SMSC Leaders Audit grids
advertisement

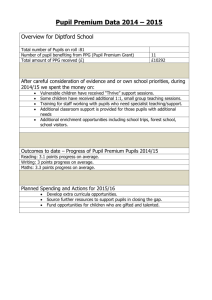
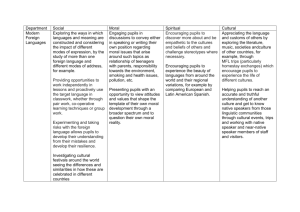
SMSC Leader’s Audit Grids (September 2015) SMSC Evidence Folder Include best practice examples, any evidence you have on the impact it has had and any next steps on aspects of school life that connect to SMSC, for example: Ethos Relationships in all areas of school and all classrooms Behaviour in unstructured time and in lessons Provision through enrichment Student leadership Pupil voice Assemblies Tutorials School environment School website British values: democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty and mutual respect and tolerance of those with different faiths and beliefs Provision in the core curriculum: 1. Spiritual 2. Moral 3. Social 4. Cultural 3 pieces of evidence/best practice examples that as a school we are: Thoughtful Wide ranging Pupils thrive Next steps – chosen due to your knowledge of your school community, culture and ethos. Schools Linking 2015 Ofsted references you might choose to have in an evidence folder: The school’s thoughtful and wide ranging promotion of pupils’ spiritual, moral, social and cultural development and their physical wellbeing enables pupils to thrive. Ofsted: School Inspection Handbook, Outstanding Overall Effectiveness September 2015 Pupils’ spiritual, moral, social and cultural development and, within this, the promotion of fundamental British values, are at the heart of the school’s work. Ofsted: School Inspection Handbook, Outstanding Leadership and Management September 2015 Teachers are quick to challenge stereotypes and the use of derogatory language in lessons and around the school. Resources and teaching strategies reflect and value the diversity of pupils’ experiences and provide pupils with a comprehensive understanding of people and communities beyond their immediate experience. Pupils love the challenge of learning. Ofsted: School Inspection Handbook, Outstanding Quality of Teaching, Learning and Assessment September 2015 Pupils’ spiritual, moral, social and cultural development equips them to be thoughtful, caring and active citizens in school and in wider society. Ofsted: School Inspection Handbook, Outstanding Personal Development, Behaviour and Welfare September 2015 Schools Linking 2015 Grid 1: Breaking Down the S.M.S.C. You might find it useful to analyse your school’s SMSC provision by looking at aspects of SMSC including British Values broken down by the different aspects. This can sometimes be useful to give to middle leaders – but only in order to identify strengths, clarify staff understanding of the breadth of spiritual, moral, social and cultural development and identify gaps in provision across the whole school. Be cautious of this becoming a time consuming task. Spiritual Development The spiritual development of pupils is shown by their: Current Provision: Activities/Resources Identify what is happening in school Evidence of Impact (Qualitative, Quantitative) Possible Areas for Development ability to be reflective about their own beliefs, religious or otherwise, that inform their perspective on life and their interest in and respect for different people’s faiths, feelings and values sense of enjoyment and fascination in learning about themselves, others and the world around them use of imagination and creativity in their learning willingness to reflect on their experiences Schools Linking 2015 Moral Development The moral development of pupils is shown by their: Current Provision: Activities/Resources What is happening in school? Evidence of Impact (Qualitative, Quantitative) Possible Areas for Development ability to recognise the difference between right and wrong and to readily apply this understanding in their own lives, recognise legal boundaries and, in so doing, respect the civil and criminal law of England understanding of the consequences of their behaviour and actions interest in investigating and offering reasoned views about moral and ethical issues and ability to understand and appreciate the viewpoints of others on these issues Schools Linking 2015 Social Development The social development of pupils is shown by their: Current Provision: Activities/Resources What is happening in school? Evidence of Impact (Qualitative, Quantitative) Possible Areas for Development use of a range of social skills in different contexts, for example working and socialising with other pupils, including those from different religious, ethnic and socioeconomic backgrounds willingness to participate in a variety of communities and social settings, including by volunteering, cooperating well with others and being able to resolve conflicts effectively Acceptance and engagement with the fundamental British values of: democracy, Acceptance and engagement with the fundamental British values of the rule of law, Acceptance and engagement with the fundamental British values of individual liberty Acceptance and engagement with the