Complications of Labor and Delivery
advertisement
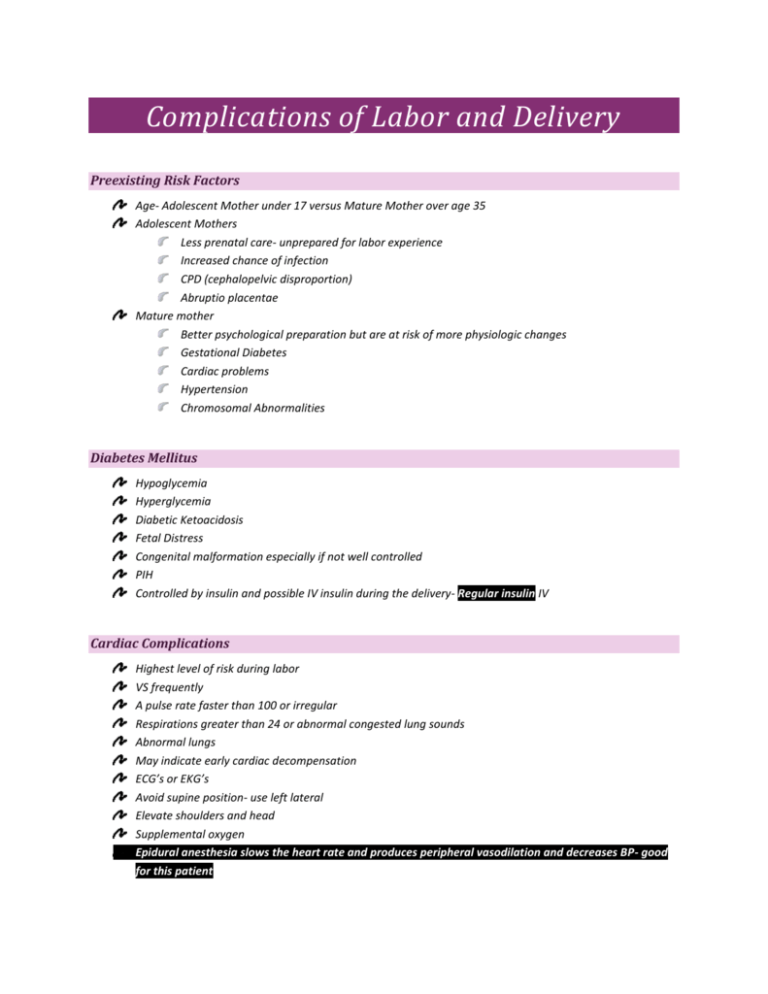
Complications of Labor and Delivery Preexisting Risk Factors Age- Adolescent Mother under 17 versus Mature Mother over age 35 Adolescent Mothers Less prenatal care- unprepared for labor experience Increased chance of infection CPD (cephalopelvic disproportion) Abruptio placentae Mature mother Better psychological preparation but are at risk of more physiologic changes Gestational Diabetes Cardiac problems Hypertension Chromosomal Abnormalities Diabetes Mellitus Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Diabetic Ketoacidosis Fetal Distress Congenital malformation especially if not well controlled PIH Controlled by insulin and possible IV insulin during the delivery- Regular insulin IV Cardiac Complications Highest level of risk during labor VS frequently A pulse rate faster than 100 or irregular Respirations greater than 24 or abnormal congested lung sounds Abnormal lungs May indicate early cardiac decompensation ECG’s or EKG’s Avoid supine position- use left lateral Elevate shoulders and head Supplemental oxygen Epidural anesthesia slows the heart rate and produces peripheral vasodilation and decreases BP- good for this patient Cardiac Monitor FHR Do not elevate legs during delivery- excessive venous return back to weak heart Use short, open glottis bearing down efforts- no Valsalva Vacuum assistance Hypertensive Disorders Seizures are more likely to occur during labor and 48-72 hours afterward Padded side rails Magnesium Sulfate decreases cerebral edema and slows neuromuscular impulse transmission Watch for toxicity- deep tendon reflexes and respirations Watch urinary output Blood levels of magnesium sulfate assessed- 2.5-7.5 is therapeutic range for MgSO4 Calcium Gluconate is the antidote Drug Abuse Analgesics and Regional anesthetics are not withheld from suspected substance abusers but must be used with caution! Track marks Dilated or constricted pupils Disorientation/agitation Inflamed nasal mucosa Premature Onset of Labor Associated with UTI’s and RTI’s Any delivery that occurs before 37 weeks Stay at home-no chores-bed rest Early recognition is important and call doctor Vaginal bleeding and cramps Treatment Bed rest in the left lateral recumbent position External fetal monitoring only Encouragement to Mom and family Nothing in the vagina Tocolytic Drugs Suppress Contractions and stop labor Ritrodine (Yutopar)- causes maternal tachycardia Terbutaline sulfate (Brethine)- causes maternal tachycardia Magnesium Sulfate- depresses CNS and relaxes muscles of uterus PROM ROM- “bag of waters” rupture before labor Infection- amniochorionitis Endometritis Parametritis Peritonitis Monitor temperature every 2 hours Nitrazine test- turns blue May give antibiotics and use bed rest if only a small amount trickles out Cord prolapse/gray/bulging/pulsates FHR- Trendelenburg/Knee chest/ Oxygen-C section Problems with Umbilical Cord Lifeline that provides oxygen to the fetus Nuchal Cord FHR Loosen if not too tight and unwrap Clamp and sever the cord before delivery- done