Co-variance risk and capital modelling in Micro Insurance
advertisement
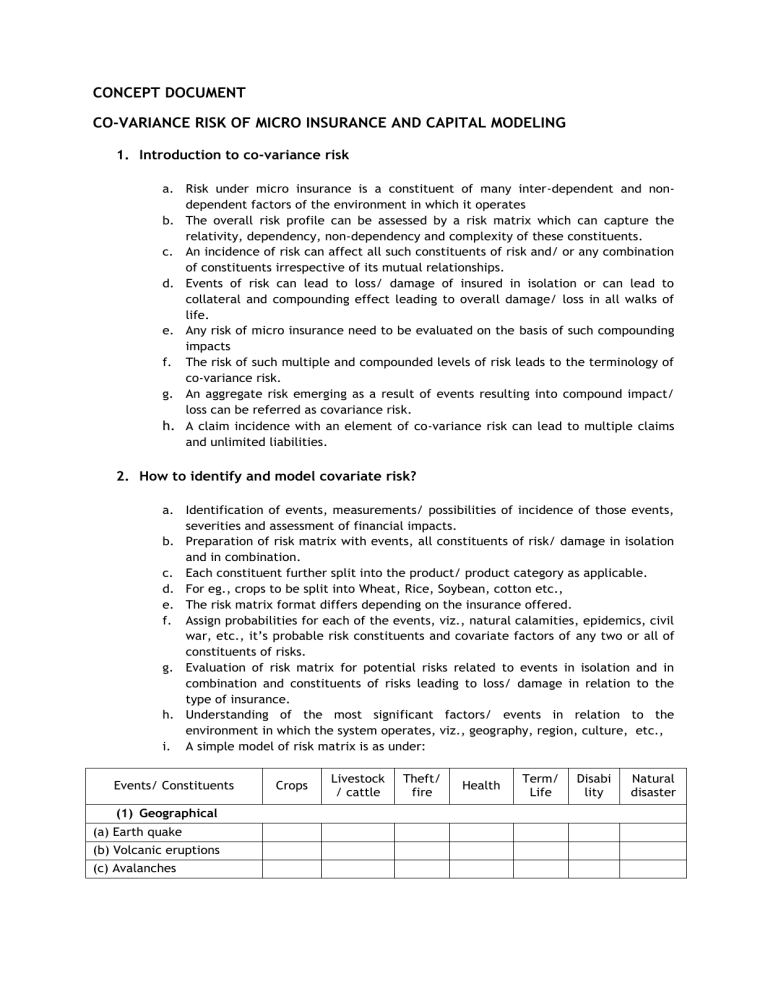
CONCEPT DOCUMENT CO-VARIANCE RISK OF MICRO INSURANCE AND CAPITAL MODELING 1. Introduction to co-variance risk a. Risk under micro insurance is a constituent of many inter-dependent and nondependent factors of the environment in which it operates b. The overall risk profile can be assessed by a risk matrix which can capture the relativity, dependency, non-dependency and complexity of these constituents. c. An incidence of risk can affect all such constituents of risk and/ or any combination of constituents irrespective of its mutual relationships. d. Events of risk can lead to loss/ damage of insured in isolation or can lead to collateral and compounding effect leading to overall damage/ loss in all walks of life. e. Any risk of micro insurance need to be evaluated on the basis of such compounding impacts f. The risk of such multiple and compounded levels of risk leads to the terminology of co-variance risk. g. An aggregate risk emerging as a result of events resulting into compound impact/ loss can be referred as covariance risk. h. A claim incidence with an element of co-variance risk can lead to multiple claims and unlimited liabilities. 2. How to identify and model covariate risk? a. Identification of events, measurements/ possibilities of incidence of those events, severities and assessment of financial impacts. b. Preparation of risk matrix with events, all constituents of risk/ damage in isolation and in combination. c. Each constituent further split into the product/ product category as applicable. d. For eg., crops to be split into Wheat, Rice, Soybean, cotton etc., e. The risk matrix format differs depending on the insurance offered. f. Assign probabilities for each of the events, viz., natural calamities, epidemics, civil war, etc., it’s probable risk constituents and covariate factors of any two or all of constituents of risks. g. Evaluation of risk matrix for potential risks related to events in isolation and in combination and constituents of risks leading to loss/ damage in relation to the type of insurance. h. Understanding of the most significant factors/ events in relation to the environment in which the system operates, viz., geography, region, culture, etc., i. A simple model of risk matrix is as under: Events/ Constituents (1) Geographical (a) Earth quake (b) Volcanic eruptions (c) Avalanches Crops Livestock / cattle Theft/ fire Health Term/ Life Disabi lity Natural disaster (2) Meteorological (a) Cyclic storms (b) Droughts (c) Blizzards (d) Tornadoes (e) Heat wave/ cold wave (f) Hail storms (3) Hydrological (a) Floods (b) Tsunamis (c) Limnic eruptions (4) Health (a) Epidemics (5) Space disasters (a) Solar flames (b) Impact events (c) Gamma ray burst (6) Fire (7) Others (a) Civil war (b) Sanctions (c) War (d) Ruling regime 3. Risk mitigation and capital modelling a. Risk mitigation and capital modelling of covariate risk is based on the environment in which the society lives in and all players in the scene. b. The success of mitigation depends on how best the pooling of risks by way of diversification and re-insurance c. This also based on social needs of the society and duration for which the solutions to be implemented. d. The capital management is based on a number of factors of the society and systems in place. e. The interaction of society, systems and needs can also be viewed in a matrix and can be a basis of capital management. f. A matrix on which the risk mitigation and capital modelling can be built is as under: Items Social Policy Approach Social Risk Manage ment Basic Social security Social Insurance Social Assista nce Safety nets Social Security Legislation X X X X X X X Actors (a) Public Action (b) Collective Private Action (c) Market-based (d) Individual Private Action Risk focus (a) Risk prevention and mitigation X X X X X X X X X X X X X X (b) Risk Coping (c) Non-risk management policies that may affect risk management Duration of Action X X X X X (a) Short term measure X X (b) Long term measure X X X X X X X X X X X Type of capacity deficit (a) Measures to support those who cannot help themselves (b) Focus on the ablebodied (c) Measures to provide basic food, health, housing and education security for all Key function X X X X X X X (b) Assistance X X (c)Enabling/empowering social services & infrastructure X Explicit focus on the poor and deprived X X X X (a) Insurance Type of risk addressed (a) Co-variant X (aggregate) Dimension of well-being addressed (a) Income and X consumption (b) Non-income dimensions of wellX being (social, political etc) Includes a right focus X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X