KEY
advertisement

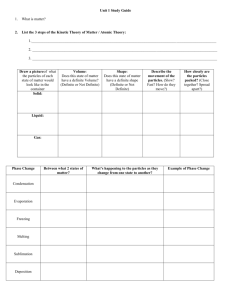
KEY ESCS Unit 2 Study Guide 1) Define: Matter – ANYTHING THAT HAS MASS AND TAKES UP SPACE Substance – MATTER THAT ALWAYS HAS THE EXTACT SAME COMPOSITION Mixture – 2 OR MORE SUBSTANCES TOGETHER - COMPOSITION CHANGES Element – SUBSTANCE THAT CAN’T BE BROKEN DOWN INTO SIMPLER SUBSTANCES Compound – COMPOSED OF 2 OR MORE ELEMENTS IN FIXED RATIO 2) Name two examples each of an element, and a compound Element: OXYGEN, CARBON, GOLD, SILVER, ETC. Compound: WATER, SALT, SUGAR, CARBON DIOXIDE, SILICON DIOXIDE, ETC. 3) How are a compound and a mixture different? MIXTURE RETAINS MANY PROPERTIES OF THE COMPONENTS; NO FIXED RATIO COMPOUNDS- PROPERTIES ARE DIFFERENT; FIXED RATIO 4) Describe and give an example of each: Heterogeneous mixture: SAND, RIVER WATER, SALSA, CHOCOLATE CHIP COOKIE Homogeneous mixtures. Record which picture represents each type: a - HOMOGENEROUS; b - HETEROGENEOUS MILK, KOOL-AID, SUGAR COOKIE, GASOLINE 5) Define: Solution – HOMOGENOUS MIXTURE OF SOLUTE DISSOLVED IN SOLVENT o Solvent – DOES THE DISSOLVING o Solute – IS DISSOLVED Suspension – HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE THAT SEPARATES INTO LAYERS OVER TIME Colloid – HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE WITH PARTICLE SIZE BETWEEN SUSPENSION AND SOLUTION – MEDIUM SIZE PARTICLES Alloy – HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE OF 2 OR METALS 6) Describe methods you could use to separate the following mixtures: Salt and water - EVAPORATION Sand and water - FILTERATION Iron and sulfur - MAGNET 7) What physical property does distillation use to separate fluids from each other? BOILING POINT 8) What is filtration? Give an example of a mixture that cannot be separated by filtration. Why can’t it? METHOD TO SEPARATE MATERIALS BASED ON PARTILCE SIZE; SOLUTIONS – PARTICLES ARE TOO SMALL 9) Pictures: a – CHEMICAL CHANGE and b - PHYSICAL CHANGE 10) Define: Solubility – ABILITY TO DISOLVE o Soluble – WILL DISSOLVE o Insoluble – WILL NOT DISSOLVE Super-Saturation – SOLUTION HOLDS AS MUCH DISSOLVED SOLUTE AS POSSIBLE 11) Describe the following: (in terms of volume & shape) Solid – DEFINITE VOLUME; DEFINITE SHAPE Liquid – DEFINITE VOLUME; INDEFINITE SHAPE Gas – INDEFINITE VOLUME; INDEFINITE SHAPE 12) Define each of the following (Ex: melting point: substance changes from a _______ to a _________) Freezing point – LIQUID SOLID Boiling point – LIQUID GAS Melting point - SOLID LIQUID 13) Describe the difference between a physical change and a chemical change. Provide 3 examples of each. PHYSICAL – NO NEW SUBSTANCES FORM; CHEMICAL – NEW SUBSTANCES 14) Describe these changes as physical or chemical. Substances are…… Mixed P Burned C Melted P Rusted C Cut P Cooked C Spoiled C Dissolved P Digested C Bent P Frozen P Reacted C 15) How do gases differ from solids and liquids? GASES NO DEFINITE SHAPE; NO DEFINITE VOLUME; TAKE SIZE & SHAPE OF CONTAINER - SOLIDS HAVE BOTH DEFINITE SHAPE & VOLUME - LIQUID DEFINITE VOLUME & VARIABLE SHAPE 16) Describe some of the properties of the particles in a gas: When do the particles stop moving? NEVER What type of event makes the particles change their path? COLLISION What happens to the total kinetic energy after two particles collide? REMAINS THE SAME 17) What does the Kinetic Theory state? ALL PARTICLES OF MATTER ARE IN CONSTANT MOTION 18) Describe some of the properties of particles in a liquid or a solid: Why do liquids have variable shapes and definite volumes according to the kinetic theory? ATTRACTION KEEPS VOLUME DEFINITE; MOVEMENT LETS SHAPE SHIFT Why do solids have definite volumes and definite shapes according to the kinetic theory? ATOMS LOCKED IN PLACE, SO SHAPE AND VOLUME IS DEFINITE (KINETIC MOVEMENT EXPRESSED AS VIBRATION) 19) Other states of matter include? At what temperatures? PLASMA – EXTREMELY HIGH and BEC (BOSE EINSTEIN CONDENSATE) – EXTREMELY LOW 20) What are the SI Units for Pressure? N/m2 = Pa = kPa 21) What factors affect the pressure of an enclosed gas? TEMPERATURE, VOLUME, and NUMBER OF PARTICLES 22) Absolute zero = 0K 23) What is Charles’s Law? V1/T1 = V2T2 24) What is Boyle’s Law? P1V1 = P2V2 25) What is the Combined Gas Law? How does it relate to Charles and Boyle’s? P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 IT IS A COMBINATION OF THE 2 LAWS – DIRECTLY RELATED 26) Methane gas occupies a volume of 45ml at 350K. What volume will it occupy at 750K? (45mL)/350K = V2/(750K) 96.43mL = V2 27) A sample of neon occupies a volume of 180mL at 80kPa pressure. What would the pressure become if the volume was increased to 250mL? (180mL)(80kPa) = (250mL)P2 57.6kPa = P2 28) The temperature of a substance does not change during a PHASE CHANGE 29) Define Endothermic – ABSORBS ENERGY FROM SURROUNDINGS Exothermic – RELEASES ENERGY INTO SURROUNDINGS Heat of Fusion – ENERGY THAT MUST BE ABSORBED TO CHANGE FROM SOLID TO LIQUID Heat of Vaporization – ENERGY THAT MUST BE ABSORBED TO CHANGE FROM LIQUID TO GAS 30) Complete this diagram with the 6 common phase changes: A. DEPOSITION B. SUBLIMATION C. VAPORIZATION D. CONDENSATION E. MELTING F. FREEZING