell membranes, reproduction, synthesis of cellular products, etc. Only 10% of the Earth’s 40 million species are autotrophs Other autotrophs use inorganic compounds instead of sunlight to make food; process known as chemosynthesis Producers make food for themselves and heterotrophs or consumers that cannot make food for themselves Photosynthesis summary equation: 6CO2 + carbon dioxide 6H2O + light water II. Phases (controlled by enzymes) 1. Light Reactions also called photolysis Light absorption in grana of chloroplasts Light and Pigments o light from sun appears white but is composed of many colors least energy red orange 2 C6H12O6 + glucose oxygen 6O2 yellow visible spectrum green blue indigo most energy violet o Blue/violet is most absorbed, and used most by the plant o green is most reflected, leased used Chloroplast Pigments o trap energy from light (sun or artificial) o chlorophyll a: directly involved in light reactions Accessory Pigments o chlorophyll b: red pigment o carotenoids: orange pigment o pigments easily separated by chromatography Chloroplast Pigments o trap energy from light (sun or artificial) o chlorophyll a: directly involved in light reactions Accessory Pigments o chlorophyll b: red pigment o carotenoids: orange pigment o pigments easily separated by chromatography o chlorophyll traps light energy o water molecules split (photolysis) and oxygen is released from water; proved with oxygen-18 o leftover energy produced stored in ATP 2. Dark Reactions also called carbon fixation take place in stroma of chloroplasts; carbon dioxide is fixed in carbohydrate PGAL (phosphoglyceraldehyde; 3 carbon) is formed glucose is synthesized from two 3-C PGAL molecules; called C-3 pathway Alternative Pathways a. The Calvin cycle is the most common pathway used by autotrophs called C 3 Plants b. Plants in hot, dry climate use alternate pathways to fix carbon & then transfer it to the Calvin cycle c. stomata are small openings on the underside of leaves for gas exchange (O 2 & CO2) d. guard cells on each side of the stoma help open & close the stomata e. Plants also lose H2O through stoma so they are closed during the hottest part of the day f. C4 plants fix CO2 into 4-Carbon Compounds during the hottest part of the day when their stomata are partially closed g. C4 plants include corn, sugar cane and crabgrass h. CAM plants include cactus & pineapples i. CAM plants open their stomata at night and close during the day so CO2 is fixed at night j. During the day, the CO2 is released from these compounds and enters the Calvin Cycle Rate of Photosynthesis Affected by: a. Light intensity - As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis 3 initially increases and then levels off to a plateau b. Temperature - Only the dark, not the light reactions are temperature dependent because of the enzymes they use (25 oC to 37oC) c. Length of day d. Increasing the amount of carbon dioxide available improves the photosynthesis rate e. Level of air pollution Practice Questions: _____1. If the leaves of a geranium plant receive an adequate supply of raw materials, which graph below shows how the rate of photosynthesis is related to increasing light intensity received by the plant? B. D. C. A green plant is kept in a brightly lighted area for 48 hours. What will most likely occur if the light intensity is then reduced slightly during the next 48 hours? A. Photosynthesis will stop completely. B. The rate at which nitrogen is used by the plant will increase. C. The rate at which oxygen is released from the plant will decrease. D. Glucose production inside each plant cell will increase. A. _____2. The equation below represents a summary of a biological process. carbon dioxide + water → glucose + water + oxygen This process is completed in A. mitochondria C. cell membranes B. ribosomes D. chloroplasts _____3. An enzyme known as rubisco enables plants to use large amounts of carbon dioxide. This enzyme is most likely active in the A. nucleus C. mitochondria B. vacuoles D. chloroplasts _____4. The diagram below represents a cross section of part of a leaf. Which life functions are directly regulated through feedback mechanisms associated with the actions of the structures labeled X? A. excretion and immunity C. circulation and reproduction B. digestion and coordination D. respiration and photosynthesis 4 _____5. Which process is directly used by autotrophs to store energy in glucose? A. diffusion C. respiration B. photosynthesis D. active transport _____6. The diagram represents part of a life process in a leaf chloroplast. If the process illustrated in the diagram is interrupted by a chemical at point X, there would be an immediate effect on the release of A. chlorophyll C. carbon dioxide B. nitrogen D. oxygen _____7. The diagram below represents a biological process. Which set of molecules is best represented by letters A and B? A. A: oxygen and water B: glucose B. A: glucose B: carbon dioxide and water C. A: carbon dioxide and water B: glucose D. A: glucose B: oxygen and water _____8. Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. A small water plant (elodea) was placed in bright sunlight for five hours as indicated below. Bubbles of oxygen gas were observed being released from the plant. Since oxygen gas is being released, it can be inferred that the plant is A. producing glucose C. releasing energy from water B. making protein D. carrying on active transport _____9. A small water plant (elodea) was placed in bright sunlight for five hours as indicated below. Bubbles of oxygen gas were observed being released from the plant. What substance did the plant most likely absorb from the water for the process that produces the oxygen gas? A. dissolved nitrogen C. an enzyme B. carbon dioxide D. a hormone _____10. Starch molecules present in a maple tree are made from materials that originally entered the tree from the external environment as A. enzymes C. amino acids 5 B. simple sugars D. inorganic compounds _____11. An enzyme known as rubisco enables plants to use large amounts of carbon dioxide. This enzyme is most likely active in the A. nucleus C. mitochondria B. vacuoles D. chloroplasts ___C_12. Which set of terms best identifies the letters in the diagram below? A. row (1) B. row (2) C. row (3) D. row (4) _____13. The photograph below shows a microscopic view of the lower surface of a leaf. What is the main function of the cells indicated by the black pointer? A. regulate the rate of gas exchange C. undergo mitotic cell division B. store food for winter dormancy D. give support to the veins in the leaf _____14. The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms. The process illustrated occurs within A. chloroplasts B. mitochondria C. ribosomes D. vacuoles _____15. Which process usually uses carbon dioxide molecules? A. cellular respiration C. active transport B. asexual reproduction D. autotrophic nutrition _____16. The green aquatic plant represented in the diagram below was exposed to light for several hours. 6 Which gas would most likely be found in the greatest amount in the bubbles? A. oxygen B. nitrogen C. ozone D. carbon dioxide The Absorption of Chlorophyll A pigment is a substance that absorbs and reflects light of particular wavelengths. For example, the yellow-green color of a leaf is due to a pigment in the leaf called chlorophyll. When white light (which contains all of the colors of the spectrum) shines on chlorophyll, the chlorophyll absorbs most of the red, orange, blue, and violet and reflects most of the green and yellow. That is why you see a yellow – green color. Think of a pigment as a sponge that soaks up all of the other colors of the spectrum except the one you see. A spectrophotometer is an instrument that is used to measure the amount of light absorbed by a pigment. Following is a graph showing the percentage of light energy reflected for the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll. The highest peaks represent colors that chlorophyll absorbs the most. Therefore, they are the least visible. Use the graph to answer the following questions. 1. Which of the colors absorbed by chlorophyll is least visible? violet 2. What is its approximate wavelength? 4100 angstroms 3. What percentage of light energy absorbed does this peak represent? 75% 4. How much of this color is being reflected? 25% 5. What percentage of light energy absorbed by chlorophyll does the orange spectrum peak represent? 35% 6. Why would you say there are no peaks in the range between 5000 and 6100 angstroms? green & yellow- most reflected, least absorbed 7. Are you able to see the light in the yellow - green part of the spectrum? Explain yes- it’s being most reflected 8. Arrange the colors in the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll in order of their visibility. Place the most visible color first? green, yellow, orange, red, blue, violet Percent Of Light Energy Reflected By Chlorophyll Use the bar graph, which represents the percentage of light energy reflected by chlorophyll, to answer the following questions. The graph was derived from the chlorophyll absorption spectrum. 