DNA Nucleotides - Moore Public Schools
advertisement

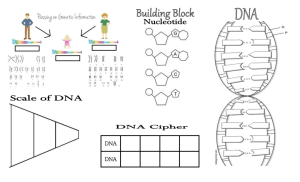
Name Date Hour STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF DNA AND CHROMOSOMES Vocab DENUCLCHROM-SOME; SOMA- What are the traits of your DNA puppies? Body: _______________________ Head: _______________________ Ears: ________________________ Legs: ________________________ Eyes: ________________________ Tail: ________________________ C Color: _____________________ Hair: ________________________ What do you think creating a “DNA puppy” has to do with DNA? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1 Name Date Hour 6. A real DNA molecule consists of THOUSANDS of these pairs of nucleotides. What is the pairing arrangement of nitrogen bases? Discovering DNA Structure _________ pairs with ________and _________ pairs with __________ D = deoxyribo N = nucleic A = acid 7. Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of adenine and thymine nucleotides in a molecule of DNA? Why? DNA contains the information for carrying out the activities of the cell. How this information is coded or passed from cell to cell was at one time unknown. To break the code, today you will do a paper lab to determine the structure of DNA and show how the genetic code is carried. You have four molecules called NUCLEOTIDES. DNA is made up of repeating units of nucleotides. 8. Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of guanine and cytosine nucleotides in a molecule of DNA? Why? 9. Scientists abbreviate the nitrogen bases by using the first letter of each base. So, A always binds to ____ G always binds to ____ 1. Look at your four nucleotides. What are the THREE common parts of a nucleotide? 2. What is the ONE part of a nucleotide that differs among the four DIFFERENT nucleotides? 10. In the space below, use the letters to show the sequence (order) of the bases in the DNA molecule that you constructed. Begin at the top left side of your molecule. 3. List the four different kinds of nitrogen bases. ____goes with ____ ____goes with ____ The structure of DNA is actually in a DOUBLE HELIX arrangement. 4. Manipulate the nucleotide pieces until you find the best fit. Join the nucleotide molecules together like a puzzle. Use tape to connect and reinforce the molecules. You now have a molecule of DNA. DOUBLE HELIX means that the two long chains of nucleotides are arranged in a spiral like a twisted ladder. 5. In the space below, explain WHERE the nucleotide molecules connect to each other. 2 Name Date Hour 11. The sides (or "uprights") of the ladder are made up of alternating _____________ and _____________ molecules. The steps (or "rungs") of the ladder are made of _______________ held together by HYDROGEN BONDS. NUCLEOTIDE NUMBERS Below is a data table indicating the number of each type of nitrogen base in a sequence of DNA. Fill in the blanks. Bring your molecule to the front of the room and join it to the molecules of the other groups. We now have one large DNA molecule. Total Sequence nucleotides A T A 1,000 250 B 500 C 2,500 D 5,000 1,800 E 2,000 625 F 250 G 100 30 H 750 USE THIS SPACE AS SCRATCH PAPER: VOCAB DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID NUCLEOTIDE DOUBLE HELIX CHROMOSOME GENE DNA REVIEW PROBLEMS 1. Describe the basic components of DNA. 2. Which of the following is not a subunit of a nucleotide? a) phosphate b) nitrogen base c) sugar d) glycerol 3 C G 150 700 55 200 Name Date Hour DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes From http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ 10.How can all of that fit in a cell? 1. What is DNA? 11.What is a chromosome? 2. Where, in the cell, is DNA located? 12.How many chromosomes do humans have? 3. What shape is DNA? 13.How many SETS of chromosomes do humans have? 4. What does DNA stand for? 14.Where does each set of chromosomes come from? 5. What are genes? 15.What are sex chromosomes? 6. Genes are made of ___________________________. 16.How many sex chromosomes does each individual have? 7. One strand of DNA contains many _________________________. 17.Which sex chromosomes do males have? 8. How many genes do humans have? 18.Which sex chromosomes do females have? 9. If you stretched out human DNA, how long would it be? 4 Name Date Hour DNA Nucleotides Color the nucleotides on front AND back using the following key, then cut out your nucleotides: Deoxyribose = red Phosphate = blue A (Adenine) = green C (Cytosine) = yellow G (Guanine) = purple T (Thymine) = orange 5