AAWC Pressure Ulcer Guideline Checklist 7.13
advertisement

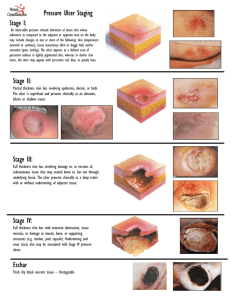
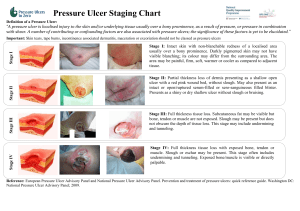
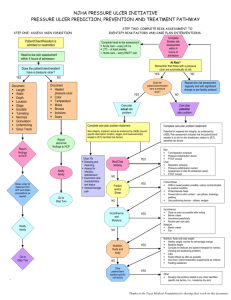
Pressure Ulcer Checklist ASSESS Trained personnel or interdisciplinary team Evaluate and document patient medical/surgical history, physical exam/posturing limitations, psychosocial condition, environment and goals. Perform whole body visual and tactile skin inspection within 72 hours after admission and Regularly per setting protocol and On change in patient status Pay special attention to more darkly pigmented skin as changes may be obscure Within 72 h after admission, assess PU risk using clinical judgment and reliable, valid scale (circle one) Braden, Norton, Waterlow or _____ Check for other PU-risk factors including: Diabetes Extremes of age Body mass index (BMI) extremes As feasible, assess skin where devices may cause pressure, e.g. splints, casts, tubes Document ulcer progress weekly using reliable, valid measures, e.g. length x width to estimate area. Document partial- or full-thickness depth. Ensure all formal assessments are accessible to those providing/consulting on pressure ulcer care Improve Patient Outcomes PREVENT HEAL + Individual receiving care, family and caregivers = Address identified patient PU risk factors Limited mobility, activity, cognition, sensation: Redistribute pressure every 4 hr or as indicated and feasible Properly trained staff select and use indicated pressure redistribution devices for beds, chairs and wheelchairs that meet psychological, social, anatomic and physiologic needs for those at PU risk if patient-appropriate Use patient-appropriate positioning standards of care per institution protocol. Implement patient-appropriate exercise program Consistently train patient and care providers on PU prevention, treatment as appropriate and feasible Excess moisture: Protect skin with barrier and wick fluid away from skin Restore, maintain good nutrition, hydration, circulation and infection control consistent with patient and family goals and professional consult advice as appropriate and feasible. Protect skin from chemical or physical trauma, e.g. appropriate incontinence plan, lift sheet. Avoid vigorous massage on boney prominences Moisturize dry skin to prevent cracking Complete pressure ulcer (PU) team Treat patient and pressure ulcer (PU) to optimize healing Continue or implement all measures to prevent PU Properly trained staff select and use appropriate pressure redistribution devices with verified functionality for the stage of PU as feasible. If appropriate, use a dynamic air support surface if individual cannot be positioned without pressure on PU (e.g. if static support surface bottoms out) Avoid positioning directly on PU on any surface Manage local and systemic factors per institutional protocols and to meet patient / family needs / goals Nutrition Circulation Infection Other____ Cleanse PU (4-15 psi: water, saline, non-toxic cleanser ) Debride autolytically surgically with enzyme Evaluate PU at each dressing change for signs and symptoms of clinical infection Dress PU to maintain a moist environment, protect it and local skin from friction, shear, pressure, trauma, irritation, excess fluid (e.g. fiber, foam, hydrocolloid ) Manage PU-related pain to meet patient needs. Identify and address nutrient deficiencies. After 4 weeks if there is no PU area decrease, Revaluate and improve care plan Try adjunct therapy e.g. electrical stimulation