9. Which color in this spectrum is most visible? green 10. What is the approximate percentage of light energy reflected for this color? 95% 11. What percentage of light energy absorbed does this represent? 5% 12. If everything above 50 percent of light energy reflected is visible to the human eye, is red light part of the mixture of colors in light reflected by chlorophyll visible? no 7 Cellular Respiration making ATP by breaking down organic compounds summary equation: C6H12O6 + glucose 6O2 oxygen 6CO2 + carbon dioxide 6H2O + 36 ATP water energy Steps: 1. Glycolysis 2. Anaerobic Respiration (no oxygen) OR aerobic Respiration (oxygen) Glycolysis occurs outside the mitochondria (in the cytoplasm) glucose + 2 ATP 2 PGAL 2 pyruvic acid + 4 ATP Net gain: 2 ATP Aerobic Respiration: if oxygen is available occurs in the mitochondria 2 pyruvic acid + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + 34 ATP Net gain of ATP during aerobic respiration = 34 Total ATP from both stages = 36 Fermentation: no oxygen available a. Lactic Acid Fermentation o occurs in muscle cells o glucose pyruvic acid lactic acid + 2 ATP o muscle sore, cramps b. Alcoholic Fermentation o some plant cells, yeast o glucose pyruvic acid ethyl alcohol + 2 ATP + CO2 o 8 alcohol making Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration in animals in plants and yeast Oxygen required? yes no no Glycolysis occurs yes yes yes ATP yield 36ATP 2ATP 2ATP Glucose completely broke down? yes no no End products Carbon dioxide and water Lactic acid Ethanol and carbon dioxide Analyzing Photosynthesis and Respiration During photosynthesis, green plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce food in the form of glucose. During respiration, the glucose is broken down to be used as energy by the plant. As the glucose is broken down, the plant releases oxygen. Carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water form a continuous cycle during these two processes. Study the diagram of the carbon cycle that is shown in Figure 1. Then answer the questions, based on the diagram and your knowledge of photosynthesis and respiration. 1. The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere remains at a stable 0.004 percent. Which two processes keep this concentration stable? Photosynthesis & respiration 2. Plants depend upon the activities of animals for a continuing supply of which substance? CO2 3. Which process removes CO2 from the atmosphere? photosynthesis 4. Which process adds CO2 to the atmosphere? respiration 5. Into which organic compound does photosynthesis convert the carbon of CO2? glucose 6. After plants are eaten by animals, what process changes the carbon in these organic compounds back to CO 2? respiration 7. Respiration and photosynthesis play a role in the O2 cycle. In the box below, make a diagram that shows how photosynthesis and respiration take part in the O2 cycle. O2 photosynthesis respiration CO2 Use the following boxes to summarize the relationship between anaerobic and the aerobic phases of respiration 8. Anaerobic phase (in cytoplasm) 9. Aerobic phase (in mitochondria) glucose + 2ATP 2 pyruvic acid + 4 ATP 2 pyruvic acid + O2 CO2 + H2O + 34 ATP 10. Summarize the light and the dark reactions of photosynthesis. Circle the raw materials and draw a line under the products. 9 Respiration Questions _____1. Certain organisms break down glucose in a series of enzyme-controlled reactions. This series of reactions, which results in the productions of alcohol and carbon dioxide, is an example of A. dehydration synthesis C. hydrolysis B. anaerobic respiration D. photosynthesis _____2. A product of cellular respiration is A. oxygen B. ATP C. PCB D. glucose _____3. During the process of aerobic respiration, energy stored in food is transferred to molecules of A. ATP B. DNA C. glucose D. enzymes _____4. The energy released from the anaerobic respiration of a glucose molecule is less than that released from the aerobic respiration of a glucose molecule because A. fewer bonds of the glucose molecules are broken in anaerobic respiration than in aerobic respiration B. more enzymes are required for anaerobic respiration than for aerobic respiration C. anaerobic respiration occurs 24 hours a day while aerobic respiration can only occur at night D. anaerobic respiration requires oxygen but aerobic respiration does not