IOC and Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement
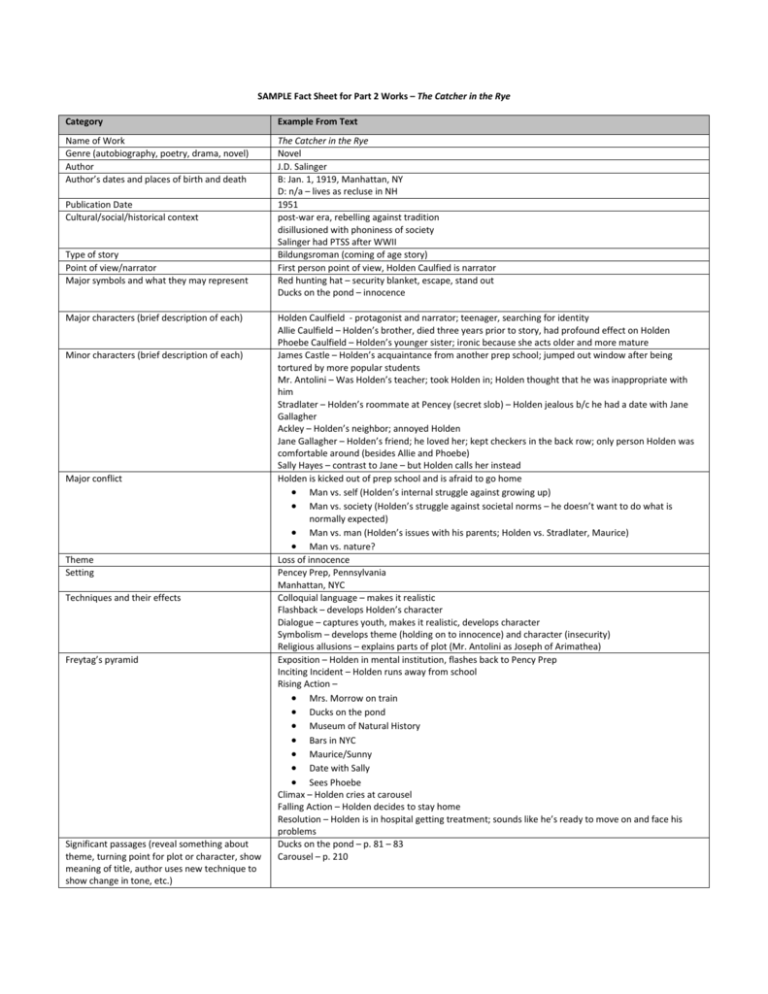
SAMPLE Fact Sheet for Part 2 Works – The Catcher in the Rye Category Example From Text Name of Work Genre (autobiography, poetry, drama, novel) Author Author’s dates and places of birth and death The Catcher in the Rye Novel J.D. Salinger B: Jan. 1, 1919, Manhattan, NY D: n/a – lives as recluse in NH 1951 post-war era, rebelling against tradition disillusioned with phoniness of society Salinger had PTSS after WWII Bildungsroman (coming of age story) First person point of view, Holden Caulfied is narrator Red hunting hat – security blanket, escape, stand out Ducks on the pond – innocence Publication Date Cultural/social/historical context Type of story Point of view/narrator Major symbols and what they may represent Major characters (brief description of each) Minor characters (brief description of each) Major conflict Theme Setting Techniques and their effects Freytag’s pyramid Significant passages (reveal something about theme, turning point for plot or character, show meaning of title, author uses new technique to show change in tone, etc.) Holden Caulfield - protagonist and narrator; teenager, searching for identity Allie Caulfield – Holden’s brother, died three years prior to story, had profound effect on Holden Phoebe Caulfield – Holden’s younger sister; ironic because she acts older and more mature James Castle – Holden’s acquaintance from another prep school; jumped out window after being tortured by more popular students Mr. Antolini – Was Holden’s teacher; took Holden in; Holden thought that he was inappropriate with him Stradlater – Holden’s roommate at Pencey (secret slob) – Holden jealous b/c he had a date with Jane Gallagher Ackley – Holden’s neighbor; annoyed Holden Jane Gallagher – Holden’s friend; he loved her; kept checkers in the back row; only person Holden was comfortable around (besides Allie and Phoebe) Sally Hayes – contrast to Jane – but Holden calls her instead Holden is kicked out of prep school and is afraid to go home Man vs. self (Holden’s internal struggle against growing up) Man vs. society (Holden’s struggle against societal norms – he doesn’t want to do what is normally expected) Man vs. man (Holden’s issues with his parents; Holden vs. Stradlater, Maurice) Man vs. nature? Loss of innocence Pencey Prep, Pennsylvania Manhattan, NYC Colloquial language – makes it realistic Flashback – develops Holden’s character Dialogue – captures youth, makes it realistic, develops character Symbolism – develops theme (holding on to innocence) and character (insecurity) Religious allusions – explains parts of plot (Mr. Antolini as Joseph of Arimathea) Exposition – Holden in mental institution, flashes back to Pency Prep Inciting Incident – Holden runs away from school Rising Action – Mrs. Morrow on train Ducks on the pond Museum of Natural History Bars in NYC Maurice/Sunny Date with Sally Sees Phoebe Climax – Holden cries at carousel Falling Action – Holden decides to stay home Resolution – Holden is in hospital getting treatment; sounds like he’s ready to move on and face his problems Ducks on the pond – p. 81 – 83 Carousel – p. 210 Fact Sheet for Part Two Works – Prose and Drama Category Name of Work Genre (autobiography, poetry, drama, novel) Author Author’s dates and places of birth and death Publication Date Cultural/social/historical context Type of story Point of view/narrator Major symbols and what they may represent Major characters (brief description of each) Minor characters (brief description of each) Major conflict Theme Setting Example From Text Category Techniques and their effects Freytag’s pyramid (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, denouement) Significant passages (reveal something about theme, turning point for plot or character, show meaning of title, author uses new technique to show change in tone, etc.) Example From Text Fact Sheet for Part Two Works – Poetry Category Name of poem and first line Poet Poet’s dates and places of birth and death Publication Date (if known) Cultural/social/historical context Speaker of poem (persona) Theme (and how does poet develop it?) Tone Length Structure (structured or free verse?) Rhyme scheme Sound effects Figurative language Major symbols and what they represent Relationship to poet’s work as a whole Example From Poem Consider also a line-by-line study (especially of those works you’re uncomfortable with): Line Paraphrase Elements of Style Effects or Functions







