Chapter1 - Assumption University
advertisement

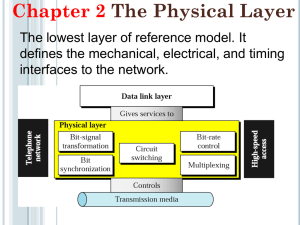
Chapter1 Telecommunication: a long-distance communication (of multimedia) via a groups of informationsharing networks all tied together. Data –It is an entity that convey meaning or information. Signal –It is an electrical or light signals or electromagnetic representations of data. Transmission –It is a communication of data by propagating and processing of signals. Analog Analog signals is a representation of data –e.g., the electrical signals (voltage and current) produced by a microphone that are analogs of the mechanical pressure waves of the sound on the microphone. Analog Data: has a continuous range of value as a function of time (e.g. sine wave, sawtoothwave) such as sound, temperature, etc. Analog Bandwidth is a usable frequency range of a connection. e.g. telephone connection can handle frequencies between 300 -3400 Hz (for voice) => bandwidth is 3.1 kHz. Digital Digital Data: has two discrete sets of value as a function of time e.g. binary data ( logic ‘1’and ‘0’). Digital signals are numerical representations of the original information. Digital Bandwidth (Data Rate) It is the amount of information that can be transmitted in a given amount of time e.g. 10 Mbps. Data rate is influenced by: –Physical media that make up the network. –Modulation techniques. –Amount of network traffic. –Software protocols of the network. Transmission media can be generally categorized into two types: guided and unguided media. •Guided or wire media include twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable. •Unguided or wireless media include satellite, microwave radio, and cellular transmission. •For guided media, the transmission characteristics determine the limitations of bit rate, bandwidth, and repeater (or amplifier) spacing. •For unguided media, the transmitting antenna is very important in determining the limitations of the system. Twisted pair •It is the most common transmission medium for both analog and digital data. •It simply consists of two insulated copper wires arranged in a spiral pattern •Twisted pair can carry analog and digital signals, however, amplification of the signal will be required at every certain distance. •Twisted pair is limited in distance, data rate, and bandwidth as compared to other types of transmission media. Coaxial Cable •Coaxial cables have better shielding than twisted pairs. Therefore signals can travels longer distances at higher transmission speed. •Two kinds of coaxial cables are widely in use : a 50-ohm cable usually used in digital transmission and a-75 ohm cable used in analog transmission. •Coaxial cable structure : a single copper wire covered by insulating material is at the center of the coaxial cable. -the insulated material is encased in a cylindrical conductor usually woven as a braided mesh. Optical Cable •An optical transmission system has three components: a light source, a transmission medium, and a detector. •A pulse of light indicates a 1 bit and the absence of light indicates a 0 bit. •The optical cable (transmission medium) is an ultra- thin (about human hair size) fiber glass. •The detector generates an electrical pulse when light falls on it. •Construction of optical cable is similar to coaxial cable construction Modulation: Manipulation of the carrier wave for transferring information. Types of modulation: –Amplitude modulation (AM). –Frequency modulation (FM). –Phase modulation (PM). Modem : a hardware device that connects a computer’s serial port (USB or universal serial bus for ADSL modem) to a telephone line (for remote access). Types of Communication •Simplex –data can be transmitted only one direction. •Half duplex –data can be transmitted on both directions, however, one direction at a time. •Full duplex –data can be transmitted on both directions simultaneously as shown in the Figure. Types of Transmission •Parallel transmission –many data (or signals) can be transmitted simultaneously. •Serial transmission –data (or signal can be transmitted one after another and can be categorized in to: –Synchronous transmission. –Asynchronous transmission. •Channel sharing can be done utilizing the multiplexing techniques. Two common techniques are – Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). –Time Division Multiplexing (TDM). 2 methods of Serial Transmission –Asynchronous Transmission–Bits are divided into small groups, usually bytes (groups of 8 bits), and sent independently. –Timing only needs to maintain within a character. –Start and stop bits are required for each byte. –Synchronous Transmission.–Large groups of data are transmitted. –Synchronization is required for transmission. Multiplexing Techniques Two Common Techniques are: •Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM): Multiple signals are transmitted simultaneously in the same channel. •Each channel is divided into portions of the bandwidth (called bands). These bands of frequency are allocated to multiple signals for transmission. •Time Division Multiplexing (TDM): Only one item can be sent at a time on shared channel. Item (signal) marked to identify source. Each channel allowed to be carried during pre- assigned timeslots only.