Shoulder Dystocia/ Neonatal Resuscitation SIM
advertisement

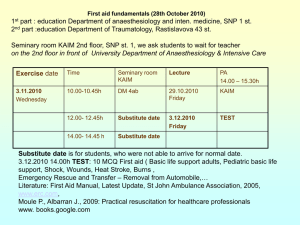
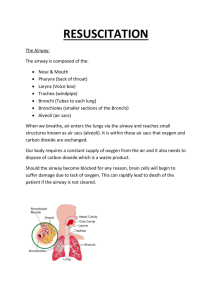
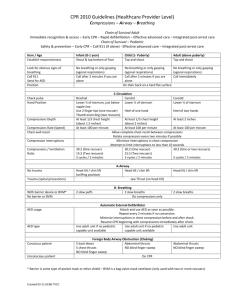
Shoulder Dystocia Scenario and Skill Stations Scenario You are a registrar on a night shift and the priority 1 phone goes off. 34yo G2P1 36/40 in labour and the shoulders are stuck. They are 30 minutes away. You are informed by the nurse coordinator that she has already spoken to the birthing suite and their doctors have just scrubbed in to perform an emergency C-section. The Paediatric registrar is also at this birth. Skill Stations This skill stations will be performed one after the other. There will be two doctors and two nurses assigned to each station. Gareth Kameron is nearby and may be available to assist if he’s not busy on the wards. Station 1: Preparation of the Neonatal Resuscitare, with equipment, drug and demonstrate umbilical vein cannulation. Doctors: Faheem and Richie Station 2: Demonstrate manoeuvres for shoulder dystocia using the baby dummy Doctors: Kris and Larissa Station 3: Demonstrate your competence with neonatal resuscitation Doctors: Marie and Kevin Station 1 How to Prepare for a Neonatal Resuscitation At least one person capable of resuscitating a newborn and this is there only responsibility Equipment Suction equipment Mechanical suction and tubing Meconium aspirator Bag and mask equipment Bag mask with cushion rim face mask capable of providing positive pressure ventilation Oxygen source (flow rate up to 10L/min) and tubing Intubation equipment Laryngoscope with straight blade, No. 0 (preterm) and No. 1 (term) ETT 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4 Stylet Scissors Securing tape C02 detector LMA *extra bulbs, batteries for laryngoscope NGT tube Medications Epinephrine 1:10, 000 (0.1ml/kg) Normal Saline Umbilical vessel catheterization supplies Sterile gloves Scalpel or scissors Antiseptic Umbilical tape Catheters 3.5F, 5F Three-way stopcock Syringes Needles How to Perform an Umbilical Vein Catheterization 1) 2) 3) 4) Clean the cord with antiseptic Place a tie around the base of the cord. Tightened. Pre-fill the umbilical catheter size 5 with normal saline OR size 5 feeding tube Using sterile technique cut the cord below the clamp that has been placed at birth about 12cm from the skin line 5) Insert the catheter pointing up towards the heart. Insert 4cm below the level of the skin until you get free flow of blood on aspiration 6) Set aside the dilute blood (2ml), take off an additional 1ml for the blood test, give back the 2ml of bloods. 7) The line I now ready to use for fluid bolus or adrenaline Station 2 Manoeuvres for Shoulder Dystocia Station 3 Neonatal Resuscitation Initial Assessment At the time of birth, ask yourself 4 questions, if the answer is No to any of them continue the initial steps of resuscitation Term gestation? Clear amniotic fluid? Breathing or crying? Good muscle tone? Airway To establish an airway Provide warmth Position the head and clear airway (suck nose then mouth) Dry the skin and stimulate to breathe Evaluation of Airway 30 seconds after the commencement of resuscitation Evaluate respirations, heart rate and colour If apneic or HR <100 proceed to assisted breathing Breathing Provide positive pressure ventilation for 30 seconds Evaluation of the effect of breathing after 30 seconds If the HR is less than 60bpm proceed to circulation (chest compressions 3:1) Circulation Support the circulation by providing chest compressions whilst continuing positive pressure ventilation Evaluation of the circulation after 30 seconds of chest compressions If the HR is still below 60bpm proceed to giving drugs Drugs Administer epinephrine as you continue positive pressure ventilation and chest compressions If HR remains less than 60bpm repeat chest compressions and adrenaline *When HR above 60bpm chest compressions are stopped *Positive pressure ventilation can be stopped when the HR is above 100 and the baby is breathing