Chemistry Quarterly 3 Review: Stoichiometry, Gases, Solutions
advertisement

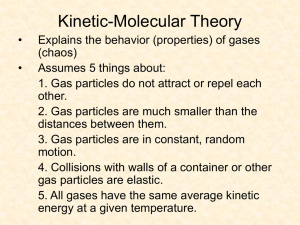
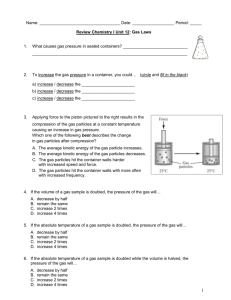
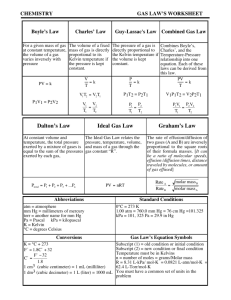
QUATERLY 3 REVIEW CHAPTER 12- Stoichiometry 1. Define the law of conservation of mass 2. Calculate the mass of a product when given the mass / moles of reactant(s) 3. Define Limiting and excess reagent 4. Determine the limiting and excess reagents from given data 5. Define Percent Yield and calculate it from given data 6. a. What mass of iron must react with excess oxygen in order to form 4.81 moles of iron (III) oxide? b. What mass of iron is needed to react with 40.0 g of oxygen? 7. Predict the mass of barium phosphate that will be formed if 20.2g of barium nitrate reacts with 18.0g of sodium phosphate. Which substance is limiting reactant? How much of excess is left over? If in the lab 12.3 g of barium phosphate were produced, what’s the percent yield? Chapter 13 – Solids and Liquids Identify all types of intermolecular forces in 1-4: 1. Attraction between any two polar molecules. 2. Very weak force that increases with molar mass. 3. Attraction between two induced dipoles. 4. Very strong attractive force between molecules with N-H, O-H, or F-H bonds. 5. Compare and contrast solids and liquids. Identify the type of solid in 6-10: 6. Every atom is covalently bonded to another atom. 7. Atoms are surrounded by a sea of electrons. 8. Particles are connected only by IMF 9. There is no geometric pattern in the structure. 10. Charged particles in a geometric pattern Chapter 14 – Gases 13. A jar is tightly sealed at 22°C and 772 mmHg. What is the pressure inside the jar after it has been heated to 178°C? 14. 300.0 mL of gas has a pressure of 75.0 kPa. When the volume is decreased to 125.0 mL, what is its pressure? 15. 50.0 L of gas has a temperature of 75°C. What is the temp in Celsius when the volume changes to 110. L? 16. What is the volume of a container that holds 48.0 g of helium at a pressure of 4.0 atm and temperature of 52°C? 17. A gas occupies 325 L at 25°C and 98.0 kPa. What is its volume at 70.0 kPa and 15°C? Chapter 15 – Solutions 21. Explain the effect of adding more solute to unsaturated, saturated and supersaturated solutions. 22. Explain how temperature and pressure affect solubility. State whether each pair is soluble or insoluble in 23-26. 23. KCl in water 25. Wax in gasoline 24. Ammonia in oil 26. Methane in water 27. Use solubility table to answer: a. How much KClO3 is dissolved in 200 g of water at 60°C? b. What mass of additional CaCl2 is dissolved in 50 g of water if the temp. rises from 10°C to 20°C? c. How would the slope of the KClO3 line differ from CO2 28. How many grams of AlCl3 are required to make a 2.25m solution in 30.0 g of water? 29. What volume of 12M HCl is needed to prepare 250 mL of 0.20M HCl? 30. Explain the difference in preparing solutions based on molarity vs. molality. 31. Which will have the greatest effect on Tf at the same molality: C12H22O11, MgBr2, AlCl3, or NH4NO3? 32. When 26.4 g of NaBr dissolves in 0.20 kg of water, what is the freezing point and boiling point of the solution?(Kf= 1.86°C/m and Kb=0.512°C/m) 11. Explain the relationship between strong intermolecular forces and the following properties – volatility, vapor pressure and boiling point. 12. Hydrogen diffuses 3.72 times faster than an unknown gas. Find the molar mass of the unknown gas. VOCAB: surface tension crystalline vs. amorphous capillary action sublimation volatility diffusion vapor pressure effusion boiling point Dalton’s Law of PP hydrogen bond London-dispersion forces dipole-dipole forces viscosity phase diagram 18. What is the molar mass of an unknown gas if a sample has a mass of 0.290 g and occupies a volume of 148 mL at 13°C and a pressure of 107.0 kPa? 19. What volume of SO2 is produced from 32.5 g of ZnS at 23°C and 103.3 kPa? ZnS + O2 ZnO + SO2 20. What is the temperature of CO2 gas when it has a density of 0.0552 g/L and a pressure of .973 kPa? VOCAB: Kelvin STP VOCAB: solvation Dissociation percent by mass solubility ionization Extra practice problems Chapter 12 1. What relationships can be determined from a balanced chemical equation? 