Geometry I Can Statements
advertisement

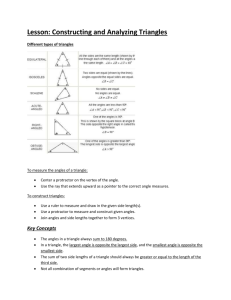
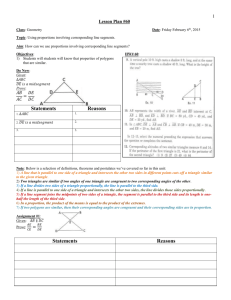
Geometry I Can Statements To prepare for the final exam, you should be able to do all of the items listed below. Chapter One “I Can” Checklist Section 1.1 I can identify and name undefined terms such as point, line, and plane. I can identify and name defined terms such as line segment and ray. Section 1.2 I can apply the segment addition postulate to solve problems. Section 1.3 I can use the distance and midpoint formulas in geometric and algebraic situations. Section 1.4 I can classify angles based on their measure. I can apply the angle addition postulate to solve problems. Section 1.5 I can use special angle relationships (supplementary, complementary, linear pair…..) to find angle measures. Section 1.6 I can classify polygons based on their number of sides, as well as identify their parts (sides, vertacies….). Chapter Two “I Can” Checklist Section 2.2 I can write and identify the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement. I can write the inverse and converse of a conditional statement. Section 2.3 I can apply the law of detachment to synthesize a logical conclusion. I can apply the law of syllogism (chain rule) to synthesize a logical conclusion. Section 2.4 I can use postulates about points, lines, and planes to interpret a diagram. Section 2.5 I can synthesize logical conclusions about geometric figures using algebraic properties of equality. Section 2.6 I can use theorems to write proofs about segments and angles. Section 2.7 I can use theorems and properties of special pairs of angles to write proofs. Chapter Three “I Can” Checklist To prepare for the final exam, you should be able to do all of the items listed below. Section 3.1 I can identify pairs of angles formed by three intersecting lines. (corresponding, alt. interior, alt. exterior, consecutive) I can identify the properties of parallel and skew lines. Section 3.2 I can identify and use the relationships between angle pairs formed by parallel lines and a transversal. Section 3.3 I can prove two lines are parallel. Section 3.4 I can find and use the slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines. Section 3.5 I can write and graph equations of parallel and perpendicular lines. Section 3.6 I can identify the many properties of perpendicular lines, and perpendicular transversals. Chapter Four “I Can” Checklist Section 4.1 I can classify triangles by their angle measure and their sides. I can use and identify relationships of angle measures within triangles. Section 4.2 I can identify and use properties of congruent figures. Section 4.3 I can prove triangles are congruent by using the SSS theorem. Section 4.4 I can prove triangles are congruent using SAS and HL. Section 4.5 I can prove triangles are congruent using ASA and AAS Section 4.6 I can prove parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Section 4.7 I can use and identify properties of isosceles and equilateral triangles Chapter Five “I Can” Checklist Section 5.1 I can identify and apply the properties of a midsegment of a triangle. Section 5.2 I can apply the properties of perpendicular bisectors. I can draw and apply the properties of the circumcenter of a triangle Section 5.3 I can use the properties of angle bisectors I can identify and use the properties of the incenter of a triangle Section 5.4 I can use and identify properties of the medians and altitudes of a triangle, as well as their points of concurrency. Section 5.5 I can determine the possible lengths of sides for any given triangle. NO CHAPTER 6 STATEMENTS AS OF NOW Chapter Seven “I Can” Checklist Section 7.1 I can apply the Pythagorean Theorem in order to find the side lengths of right triangles. Section 7.2 I can use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to prove that a triangle is a right triangle. Section 7.3 I can identify multiple similar triangles within a single picture I can use the properties I have learned about similar figures to find missing side lengths. Section 7.4 I can use and understand the relationships between the side lengths in special right triangles. I can simplify radicals. Section 7.5 I can apply the tangent ratio to find sides lengths of triangles and for indirect measurement. Section 7.6 I can apply the sine and cosine ratios to find sides lengths of triangles. Section 7.7 I can solve any right triangle given a combination of sides and/or angles. Section 7.7A I can apply the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to solve for all angles and sides of any type of triangle QUADRILATERALS Chapter Eight “I Can” Checklist Section 8.1 I can find the sum of the interior angles and a single interior or exterior angle in any polygon Section 8.2 I can I can apply the properties of parallelograms in order to find a side length or angle measures of a parallelogram. Section 8.3 I can prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Section 8.4 I can identify and apply the properties of rhombuses, rectangles, and squares. Section 8.5 I can identify and apply the properties of trapezoids and kites. I can identify any special quadrilaterals based on its observed properties. Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Chapter Nine “I Can” Checklist Section 9.1 I can use vectors to write translation rules for isometries. Section 9.2 I can organize information into a matrix and perform operations with matrices such as addition and multiplication. Section 9.3 I can reflect a figure across any given line of reflection. Section 9.4 I can rotate figures around any point given a degree of rotation. Section 9.5 I can perform a combination of two or more transformations including translations, reflections, and rotations. Section 9.6 I can identify line and/or rotational symmetry in any given image. Section 9.7 I can create dilations of an image by using a scale factor. Circles Chapter Ten “I Can” Checklist Section 10.1 I can identify the different types of segments lines within a circle including tangent, secant, chord, diameter, and radius. I can apply the properties of a tangent to a circle. Section 10.2 I can use angle measures to find arc measures of a circle. Section 10.4 I can apply properties of inscribed angles to polygons inscribed in a circle. Section 10.7 I can write and graph the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Measuring Length and Area Chapter Eleven “I Can” Checklist Section 11.1 I can apply the area formulas for both triangles and parallelograms. Section 11.2 I can apply the area formulas for trapezoids, rhombuses, and kites. Section 11.3 I can use the ratio of perimeters, and the ratio of areas, to find a perimeter or area using similar figures. Section 11.4 I can find both the circumference of a circle, and the length of any arc on that circle. Section 11.5 I can find both area of a circle, and of a sector of a circle. Section 11.6 I can find the area of a regular polygon using the apothem and perimeter. Section 11.7 I can use the areas of figures to calculate geometric probabilities. Surface Area and Volume of Solids Chapter Twelve “I Can” Checklist Section 12.1 I can classify different types of polyhedra and non-polyhedra. I can identify the number of faces, vertices, and edges on convex and concave polyhedra. Section 12.2 I can apply the area formulas I learned in chapter 11 to find the surface area of prisms and cylinders. Section 12.3 I can apply the area formulas I learned in chapter 11 to find the surface area of pyramids and cones. Section 12.4 I can find the volume of both prisms and cylinders. Section 12.5 I can find the volume of both pyramids and cones. Section 12.6 I can find both the surface area and volume of any given sphere. Section 11.7 I can apply properties of similar solids, including ratios of lengths, areas, and volumes