Supplemental Table 1 Genes upregulated in cell lines, prostate
advertisement
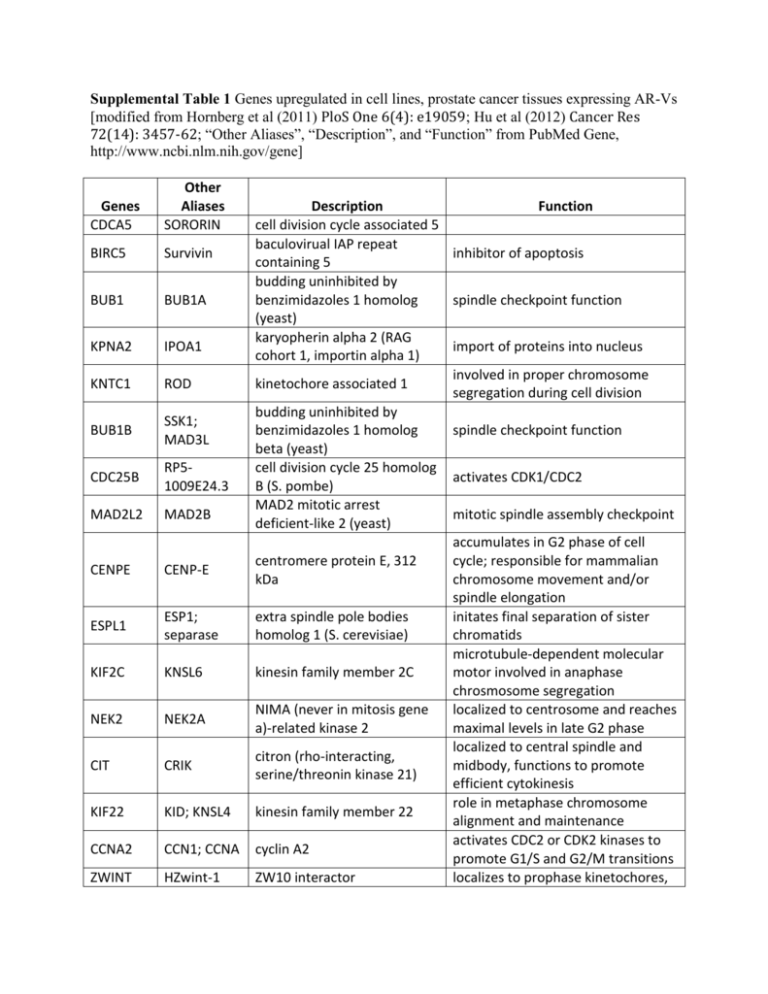
Supplemental Table 1 Genes upregulated in cell lines, prostate cancer tissues expressing AR-Vs [modified from Hornberg et al (2011) PloS One 6(4): e19059; Hu et al (2012) Cancer Res 72(14): 3457-62; “Other Aliases”, “Description”, and “Function” from PubMed Gene, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene] Genes CDCA5 Other Aliases SORORIN BIRC5 Survivin BUB1 BUB1A KPNA2 IPOA1 KNTC1 ROD BUB1B SSK1; MAD3L CDC25B RP51009E24.3 MAD2L2 MAD2B CENPE CENP-E ESPL1 ESP1; separase KIF2C KNSL6 NEK2 NEK2A CIT CRIK KIF22 KID; KNSL4 CCNA2 CCN1; CCNA ZWINT HZwint-1 Description Function cell division cycle associated 5 baculovirual IAP repeat inhibitor of apoptosis containing 5 budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog spindle checkpoint function (yeast) karyopherin alpha 2 (RAG import of proteins into nucleus cohort 1, importin alpha 1) involved in proper chromosome kinetochore associated 1 segregation during cell division budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog spindle checkpoint function beta (yeast) cell division cycle 25 homolog activates CDK1/CDC2 B (S. pombe) MAD2 mitotic arrest mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint deficient-like 2 (yeast) accumulates in G2 phase of cell centromere protein E, 312 cycle; responsible for mammalian kDa chromosome movement and/or spindle elongation extra spindle pole bodies initates final separation of sister homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) chromatids microtubule-dependent molecular kinesin family member 2C motor involved in anaphase chrosmosome segregation NIMA (never in mitosis gene localized to centrosome and reaches a)-related kinase 2 maximal levels in late G2 phase localized to central spindle and citron (rho-interacting, midbody, functions to promote serine/threonin kinase 21) efficient cytokinesis role in metaphase chromosome kinesin family member 22 alignment and maintenance activates CDC2 or CDK2 kinases to cyclin A2 promote G1/S and G2/M transitions ZW10 interactor localizes to prophase kinetochores, remains on kinetochore until late anaphase TPX2 DIL-2 KIF15 HKLP2 MAD2L1 MAD2 PKMYT1 MYT1 UBE2C UBCH10 PLK1 PLK NUSAP1 LNP; ANKT ETV4 PEA3 FABP5 E-FABP HES6 HES-6 UGT2B17 UDPGT2B17 AR DHTR BARD1 BARD-1 CDK1 CDC2 TOP2A TOP2; TP2A CDC20 CDC20A TPX2, micotubule-associated, homolog (Xenopus laevis) kinesin family member 15 MAD2 mitotic arrest mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint deficient-like 1 (yeast) protein kinase, membrane negatively regulates G2/M transition associated tyrosine/threonine of cell cycle 1 member of E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family, required for ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme destruction of mitotic cyclins and E2C progression of cell cycle polo-like kinase 1 nucleolar and spindle role in spindle microtubule associated protein 1 organization ets variant 4 fatty acid binding protein 5 may play role in fatty acid uptake, (psoriasis-associated) transport, and metabolism basic helix-loop-helix transcription hairy and enhancer of split 6 repressor that regulates cell (Drosophila) differentiation involved in glucuronidation, an UDP glucuronosyltransferase intermediate step in the metabolism 2 family. polypeptide B17 of steroids steroid-hormone activated transcription factor; stimulates androgen receptor transcription of androgen responsive genes interacts with N-terminal region of BRCA1 associated RING BRCA1, may be target of oncogenic domain 1 mutations cyclin-dependent kinase 1, essential for G1/S and G2/M cell division cycle 2 transitions involved in chromosome condensation, chromatid topoisomerase (DNA) II alpha separation, and relief of torsional 170kDa stress that occurs during DNA transcription and replication required for two microtubulecell division cycle 20 homolog dependent processes: nuclear (S. cerevisiae) movement prior to anaphase and chromosome separation SLC7A5 CD98 solute carrier family 7 (amino acid transporter light chain, L system), member 5 E2F2 E2F-2 E2F