require oxygen _____5. In the diagram, what gas is probably present in the second fermentation tube? A. O2 B. N2 C. CO2 D. CO _____6. Most animals make energy available for cell activity by transferring the potential energy of glucose to ATP. This process occurs during A. aerobic respiration, only B. anaerobic respiration, only C. both aerobic and anaerobic respiration D. neither aerobic nor anaerobic respiration _____7. Compared to a cell that is carrying on anaerobic respiration, a cell carrying on aerobic respiration A. uses less oxygen C. uses less carbon dioxide B. produces more ATP D. produces more alcohol _____8. Which of the following processes releases the greatest amount of energy? A. the oxidation of one glucose to lactic acid molecules B. the oxidation of one glucose molecule to carbon dioxide and water C. the conversion of two glucose molecules to a maltose molecule D. the conversion of one glucose molecule to alcohol and carbon dioxide _____9. The site of aerobic cellular respiration is the A. nucleus B. ribosome C. chromosome D. mitochondria _____10. Which process is illustrated by the summary equation below? glucose + oxygen water + carbon dioxide + 36 ATP A. hydrolysis B. photosynthesis C. dehydration synthesis 10 D. aerobic respiration _____11. Two end products of aerobic respiration are A. oxygen and alcohol C. oxygen and water B. carbon dioxide and water D. carbon dioxide and oxygen _____12. The aerobic respiration of a molecule of glucose releases more energy than the anaerobic respiration of a molecule of glucose because in aerobic respiration A. carbon dioxide is used C. more chemical bonds are broken B. oxygen is released D. lactic acid is formed Base your answers to questions 13 and 14 on the equation below concerning anaerobic cellular respiration. glucose + 2X 2 pyruvic acid + 4 ATP enzymes _____13. The substance indicated by X is A. O2 B. H2O C. ATP D. CO2 _____14. In muscle cells, the pyruvic acid can be converted to A. lactic acid B. alcohol C. oxygen D. chlorophyll _____15. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the following chemical reaction? A. B. C. D. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. Fermentation is taking place, resulting in the synthesis of ATP. Energy is being released for metabolic activities. Photosynthesis is taking place, resulting in the storage of energy. _____16. What is the net gain in ATP following the completion of aerobic cellular respiration of one molecule of glucose in a brain cell? A. 30 B. 2 C. 36 D. 4 _____17. Select the metabolic process that is most closely associated with the statement. This process occurs in humans only when certain cells do not receive an adequate supply of oxygen. A. B. C. Cumulative Questions: _____1. Carbon dioxide makes up less than 1 percent of Earth’s atmosphere, and oxygen makes up about 20 percent. These percentages are maintained most directly by A. respiration and photosynthesis C. synthesis and digestion B. the ozone shield D. energy recycling in ecosystems _____2. In what way are photosynthesis and cellular respiration similar? A. They both occur in chloroplasts. C. They both involve organic and inorganic molecules. B. They both require sunlight. D. They both require oxygen and produce carbon dioxide. 11 Base your answers to 3 through 5 on the two different cells shown. Only cell A produces substance X. Both cells A and B use substance X. 3. Identify substance X. oxygen/ glucose 4. Identify the type of organelle in cell A that produces substance X. chloroplast 5. Identify the type of organelle found in both cell A and cell B that uses substance X. mitochondria _____6. The main result of aerobic respiration is the A. conversion of radiant energy into chemical energy B. production of lactic acid as an end product C. storage of energy in a polysaccharide D. production of ATP from the breakdown of glucose _____7. If the chemical reaction shown in the diagram takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce substance X, the organism must be A. a heterotroph B. an annelid C. an autotroph D. a fungus _____8. Select the metabolic process that is most closely associated with the statement. Part of this process takes place in structures known as grana. A. B. C. 12 9. The diagram below represents a cell found in some complex organisms. The enlarged section represents an organelle, labeled X, found in this cell. Describe the function of organelle X and explain how it is important to the survival of the cell. In