Ch. 16- Biotech Notesheet 1
advertisement

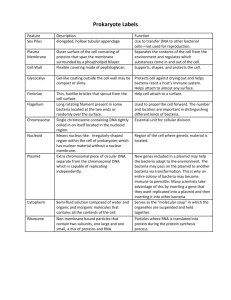
Name ____________________________________ Date ____________ Period _____ GENE TECHNOLOGY (BIOTECHNOLOGY) Raven, 7th ed. Ch. 16 (Ch. 17, 10th ed.) Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information essential to life processes. Essential Knowledge: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular mechanisms. The processing of genetic information is imperfect and is a source of genetic variation. Cells communicate by generating, transmitting and receiving chemical signals. Transmission of information results in changes within and between biological systems. Biotechnology (Genetic Engineering)- ________________________________________________________ Our tool kit… 1. ________________________ one-celled ______________________ reproduce by ____________________ binary fission rapid growth generation every ~______________________ 108 (100 million) colony overnight! dominant form of life on Earth incredibly __________________________ Bacterial genome __________________ chromosome haploid _______________ DNA no histone proteins ~4 million base pairs ~4300 genes 1/1000 DNA in eukaryote __________________ 1 Transformation Bacteria are ______________________________ pick up naked _____________________ wherever it may be hanging out have surface transport proteins that are specialized for the uptake of naked DNA import bits of chromosomes from _______________________________ incorporate the DNA bits into their own ___________________________ express new genes ___________________________________ form of ___________________________ 2. _______________________ Small ______________________ circles of DNA 5000 - 20,000 base pairs __________________________ carry extra __________________ 2-30 genes genes for __________________________________ can be exchanged between bacteria bacterial sex!! rapid evolution can be imported from environment How can plasmids help us? A way to get genes into bacteria easily insert new gene into plasmid insert plasmid into bacteria = ________________ bacteria now ___________________ new gene bacteria make new _____________________ 2 How do we cut DNA? 3. _______________________ ______________________________________ discovered in 1960s evolved in ____________________ to cut up foreign DNA “restrict” the action of the attacking organism protection against viruses & other bacteria bacteria protect their own DNA by _______________________________ & by not using the base sequences recognized by the enzymes in their own DNA Action of enzyme cut DNA at specific sequences ___________________________________ symmetrical “palindrome” produces protruding ends ___________________________________ will bind to any complementary DNA Many different enzymes named after organism they are found in Examples: ___________________________________ Restriction enzymes are named for the organism they come from: EcoRI = 1st restriction enzyme found in E. coli 1. Cut DNA of wanted gene at specific sites leaves “sticky ends” 2. Cut other DNA with same enzymes leave “sticky ends” on both 3. Can glue DNA together at “sticky ends” 1. 2. 3. 3 Why mix genes together? Gene produces protein in different organism or different individual Example: _______________________________ How can bacteria read human DNA ……… The code is ___________________________ Since all living organisms… use the same DNA use the same code book read their genes the ______________ Copy (& Read) DNA Transformation ______________recombinant plasmid into bacteria ______________recombinant bacteria in agar cultures bacteria make lots of copies of plasmid “______________” the plasmid ______________of many copies of inserted gene production of “new” protein transformed phenotype 4 Uses of genetic engineering: Genetically modified organisms (_____________) enabling plants to produce new _________________ Protect crops from insects: ___________________ o corn produces a bacterial toxin (Bacillus thuringiensis) that kills corn borer (caterpillar pest of corn) Extend growing season: __________________________ o strawberries with an anti-freezing gene from flounder Improve quality of food: _________________________ o rice producing vitamin A improves nutritional value Transforming Vertebrates? Plants, animals or microorganisms that have changed through genetic engineering are termed genetically modified organisms or GMOs. Bacteria were the first organisms to be genetically modified. Plasmid DNA containing new genes can be inserted into the bacterial cell and the bacteria will then express those genes. These genes can code for medicines or enzymes that process food and other substrates. Plants have been modified for insect protection, herbicide resistance, virus resistance, enhanced nutrition, tolerance to environmental pressures and the production of edible vaccines. Most commercialized GMO's are insect resistant and/or herbicide tolerant crop plants. Genetically modified animals have been used for research, model animals and the production of agricultural or pharmaceutical products. They include animals with genes knocked out, increased susceptibility to disease, hormones for extra growth and the ability to express proteins in their milk. 5