Why to learn OSI reference Model?

Why to learn OSI reference Model?
The answer is too simple that It tells us that how communication takes place between computers on internet but how??
Nowadays, When we talk about communication of computer we got to know a term communication protocols. What are they??
Set of rules which defines the rules followed by all involved in the process of communication but what are they actually??
What if someone is using some other rules/Protocols?
If it is necessary to communicate with computers following totally different protocols then we have to connect a device called Gateway between such systems. Gateways are computers loaded with special software, which do the job of translation work from one protocol to other so that communication between heterogeneous systems may take place.
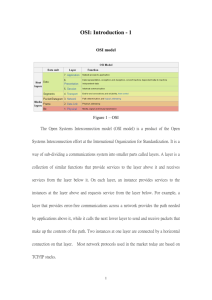
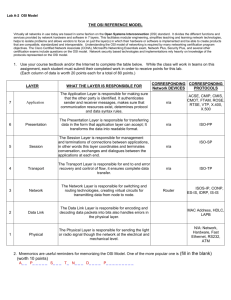
The Seven-layer Architecture of the OSI model
PHYSICAL LAYER
To Data link Layer
From Data link Layer
TRANSMISSION MEDIUM
•
Physical layer is the bottom layer of OSI model
•
It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. Such physical connection may be made by using twisted pair cable, fiberoptic, coaxial cable or wireless communication.
•
Physical layer is concerned with transmitting raw bits over a communication channel.
•
It deals with mechanical and electrical specifications of the interface and transmission medium and also defines the procedures and functions that physical device and interface have to perform for data transmission.
•
Physical layer is the bottom layer of OSI model
•
It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. Such physical connection may be made by using twisted pair cable, fiberoptic, coaxial cable or wireless communication.
•
Physical layer is concerned with transmitting raw bits over a communication channel.
•
It deals with mechanical and electrical specifications of the interface and transmission medium and also defines the procedures and functions that physical device and interface have to perform for data transmission.
Function of Physical layer
• Transforming bits into signals
• Bit Synchronization
• Provides physical characteristics of interfaces and medium
• Bit rate control
• Line configuration
• Transmission mode
• Physical topologies
• Multiplexing
• Circuit switching
DATA LINK LAYER
Functions of Data link layer
• Framing
• Physical Addressing
• Flow control
• Error control
• Access Control
• Feedback
Network Layer
Functions of Network layer
• Logical Addressing
• Routing
Transport Layer
• Transport layer provides two types of services
– Connection oriented
– Connectionless
Session Layer
Function of Transport layer
• Segmentation of message into packet and reassembly of packets into message
• Connection management
• Service point addressing
• Flow control
• Error control
Function of Session layer
• Establishment, maintaining and ending a session
• Dialog control
• Dialog separation or Synchronization
Presentation Layer
• Different computers may use different coding schemes for data transmission. For example some computers may send the most significant bit of a byte first and least significant bit last and in some other computers it may be other way round, the sequence may be different at byte level also.
The job of the presentation layer is to do the job of code translation and present the data in the format used at the destination computer.
Functions of presentation layer
• Data Presentation or Translation
• Data Encryption
• Data compression
Application Layer
• This is the layer with which users have direct interface. At the transmitting computer the message originates at this layer and at the destination computer the message is finally received by this layer and presented to the user in desired format. The data packets at the application layer are known as messages
Functions of Application Layer
• Network Virtual Terminal
• File transfer, access and management (FTAM)
• Mail services
• Directory services
THANKS
HOUSE IS OPEN FOR QUERIES