bruch_2
advertisement

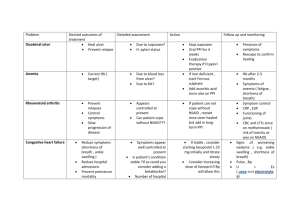
TREATMENT كيفية إنشاء منشور دعائي When H. pylori infection is present: @ combinations of 2 لطباعة (والمحافظة على) إرشادات المنشور الدعائي antibiotics (e.g. ."انقر فوق "طباعة سريعة Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Tetracycline, يمكنكإنشاء منشور دعائي احترافي باستخدام هذا ثم،" قم باإلشارة إلى "طباعة" من القائمة "ملف،هذه : فيما يلي كيفية ذلك.القالب Metronidazole) and 1 proton pump inhibitor (PPI), Peptic في مكانulcer قم بإدراج الكلمات خاصة بك 1. sometimes together with a bismuth compound. باستخدام أنماط الفقرات،هذه الكلمات المعينة مسبقا ً أو من خالل إعادة .ترتيبها In complicated, treatmentresistant cases, 3 antibiotics (e.g. amoxicillin + clarithromycin + metronidazole) may be used together with a PPI and sometimes with bismuth compound. An effective first-line therapy for uncomplicated KING SAUD UNIVERSITY cases would be Amoxicillin + Metronidazole + Rabeprazole (a PPI). بشك ٍل2 و1 قم بطباعة الصفحات .rettel متتالي على ورق متين بحجم 3. قم بطي الورقة كرسالة إلنشاء منشور دعائي ثالثي الطي (تكون اللوحة .)المتضمنة الصورة الكبيرة في المقدمة ما الذييجب أنأعرفه أيضاً؟ Pharmacy collage In the absence of H. pylori, long-term higher dose PPIs are often used. 2. Hospital pharmacy course حدد النص بواسطة وضع،إلنشاء نمط أية فقرة نمطا ً من حددIntroduction. ثم.المؤشر في أي مكان في الفقرة األدواتشريطClassification. المقطع "التنسيق السريع" على .""كتابة Signs & Symptoms. Complications. Diagnosis. Treatment. DIAGNOSIS An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), a form of endoscopy, also known as a gastroscopy, is carried out on patients in whom a peptic ulcer is suspected. By direct visual identification, the location and severity of an ulcer can be described. Moreover, if no ulcer is present, EGD can often provide an alternative diagnosis. The diagnosis of Helicobacter pylorican be made by: Urea breath test (noninvasive and does not require EGD). Direct culture from an EGD biopsy specimen; this is difficult to do, and can be expensive. Most labs are not set up to perform H. pylori cultures. Direct detection of urease activity in a biopsy specimen by rapid urease test. Measurement of antibody levels in blood (does not require EGD). It is still somewhat controversial whether a positive antibody without EGD is enough to warrant eradication therapy. Stool antigen test. Histological examination and staining of an EGD biopsy. SIGNS & SYMPTOMS abdominal pain (duodenal INTRODUCTION A peptic ulcer, also known as ulcers are classically relieved by food, while gastric ulcers are ulcus pepticum, PUD or peptic ulcer disease, is an ulcer exacerbated by it). bloating and abdominal (defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm) fullness. of an area of the gastrointestinal nausea, and lots of vomiting. tract. loss of appetite and weight loss. hematemesis (vomiting of blood). associated with Helicobacter pylori, however only 20% of Melena ( dark blood in stools or stools that are black or tarry). those cases go to a doctor. Gastrointestinal bleeding ( the most common complication). Perforation (a hole in the wall). Perforation at: @ the anterior surface of the stomach leads to acute peritonitis, the first sign is abdominal pain. @ Posterior wall perforation leads to pancreatitis; pain in this situation often radiates to the back. Penetration (when the ulcer continues into adjacent organs such as the liver and pancreas). Pyloric stenosis. Ulcers can also be caused or worsened by drugs such as aspirin and other NSAIDs. COMPLICATIONS As much as 80% of ulcers are CLASSIFICATION A peptic ulcer may arise at various locations: Stomach (called gastric ulcer) Duodenum (called duodenal ulcer) Esophagus (called esophageal ulcer) Meckel's Diverticulum (called Meckel's Diverticulum ulcer)