by Dr. or Midwife C-section Patient Teaching for Women with an infection or Preterm labor Report a temperature that is above 100.4 Avoid sexual intercourse of insertion of anything into vagina Avoid orgasms Avoid breast stimulation Maintain any activity restrictions prescribed Note any uterine contractions, reduced fetal activity, and other signs of infection Record fetal kick counts daily and report fewer than 10 kicks in a 12 hours period Obstetric Procedures Amnioinfusion with NS or Ringers Lactate Olighydramnios Umbilical cord compression Reduction of recurrent variable decelerations Dilution of meconium stained amniotic fluid Replaces the “cushion” for the umbilical cord and relieves the variable decelerations Labor Hypertonic Usually occurs during the latent phase of labor Characterized by contractions that are frequent, cramp like, and poorly coordinated Painful, but not productive Uterus is tense, even between contractions, which leads to reduced blood flow to the placenta Excessively strong or longer than expected for a certain stage Results: precipitous delivery or complete exhaustion of uterus- C section and risk of hemorrhage Hypotonic Weak contractions around 5-9 cm- amniotomy or Pit drip- contractions every 2-3 minutes Labor begins normally, but diminishes during active phase More likely to occur if uterus is over-distended Stretches the muscle fibers and reduces their ability to contract effectively Dysfunctional Labor Dystocia- failure to progress toward delivery CPD- Cephalopelvic Disproportion Abnormal uterine contractions Analgesics or Anesthetics Maternal Exhaustion CPD and Malpresentations Give chance to deliver vaginally Remarkable to see how head can mold Vacuums or forceps- watch for damage to facial nerve in baby- asymmetry Occiput anterior preferred Occiput posterior- more backache Watch FHR Version may be attempted with malpresentations Use of birthing chairs, bars, overbed tables can sometimes help Placenta Disorders Placenta Previa Abruptio Placentae C-section- low transverse Retained placenta- 15 minutes after delivery- detaches and expelled D&C Placenta accrete, increta, or percreta Accreta- most common- 75% of cases- Placenta become part of the Endometrium (D&C) Increta- 17% of cases- placenta extends into the uterine muscle (hysterectomy) Percreta- 5-7% of cases- involves the entire uterine wall (hysterectomy) Placenta succenturiate- satellite placenta tissue (extra placenta)- D&C, possible hysterectomy Care Vital Signs Examination of Placenta Pitocin Surgery Late PP hemorrhage due to retained placental fragments Infection Uterine Rupture Concern with VBAC- vaginal birth after C-section Prolonged labor Pitocin administration- stop Pit if occurring every 90 seconds and call doctor Frequently fatal to fetus High risk of death to mom Intrauterine Fetal Death (IUFD) Rh sensitization Sickle cell anemia Trauma Disease Labor continues for extended time No labor- 2 weeks and induce Grieving process Viewing infant, taking pictures if normal appearance Should be prepared if infant has anomalies Move Mom away from maternity unit