fundamental British values of mutual respect and tolerance of those with different faiths and beliefs Development of skills and attitudes that will allow them to participate fully in and contribute to life in modern Britain Schools Linking 2015 Cultural Development The cultural development of pupils is shown by their: Current Provision: Activities/Resources Evidence of Impact (Qualitative, Quantitative) What is happening in school? Possible Areas for Development understanding and appreciation of the wide range of cultural influences that have shaped their own heritage and those of others understanding and appreciation of the range of different cultures within school and further afield as an essential element of their preparation for life in modern Britain knowledge of Britain’s democratic parliamentary system and its central role in shaping our history and values, and in continuing to develop Britain willingness to participate in and respond positively to artistic, musical, sporting and cultural opportunities interest in exploring, improving understanding of and showing respect for different faiths and cultural diversity and the extent to which they understand, accept, respect and celebrate diversity, as shown by their tolerance and attitudes towards different religious, ethnic and socio-economic groups in the local, national and global communities Schools Linking 2015 SPIRITUAL DEVELOPMENT: EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES/RESOURCES MIGHT INCLUDE: Reflection on work completed and next steps(everyday AfL); reflection on an experience Exploring beliefs and values - eg: in RE, citizenship Learning Outside the Classroom – interactive learning: eg: when visiting places of worship, eg when on a residential, walk Development of gardens and quiet spaces in school that encourage reflection Use of critical thinking skills – eg: development of questions, P4C(Philosophy for children) Opportunities for the experience of awe and wonder Use of particular resources and stimuli that inspire– eg: big books / picture books / poems / picture packs/video clips Assembly/Collective Worship; Thought for the Day EXAMPLES OF THE EVIDENCE THAT COULD CONTRIBUTE: Pupil interviews give quotes in answer to questions such as ‘What have you done at school that has made you think about yourself, the world or the people in it?’ RE assessments of Learning from religion Pupil writing samples that indicate reflection, curiosity, imagination Wall displays show curiosity, imagination, creativity are encouraged Evidence of thoughtful behaviours is seen in shared spaces in school such as corridors Examples of ways pupils are responsible even when not directly instructed Observation of Assembly/Collective Worship shows children are given opportunity to reflect sometimes in pairs, sometimes on their own. Behaviour and racist logs analysis by all groups Class Projects Pupil Voice – eg School Council Lesson Observations of learning behaviours show respect for feelings and values, enjoyment, fascination, use of imagination Qualitative/quantative data on learning behaviours of students Summary of learning behaviours as reported to parents Schools Linking 2015 PUPILS’ MORAL DEVELOPMENT: EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES/RESOURCES MIGHT INCLUDE: Primary/Secondary SEAL resources Development of school motto/vision translated to ethos and practice; class code of conduct – rights and responsibilities Focus on SLN’s key questions: Who am I? Who are we? How do we all live together? Use of critical thinking skills – eg: P4C, Mysteries, Fortune Lines, Conscience Alleys UN: Rights-Respecting Schools Development of Model United Nations (Key Stages 3 and 4) Use of particular resources and stimuli – eg: big books / picture books / poems / picture packs (eg Amnesty International book, ‘We’re all Born Free’) Development of Controversial Issues differentiated to the needs and context of the class Collective Worship and Assemblies EXAMPLES OF THE EVIDENCE THAT COULD CONTRIBUTE: Formal and Lesson Observations of learning behaviour/Behaviour and safety Formal and Informal observations of unstructured time/break/lunchtime Behaviour logs, Racist incident logs Examples of Assembly/ Collective Worship that intentionally develop moral values and understanding of morals. Themed days / week Projects that develop moral awareness Debates/Dialogue opportunities – in the classroom or after school List of educational visits that develop moral values eg visits to councils, law courts, range of places of worship, museums where exhibits develop moral understanding such as Holocaust Museum, Peace Museum, Slavery museum, Visitors Pupil Leadership Pupil Voice – eg School Council, students ability to impact on the life of the school Learning Outside the Classroom – educational visits that develop moral values eg respect for diversity, understanding of democracy Charity Work- local, national, global Curriculum maps/audit/summary that demonstrates how