Chemical Kinetics: Integrated Rate Equations Lesson Plan
advertisement

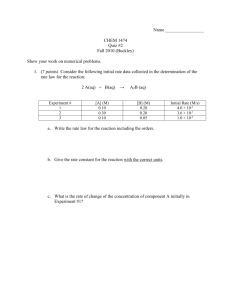
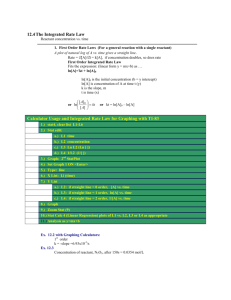
LESSON PLAN Class – XII Section – B Subject – Chemistry Period – 2nd Unit – Chemical Kinetics Topic – Integrated Rate Equations Date – 11/07/14 Time Allotted – 40 min Objectives :After studying this Unit, students will be able to derive integrated rate equations for the zero and first order reactions; determine the rate constants for zeroth and first order reactions; solve the numerical problems on zero and first order reactions. Synopsys of the topic :It is not always convenient to determine the instantaneous rate, as it is measured by determination of slope of the tangent at point ‘t’ in concentration vs time plot. In order to avoid this difficulty, we can integrate the differential rate equation to give a relation between concentrations at different times and rate constant. We shall determine these equations only for zero and first order chemical reactions. Zero Order Reactions : d[R] d[R] R P Rate = - dt = k [R]0 => - dt = k => d[R] = – k dt Integrating both sides ʃ d[R] = – k ʃ dt [R] = – k t + I where, I is the constant of integration. At t = 0, the concentration of the reactant R = [R]0, where [R]0 is initial concentration of the reactant. => I = [R]0 Substituting the value of I in the equation [R] = -kt + [R]0 => k = [R]0−[R] t First Order Reactions : R P Rate = - d[R] dt = k [R] => d[R] [R] = -k dt Integrating both sides d[R] ʃ [R] = -k ʃ dt ln [R] = – k t + I where, I is the constant of integration. At t = 0, the concentration of the reactant R = [R]0, where [R]0 is initial concentration of the reactant. => I = ln [R]0 Substituting the value of I in the equation [𝑅]𝑜 [𝑅]𝑜 ln [R] = – k t + ln[R]0 => ln[R]0 – ln [R] = kt => ln [𝑅] = kt => 2.303 log [𝑅] = kt => t = 𝟐.𝟑𝟎𝟑 𝒌 log [𝑅]𝑜 [𝑅] Role definition : Teacher The teacher will ask to solve the following problem using the concept learned : Q. A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10-3 s-1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g? Role definition : Student The students will solve the above problem with the help of the teacher. Role definition : Teacher Q.Plot the graph between ln[R] and t for a first order reaction Role definition : Student The students will plot the graph by comparing the equation with y = mx + c Role definition : Teacher The teacher will give an example of numerical problem asked in previous year’s Board Exam Q1 . The thermal decomposition of HCOOH is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 × 10 -3 s-1 at a certain temp. Calculate how long will it take to form three-fourth of its initial quantity of HCOOH to decompose ( log 0.25 = -0.6021 ) (AISSCE-2011) Q2. A first order reaction has a rate constant of 0.0051 min-1 . If we begin with 0.10 M concentration of the reactant , what conc of the reactant will be left after 3 hrs ? (AISSCE-2009) Role definition : Student The students will solve these two questions at their home.