Beta Decay Notes
advertisement

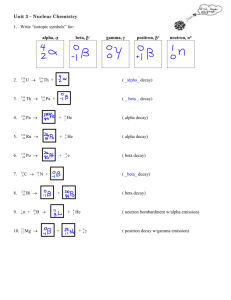
[NC.3] Date Due:_______________ Notes – Beta (β) Decay Read about beta decay on textbook page 294 AFTER reading, read and complete the notes below One of the particles that a radioisotope may emit is called a beta particle Beta particle – an electron emitted by an unstable nucleus. Fold along this line Glue this side of the page into your ISN on page _____ using 6 small dots of glue. Beta particles are produced by a neutron decomposing into a proton and an electron (the beta particle) Beta particles, like other electrons, have a 1- charge. Because this electron is from the nucleus of the atom, it is called a beta particle to distinguish it from the electrons which orbit the atom. Beta particles have a mass of ______ amu. Beta particles are symbolized using: o the Greek letter beta: β o or, the isotope symbol: 0 1 e Beta decay is a type of nuclear decay that releases a beta particle, and is an example of a nuclear reaction. Beta decay is somewhat more complex than alpha decay is. These points present a simplified view of what beta decay actually is: A neutron inside the nucleus of an atom breaks down, changing into a proton. The parent nucleus emits an electron (the beta particle) and an anti-neutrino (more on this later) which go zooming out of the nucleus. p.1 The atomic number goes UP by one and mass number remains unchanged. The following nuclear equation describes the beta decay of thorium-234: Th 234 90 Pa * 234 91 0 1 Beta Particle Symbol Looking at the symbol for a beta particle 10 e you may be wondering, “why is the atomic number of a beta particle -1?”. Let’s take a look at the thorium decay equation again: e 00 ν Th 234 90 Pa * 234 91 0 1 e 00 ν Remember that in beta decay, a neutron decomposes into a proton and an electron. • anti-neutrino Since neutrons & protons are both nucleons, the mass number, 234, does not change: 234 – (1 neutron) + (1 proton) = 234 Because of this, the mass number of the beta particle is listed as 0 0: 1 e However, since the number of protons increases by 1 during a beta decay event, the atomic number of the beta particle is listed as -1: 0 1 e to balance the equation, because mass is conserved during the reaction. • emitted anti-neutrino Notice that the equation shows the conservation of mass: Th Pa e ν 234 90 the mass number on the left (234) is the same as on the right (234+0+0) 234 91 * 0 1 0 0 the atomic number on the left (90) is the same as on the right (91 + -1 + 0) Also notice that there is an asterisk next to the Pa* symbol. This indicates that the nucleus is “excited” or still unstable. Unstable daughter nuclei are likely to decay again. p.2 Even though a proton was gained, a neutron was lost; therefore there is no overall change in mass number. Neutrinos Neutrinos are symbolized using the the Greek letter nu: ν The line over the indicates that it is an anti-matter particle. Unfortunately, the study of neutrinos (and anti-matter!) is way beyond the scope of this course. If you’re interested in finding out more about neutrinos, stop in after class and we’ll chat. Otherwise check out: http://icecube.wisc.edu/info/neutrinos/ Make one AHA connection on notebook p.nnn-nnn p.3