Social Studies - Great Schools Partnership
advertisement

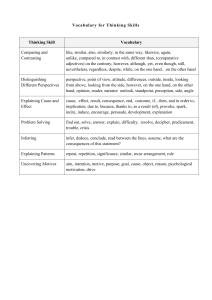
Social Studies Sample Graduation Standards & Performance Indicators Note: Items in red need further review The following Graduation Proficiencies and Performance Indicators are aligned with the learning standards required by the Vermont State Board of Education. These should be seen as a tool to assist Vermont schools and districts in developing learning requirements for their students to comply with requirements of Rule 2000, the Education Quality Standards. As such, framing local learning standards in this format is not required although using this framework would promote compliance and, as will happen, consistency across districts for transfer students. Each Graduation Proficiency has three sets of Performance Indicators differentiated by grade clusters—elementary, middle and high school. These are presented as clusters of grades to enable increased personalization and flexibility for instruction and learning. Each set has between 5 and 8 Performance Indicators. This structure builds off of the Vermont Agency of Education Proficiency Based Learning Simplified Pyramid Grid. Specifically, student achievement of the Graduation Proficiencies through the Performance Indicators will demonstrate student achievement of the expected standards. This tool can also be used to help build curriculum, although this listing of standards should not be GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES 1. INQUIRY 1A. Students make sense of the world around them through questioning. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL a. Asking relevant and focusing questions based on what they have seen, what they have read, what they have listened to, and/or what they have researched. DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 misconstrued as a curriculum. In addition, this tool can be used to steer assessment development to be used to demonstrate proficiency, but it should also not be misconstrued as outlining the full assessment activities in which teachers and students engage. Specifically, we would encourage students and teachers to make heavy use of formative assessments looking at numerous additional and more specific learning standards in order to support deeper learning for each student. We would also note, assessment methodologies will vary in accordance with the types of standards requiring schools and school unions to develop a myriad of assessment strategies including the overt use of performance assessments—which may assess multiple Performance Indicators through a single assessment. These content area Graduation Proficiencies should also be understood in combination with the Vermont Transferable Skills Graduation Proficiencies. This other set of Graduation Proficiencies outlines students skills and habits that cross content areas, and as such, should be woven into daily learning whenever possible. Assessments focused on content area Performance Indicators can simultaneously provide data and insight into achievement of the Graduation Proficiencies aligned with the Transferable Skills. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL a. Asking focused, probing, and significant questions that encourage inquiry around an issue of personal, community, or global relevance. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL a. Asking focused, probing, and significant questions that encourage inquiry around an issue of personal, community, or global relevance. GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL 1B. Students analyze information to develop reasonable explanations that support a social studies inquiry. a. Determining the validity and reliability of the document or information. [NEED APPROPRIATE GRADE LEVEL WORDING] b. Revising explanations as necessary based on personal reflection, peer critique, expert opinion, etc. c. Explaining the relevance of their findings. d. Proposing solutions to problems and asking other questions. 1C. Students communicate in ways that foster the exchange of ideas in a democratic society. 2. HISTORY Students use historical inquiry, including the use of primary and secondary sources, to gather information about the past that will help them make decisions about the future. a. Giving an oral, written, or visual presentation that summarizes their findings. b. Defining their own rights and needs – and the rights and needs of others – in the classroom, school, and community a. Explaining differences between historic and present day objects and identifying how the use of the object and the object itself changed over time. [PROGRESSING FROM IDEAS TO WAYS OF LIFE TO OBJECTS…??] b. Identifying and using various sources for reconstructing the past, such as documents, letters, diaries, maps, textbooks, photos, and others. c. Differentiating among fact, opinion, and interpretation in various events. [??] d. Making predictions and/or decisions based on an understanding of the past and the present. e. Identifying an important event in their communities and/or Vermont, and describing a cause and an effect of that event. f. Explaining how communities throughout time DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL a. Determining the validity and reliability of the document or information. b. Revising explanations as necessary based on personal reflection, peer critique, and/or expert opinion. c. Formulating recommendations and/or making decisions based on evidence [OR SAME AS HIGH SCHOOL?]. d. Proposing solutions to problems based on findings, and asking additional questions. a. Determining the validity and reliability of the document or information. a. Soliciting and responding to feedback. a. Soliciting and responding to feedback. b. Pointing out possibilities for continued or further research. b. Pointing out possibilities for continued or further research. c. b. Identifying different types of primary and secondary sources. Evaluating the credibility of differing accounts of the same event(s). d. Identifying how technology can lead to a different interpretation of history. e. Making predictions and/or decisions based on an understanding of the past and the present. f. c. Identifying important events in the United States and/or world, and describing multiple causes and effects of those events. g. Analyzing a current or historic issue related to Predicting and/or recommending how conclusions can be applied to other civic, economic or social issues. d. Proposing solutions to problems based on findings, and asking additional questions. c. After examining issues from more than one perspective, defining and defending the rights and needs of others in the community, nation, and world. a. Describing ways that life in the United States and/or the world has both changed and stayed the same over time; and explaining why these changes have occurred c. b. Revising explanations as necessary based on personal reflection, peer critique, and/or expert opinion. After examining issues from more than one perspective, defining and defending the rights and needs of others in the community, nation, and world. a. Explaining historical origins of key ideas and concepts and how they are reinterpreted over time. b. Locating appropriate primary and secondary sources to support an historical inquiry. c. Evaluating the credibility of differing accounts of the same event(s), both past and present. d. Using technology to analyze historic information. e. Making predictions, decisions, or taking a public stand based on an understanding of the past and present f. Identifying why certain events are considered pivotal and how they cause us to reorder time. g. Analyzing the impact of a current or historic issue related to human rights, and explaining how the values of the time or place influenced the issue. GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL have promoted human rights [CHANGE FROM GE…??] DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL human rights, and explaining how the values of the time or place influenced the issue PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES 3. GEOGRAPHY Students use geographic tools and analyze geographic data to understand and propose solutions to local and world issues. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL a. Observing, comparing, and analyzing patterns of national and global land use over time to understand why particular locations are used for certain human activities; speculating as to which areas might be used in the future and the impact of that usage. b. Interpreting and analyzing a variety of effective representations of the earth such as maps, globes, and photographs [??]. c. Gather information and analyze different viewpoints regarding resources use in the U.S. and world in order to draw conclusions and recommend actions. d. Analyzing the contributions of various cultural groups to the world, both past and present, including immigrants and native peoples. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL a. Observing, comparing, and analyzing patterns of national, and global land use to understand why particular locations are used for certain human activities. b. Interpreting a variety of effective representations of the earth such as maps, globes, and photographs and project future changes. c. Evaluating different viewpoints regarding resource use in the U.S. & world [same as HS?] d. Describing the contributions of various cultural groups to the world, both past and present. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL b. Observing, comparing, and analyzing patterns of local and state land use to understand why particular locations are used for certain human activities. c. Interpreting a variety of effective representations of the earth such as maps, globes, and photographs. d. Describing a community or state environmental issue. e. Describing the contributions of various cultural groups to Vermont and the U.S.” f. Identifying ways in which culture in Vermont has changed. e. Analyzing how location and spatial patterns influence the spread of culture. a. Analyzing how location, spatial patterns, and technology influence the spread of cultural traits and hypothesize about the impact of the globalization of culture. 4. CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT Students act as responsible citizens by understanding how various forms of government relate to human and civil rights, and use this understanding to advocate for positive change around current local and world issues. a. Identifying and debating issues surrounding the basic principles of American democracy. a. Describing the basic principles of American democracy. b. Identifying the rights and responsibilities of citizenship in a school and local community. b. Evaluating how and why rules and laws are created, interpreted, and changed; establish rules and/or policies for a group, school, or community. b. Describing how rules and laws are created. c. c. d. Knowing the basic rules and laws for school and community. c. Analyzing the principles in key U.S. and international documents and how they apply to their own lives. d. Describing how government decisions directly impact citizens locally, nationally, and internationally. e. Explaining and defending their own point of view on issues that affect themselves and society, using information gained from DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 Identifying key documents on which U.S. laws are based and where to find them. Explaining what makes a just rule or law. d. Describing how government decisions impact and/or relate to their lives. e. Describing how characteristics of good leadership and fair decision-making affect others. e. Explaining and defending their own point of view on issues that affect themselves and society, using information gained from reputable sources. f. f. Illustrating how individuals and groups have brought about change locally, nationally, or internationally. g. Identifying examples of interdependence among Explaining their own point of view on issues that affect themselves and society. g. Identifying problems planning and implementing solutions in the classroom, school or community. [?? Not at higher levels?] h. Identifying examples of interdependence among GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL reputable sources; explaining, critically evaluating, and defending views that are not one’s own. f. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL states and nations. h. Explaining conflicts and ways in which they can be resolved peacefully. individuals and groups. i. Explaining conflicts and ways in which they can be resolved peacefully. Illustrating how individuals and groups have brought about change locally, nationally, or internationally. g. Analyzing the impact of interdependence among states and nations. a. Explaining conditions, actions, and motivations that contribute to conflict within and among individuals, communities, and nations; proposing and defending ways to ease tensions and/or peacefully resolve conflicts. 5. ECONOMICS Students use an understanding of the interaction between humans, the environment, government, and the economy to make economic decision. a. Explaining patterns and networks of economic interdependence that exist nationally and globally. a. Explaining how goods and services around the world create economic interdependence between people in different places. b. Examining how producers in the U.S. and/or world have used natural, human, and capital resources to produce goods and services and comparing and contrasting the findings. b. Examining how producers in the U.S. and/or world have used natural, human, and capital resources to produce goods and services, and predicting the long-term effects of these uses. c. c. Drawing conclusions about how choices within various economic systems affect the environment in the state, nation, and/or world; Evaluating and debating the ideological underpinnings of government and economic programs. d. Analyze and interpret global economic issues and problems through an economic lens. e. Examining the causes and long term effects of people’s needs and/or wants exceeding their available resources, and proposing possible solutions. f. Developing and utilizing a budget. DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 Drawing conclusions about how choices within an economic system affect the environment in the state, nation, and/or world. d. Define and apply basic economic concepts such as supply and demand, price, market and/or opportunity cost in an investigation of a regional, national, or international economic question or problem. e. Examining the causes and long-term effects of people’s needs and/or wants exceeding their available resources, and proposing possible solutions. f. Comparing price, quality, and features of goods and services. b. Tracing the production, distribution, and consumption of goods in Vermont. c. Describing how producers in Vermont have used natural, human, and capital resources to produce goods and services. d. Describing the causes and effects of economic activities on the environment in Vermont. e. Examining factors that influence supply and demand. f. Explaining ways people meet their basic needs and wants. g. Comparing prices of goods and services. h. Explaining how people save. GRADUATION PROFICIENCIES PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—MIDDLE SCHOOL a. Analyzing the impact of media on buying, spending, and saving. g. Analyzing influences on buying and saving. DRAFT Social Studies, v 008, June 9, 2014 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS—HIGH SCHOOL