2. Explain why mole ratios are central to stoichiometric calculation 3. Silver nitrate and sodium phosphate are reacted in equal amounts of 200.0 g each. How many grams of silver phosphate are produced? 3AgNO3 + Na3PO4 → Ag3PO4 + 3NaNO3 4a. What volume of hydrogen at STP is produced from the reaction of 50.0 g of Mg and 75.0 g of HCl? Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 b. How much excess reactant is left over? 5. A balloon is filled with 3.0 L of helium at 1 atm. What is the volume when the balloon rises to an altitude where the pressure is only 0.25 atm? (assume temperature remains constant.) 6. The gas left in a used aerosol can is at a pressure of 1 atm at 27°C. If this can is thrown into a fire, what is the internal pressure of the gas when its temperature reaches 927°C? 7. 5.2 L of a gas is at STP. Find the new volume when the temperature rises to 38°C and the pressure drops to 600 mmHg. 8. Pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature are __________________ proportional. Why? ________________________________________________________________________ 9. Volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure are __________________ proportional. Why? _____________________________________________________________ 10. Volume and number of gas particles at constant pressure and temperature are ___________________ proportional. 11. If two containers are at the same temperature and pressure and their volumes are equal, they must contain the same ________________________________. Which scientist said this? __________________________ 12. Which travels faster CO2 or O2? How much faster? 13. Gas A travels 4 times faster than Gas B. If the molar mass of Gas B is 80 g/mole, find the molar mass of Gas A. 14. Refer to the phase diagram below when answering the questions: a. What is the normal freezing point of this substance? ________ b. What is the physical state of this substance at 300°C and 0.50 atm ? ____________ c. If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 3000 C and lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm, what phase transition(s) would occur? __________ 15. Given the following boiling point data, if the same amount of liquid of each substance was poured into separate, closed flasks at constant temperature, which substance would have the lowest vapor pressure? Formula of Boiling Name of compound compound Point (°C) Water H2O 100 Methanol CH3OH 65 Ethanol CH3CH2OH 78.5 Diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 34.5 Ethylene glycol HOCH2CH2OH 198 a. b. c. d. e. Water Methanol Ethanol Diethyl ether Ethylene glycol 16. At 1.0 atm , 0.75g of gas dissolves in 1L at 55 degrees. How much of the gas will dissolve in 4.0 atm at the same temperature? Who came up with this law?___________________________ 17. What volume of 3.7 M solution can be prepared using 89.5 grams of sulfuric acid? 18. What mass of magnesium chloride is required to prepare 2.15 liters of 6.5 M solution? 19. How would you prepare 2250 mL of a 3.25 M solution from a 16.0 M HNO3 stock solution? 20. If you mixed the following solutions, what would be the resulting molarity? 525 mL of 2.1M HCl 375 mL of 4.8 M HCl 295 mL of 7.6 M HCl 21. Circle all solutes that an “i” factor of 1. Why? a. C6H12O6 b. CF4 c. NH4Cl d. NH3 22. Why is calcium chloride more effective as rock salt in the winter than sodium chloride?