your answer, be sure to: identify organelle X state the process that this organelle perform identify the two raw materials that are needed for this process to occur identify one molecule produced by this organelle and explain why it is important to the organism mitochondria respiration glucose & oxygen ATP- energy for cellular activities _____10. A marathon runner frequently experiences muscle cramps while running. If he stops running and rests, the cramps eventually go away. The cramping in the muscles most likely results from A. lack of adequate oxygen supply to the muscle C. the runner warming up before running B. the runner running too slowly D. increased glucose production in the muscle _____11. Base your answer on the reactions shown in the graphic. Which reactions occur in the palisade layer of a maple leaf during daylight hours? A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 3 and 4 D. 4 and 1 12. In some land plants, guard cells are found only on the lower surfaces of the leaves. In some water plants, guard cells are found only on the upper surfaces of the leaves. Explain how guard cells in both land and water plants help maintain homeostasis. In your answer be sure to: • identify one function regulated by the guard cells in leaves [1] • explain how guard cells carry out this function [1] • give one possible evolutionary advantage of the position of the guard cells on the leaves of land plants [1] gas exchange control the size of stoma prevents excess evaporation 13 Base your answers to questions 12 through 16 on the information and diagrams below. The laboratory setups represented below were used to investigate the effect of temperature on cellular respiration in yeast (a single celled organism). Each of two flasks containing equal amounts of a yeast-glucose solution was submerged in a water bath, one kept at 20°C and one kept at 35°C. The number of gas bubbles released from the glass tube in each setup was observed and the results were recorded every 5 minutes for a period of 25 minutes. The data are summarized in the table below. Directions (12-16): Using the information in the data table, construct a line graph on the grid on the next page, following the directions below. 12. Mark an appropriate scale on each axis. [1] 13. Plot the data for the total number of bubbles released at 20°C on the grid on the next page. Surround each point with a small circle and connect the points. [1] 14. Plot the data for the total number of bubbles released at 35°C on the grid. Surround each point with a small triangle and connect the points. [1] 14 15. State one relationship between temperature and the rate of gas production in yeast. [1] As temperature increases, the rate of gas production also increases. (direct relationship) 16. Identify the gas that would be produced by the process taking place in both laboratory setups. [1] CO2 _____17. The diagram shows a mitochondrian. Letter X most likely represents A. ATP C. lactic acid B. maltose D. PGAL 18. Base your answer to the question on the word equation. Name the process represented by the equation. respiration 15 19. The diagram below represents a microscopic view of the lower surface of a leaf. Identify the structure labeled X in the diagram and state one problem for the organism that would result from a malfunction of the structure you identified. Guard cell. Photosynthesis won’t occur at an optimal rate. Base your answers to 20 and 21 on the statement below. Carbon exists in a simple organic molecule in a leaf and in an inorganic molecule in the air humans exhale. 20. Identify the simple organic molecule formed in the leaf and the process that produces it. Glucose; photosynthesis 21. Identify the carbon-containing molecule that humans exhale and the process that produces it. Carbon dioxide; respiration Base your answer to the question on the diagram below biology. The arrows in the diagram represent biological processes. 22. 23. 24. 25. Identify one type of organism that carries out process 1. plant Explain why process 2 is essential in humans. Breaking down materials to make them into usable form. Identify process 3. respiration Identify what letter X represents. ATP 26. The diagram represents a system in a space station that includes a tank containing algae. An astronaut from a spaceship boards the space station. State two changes in the chemical composition of the space station atmosphere that would result from turning on more lights. More oxygen, less carbon dioxide 16