Isotopes & Average Atomic Mass: Chemistry Notes
advertisement
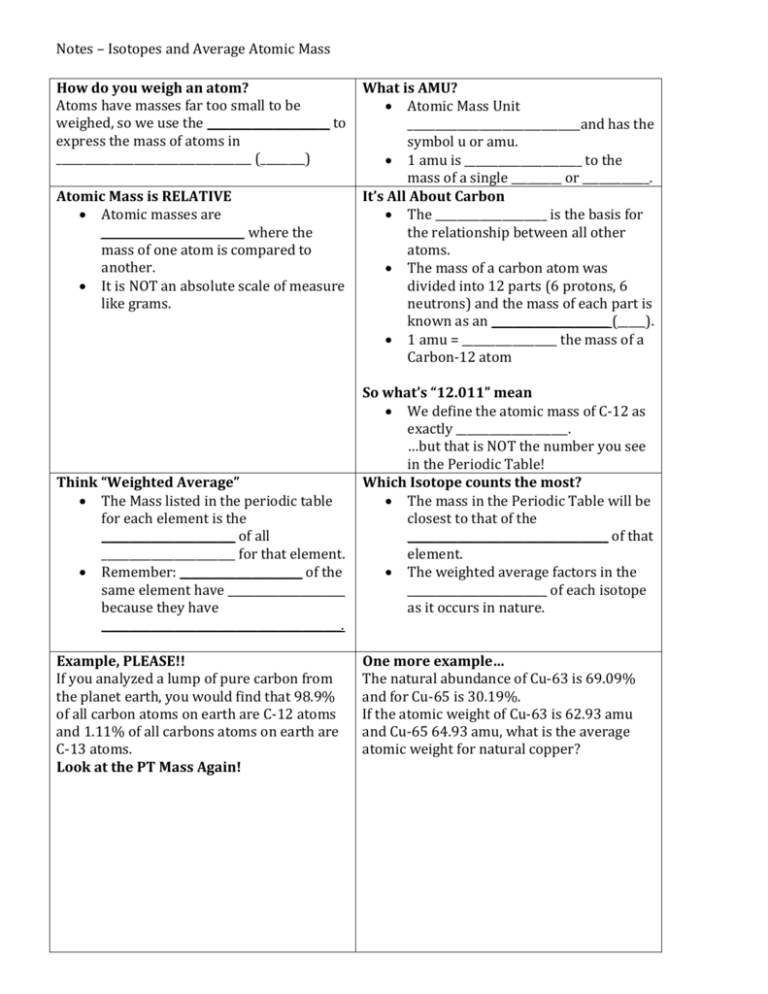
Notes – Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass How do you weigh an atom? Atoms have masses far too small to be weighed, so we use the ______________________ to express the mass of atoms in ___________________________________ (________) Atomic Mass is RELATIVE Atomic masses are ___________________________ where the mass of one atom is compared to another. It is NOT an absolute scale of measure like grams. Think “Weighted Average” The Mass listed in the periodic table for each element is the ________________________ of all ________________________ for that element. Remember: ______________________ of the same element have _____________________ because they have ___________________________________________. Example, PLEASE!! If you analyzed a lump of pure carbon from the planet earth, you would find that 98.9% of all carbon atoms on earth are C-12 atoms and 1.11% of all carbons atoms on earth are C-13 atoms. Look at the PT Mass Again! What is AMU? Atomic Mass Unit _______________________________and has the symbol u or amu. 1 amu is _____________________ to the mass of a single _________ or ____________. It’s All About Carbon The ____________________ is the basis for the relationship between all other atoms. The mass of a carbon atom was divided into 12 parts (6 protons, 6 neutrons) and the mass of each part is known as an _____________________ (_____). 1 amu = _________________ the mass of a Carbon-12 atom So what’s “12.011” mean We define the atomic mass of C-12 as exactly ____________________. …but that is NOT the number you see in the Periodic Table! Which Isotope counts the most? The mass in the Periodic Table will be closest to that of the ____________________________________ of that element. The weighted average factors in the _________________________ of each isotope as it occurs in nature. One more example… The natural abundance of Cu-63 is 69.09% and for Cu-65 is 30.19%. If the atomic weight of Cu-63 is 62.93 amu and Cu-65 64.93 amu, what is the average atomic weight for natural copper?