the development of moral values is taught in school in each subject and how this develops in the life of a child through the school School ethos, school values, curriculum content- eg respect, courage, human rights, responsibilities, freedom, fairness, compassion, truth, right, wrong, empathy, respect of property, respect for the environment, equality of opportunity, respect for minority interests, contribution to society, participation, democracy, understanding of democratic processes, thoughtfulness, honesty, kindness, valuing inclusion and community, respect for interdependence, awareness of our impact on others, selflessness, resolving conflict, combatting prejudice, awareness of and sense of connection to local, national, global society, welcoming, helpfulness Comments on sportsmanship of pupils at sporting events CPD for staff developing school ethos, vision Case studies of impact of curriculum e.g.on pupil attitudes to an issue, or pupil respect for others commented on by visitors Schools Linking 2015 PUPILS’ SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT: EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES/RESOURCES MIGHT INCLUDE: Primary/Secondary SEAL resources Participating in school linking projects, embedding into the wider curriculum Focus on SLN’s key questions: Who are we? How do we all live together? Development of Controversial Issues differentiated to the needs and context of the class Use of critical thinking skills which require group skills – eg: P4C, Memory Mapping, Talking Sticks Use of Think, Pair, Share – Dialogic Learning Use of particular resources and stimuli – eg: big books / picture books / poems / picture packs (eg SLN’s Model United Nations; Voices in the Park) Collective Worship and Assemblies EXAMPLES OF THE KINDS OF EVIDENCE OF IMPACT: Lesson Observations of social skills eg working and socialising with others eg talking partners, peer assessment, individual work, group work in science, Kagan groupings Playground/unstructured time observations, Data analysis by all groups of participation in optional opportunities provided by the school Qualitative observation and list of stratgeies employed by the school of social skills in Lessons that teach Collective Worship Themed days / week Examples of curriculum work that develops social skills eg after school clubs, on visits, with visitors in school, circle time in primary, on educational visits, Learning Outside the Classroom, circle games, structured discussions in lesson time, PE lessons as a social setting, Science experiments as a social setting, Plays/Performances, Examples of projects that develop social skills eg Linking projects, debating, Fundraising, Competitions Pupil Voice – eg School Council Pupil Leadership CPD for staff on quality first teaching/classroom management that develops social skills of pupils Case study of a child who is new and the way they have been inducted and welcomed by the class. Case study of a child who has gained confidence Schools Linking 2015 PUPILS’ CULTURAL DEVELOPMENT: EXAMPLES OF ACTIVITIES/RESOURCES MIGHT INCLUDE: Participating in school linking projects, embedding into the wider curriculum – focusing on the 4 Questions of identity: Who am I? Who are we? Where do we live? How do we all live together? Participation in Who Do We Think We Are? Week and other such initiatives Use of critical thinking skills – eg: P4C, Mysteries, Fortune Lines, Compare and Contrast, Similar and Different School completes an audit of its context – socio-economic, ethnic and cultural, religious Use of particular resources and stimuli – eg: big books / picture books / poems / picture packs (eg: Citizenship work on Britishness, using contemporary documentary resources; Oxfam’s resources – eg Paper Bag Challenge) Collective Worship and Assemblies EXAMPLES OF THE KINDS OF EVIDENCE OF IMPACT: Pupil quotes about impact of particular lesson series on their thinking Enrichment/club/residential attendance has been undertaken and this quantifies participation by all groups (using PP, SEN, ethnicity, faith as appropriate to the school) Lesson Observations indicate outstanding attitudes to others within the classroom Pupil interviews specifically ask students about the attitudes of pupils in the school towards each other, younger/older pupils Learning Walks/photographs of evidence of wall display Photographs of pupils taking part in cultural activities Planning examples of Assembly/ Collective Worship that develops understanding, respect, celebration of cultural diversity Curriculum planning overview of why a particular theme day was planned in order to impact on particular attitudes Curriculum provision list of cultural opportunities provided by the school eg After School Clubs, Learning Outside the Classroom, Educational Visits, Plays/performances, civic engagement, sports events, international work, competitions Powerpoint of Teacher CPD on eg Knowing school community, Bullying. Extremism Schools Linking 2015