Investigating Mutations
advertisement

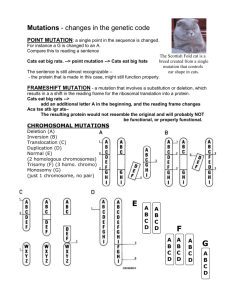
Investigating Mutations with Legos Names:____________________________________ __________________________________________ Introduction: We have been learning about DNA and protein synthesis. We know that the genes on DNA carry the genetic code for amino acid sequences that determine protein structure and function. In the processes of transcription and translation, two types of RNA – mRNA & tRNA- are necessary for copying the code of DNA to take out of the nucleus and translating nucleotide code to amino acid order. In this investigation, we are going to investigate the affect of various types of mutations on protein structure. In order to do this, please define the terms below: Point Mutation Substition Mutation Deletion Mutation Insertion Mutation Nonsense Mutation Missense Mutation Silent Mutation Purpose: You will work in groups of three to compare three different Lego block proteins. Each person will be attempting to build the SAME protein but only one will have the normal mRNA nucleotide sequence. The other two group members will have mutations affecting the mRNA sequence, and therefore the protein. After building, compare the three proteins to see how the mutations have changed the structure. PART 1 Procedure: 1. Decide who will build proteins A, B, and C. 2. Write the mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons in the chart below your assigned DNA sequence. 2. Write the corresponding block color in the data table. 3. Build your Lego Protein. 4. Compare your tower to your lab partners. Remember that all three sequences are supposed to yield the same protein. A. DNA sequence from the normal gene: 3’AAATTTCCCGGGGGACGACCAGGACTCCTC5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom B. DNA sequence resulting from mutation 1: 3’AAATTTCCTGGGGGACGACCAGGACTCCTC5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom C. DNA sequence resulting from mutation 2: 3’AAATTTCCCGGGGGATCGACCAGGACTCCT5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom Part 1 Questions 1. Compare all three amino acid sequences. How does the amino acid sequence differ between the normal sequence and the sequence with Mutation 1? 2. Circle the difference between sequence A and B. 3. How does the amino acid sequence differ between the normal sequence and the sequence with Mutation 2? 4. Circle the difference between DNA sequences A and C. 5. What type of mutation is mutation 1?(More than one term may describe this.) 6. What type of mutation is mutation 2?(More than one term may describe this.) 7. Of the two mutations, which type of mutation has a greater affect on the final amino acid sequence? Why? PART 2 Now take apart your Lego towers. You will follow the same procedurę as in Part 1, but with new DNA sequences. This time, you need to decide who is building protein D, E, or F D. DNA sequence for the normal gene: 3’ACCTGAAAATGGTTCCTCCCATCCCGTCCC5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom E. DNA sequence for mutation 3: 3’ACCTGAAAATGGTTGCTCCCATCCCGTCCC5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom F. DNA sequence for mutation 4 3’ACCTGAAAATGGGTCCTCCCATCCCGTCCC5’ mRNA codon Anticodon on the tRNA Lego Block Color Position in protein Top 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Bottom Part 2 Questions 1. How does the amino acid sequence differ between the normal sequence and the sequence with Mutation 3? 2. Circle the difference between sequence D and E. 3. How does the amino acid sequence differ between the normal sequence and the sequence with Mutation 4? 4. Circle the difference between DNA sequences D and F. 5. What type of mutation is mutation 3?(More than one term may describe this.) 6. What type of mutation is mutation 4?(More than one term may describe this.) 7. Of the two mutations, which type of mutation has a greater affect on the final amino acid sequence? Why? 8. How are missense and nonsense mutations different? 9. What conclusions can you draw about substitution mutations? 10. Evaluate the following statement: „Mutations are always bad for an organism.” 11. When do these DNA mutations occur? 12. It is estimated that every human carries 9 lethal mutations that they inherited from one of their parents. This means that there are 9 genes for essential proteins that are mutated in such a way that either no protein is made or a non functioning protein is made. If this is true, why do we not suffer from these disorders? Codon Color Chart U C A G U C A G green blue green yellow brown blue yellow blue blue red red yellow Black/pink green brown pink yellow black/pink green red red black/pink red blue red blue blue pink brown blue red green green black/pink brown pink brown green black/pink stop yellow brown white brown red blue pink yellow red red blue yellow blue green brown stop Black/pink green green white orange brown blue black/pink Each bag should contain: Green-4 Red-5 White-3 Black or Pink-6 Yellow-5 Blue-3 Orange-2 Brown-2 U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G