transcription factor 2 binds specifically to pRB in cell-cycle dependent manner; controls cell cycle MCM7 CDC47; MCM2 minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 essential for initiation of eukaryotic genomic replication CCNB2 HsT17299 cyclin B2 HSPB1 HSP27 heat shock 27kDa protein 1 TTK PYT TTK protein kinase E2F5 E2F-5 E2F transcription factor 5, p130-binding MCM2 BM28; CCNL1 minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 MYC c-MYC v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) NCAPG CAP-G non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G BCL2L12 BCL2L12 BCL2-like 12 (proline rich) cyclin B2 is primarily associated with the Golgi region and also binds to transforming growth factor beta RII and thus cyclin B2/cdc2 may play a key role in transforming growth factor beta-mediated cell cycle control involved in stress resistance and actin organization essential for chromosome alignment at the centromere during mitosis and is required for centrosome;tumorigenesis may occur when this protein fails to degrade and produces excess centrosomes resulting in aberrant mitotic spindles duplication control of cell cycle; this protein and E2F4 interact with tumor suppressor proteins p130 and p107, but not with pRB involved in the initiation of eukaryotic genome replication transcription factor that regulates cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation gene targets encodes a subunit of the condensin complex, which is responsible for the condensation and stabilization of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis member of BCL-2 family, which act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators; this protein contains a Bcl-2 homology domain 2 (BH2); the function of this gene has not yet been determined MELK HPK38 MCM4 NKCD TUBB TUBB1 maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 tubulin, beta class RECQL4 RECQ4 RecQ protein-like 4 MTDH LYRIC metadherin STMN1 Lag, SMN stathmin 1/oncoprotein 18 EXO1 HEX1 exonuclease 1 TUBA1B K-ALPHA-1 tubulin, alpha 1b UHRF1 Np95 ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 KIF20A RAB6KIFL kinesin family member 20A ORC6 ORC6L PTPRF LAR initiation of eukaryotic genome replication a DNA helicase, which unwinds double-stranded DNA into singlestranded DNAs; may modulate chromosome segregation prevents assembly and promotes disassembly of microtubules encodes a protein with 5' to 3' exonuclease activity as well as an RNase H activity an E3 ubiquitin ligase; plays a major role in the G1/S transition by regulating topoisomerase II alpha and retinoblastoma gene expression, and functions in the p53-dependent DNA damage checkpoint part of the origin recognition complex (ORC), it binds specifically to origins of replication and serves as a platform for the assembly of additional initiation factors such as origin recognition complex. Cdc6 and Mcm proteins; gene subunit 6 like (yeast) silencing studies with small interfering RNA demonstrated that this protein plays an essential role in coordinating chromosome replication and segregation with cytokinesis protein tyrosine phosphatase, functions in the regulation of receptor type, F RAD21 HR21 RAD21 homolog (S. pombe) HIST1H4C H4FG histone cluster 1, H4c HSPE1 HSP10 heat shock 10kDa protein 1 (chaperonin 10) PBK SPK PDZ binding kinase epithelial cell-cell contacts at adherents junctions and in the control of beta-catenin signaling highly regulated association of this protein with mitotic chromatin specifically at the centromere region suggests its role in sister chromatid cohesion in mitotic cells this gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H4 family; transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails but instead contain a palindromic termination element gene encodes a major heat shock protein which functions as a chaperonin encodes a serine/threonine kinase related to the dual specific mitogenactivated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) family; this mitotic kinase may be involved in the activation of lymphoid cells and support testicular functions, with a suggested role in the process of spermatogenesis