Review guide
advertisement

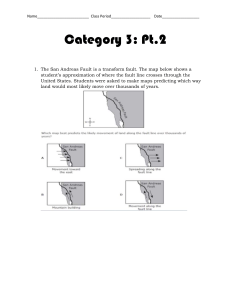
Mr. Hills Oceanography Marine Sediment, Water Chemistry and Seawater EXAM REVIEW Better ask me if you can’t find these. 1. What are manganese nodules and where on the ocean floor are the found? Why do they form here do you think? 2. Know the terms Biogenous sediment, and Lithogenous sediment and be able to tell the difference between them. 3. Find out what a diatom is? What kind of sediment does it produce? 4. Know the difference between Neretic and Pelagic sediment. Where are each found? 5. From which continent does most oceanic RIVER sediment come from? 6. What is the major force bringing sediment from the continents to the ocean? 7. What are the prime oceanic conditions for dissolving Calcium Carbonate? What is calcium carbonate? 8. What two forces determine the phases of water? What are the phases of water? 9. What are a couple of things that make water special and important to life on earth (notes and Table 5.2)? Mr. Hills Oceanography 10. What is a calorie (in energy terms)? 11. Does it take more energy to change phases from solid to liquid, or liquid to vapor? 12. What is the effect of evaporation on human and ocean temperatures? 13. Why do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules? 14. When I filled a dish in class with water, the water “piled up” above the rim. What water property allowed for this? What other things does this property allow for (insects, sticky glass)? Also, compared to other substances, how strong is this property in water (comparatively)? 15. How do temperature and salinity affect water viscosity? What is viscosity? 16. How deep does light penetrate in clear water (in Meters)? How deep is the deepest point in the ocean (in Meters)? 17. Is sound faster or slower in water than through the air? 18. How does waters ability to absorb, or conduct heat (heat capacity) compare to other liquids? 19. Why is polarity of water molecules soooooo important? Mr. Hills Oceanography 20. How does an increase in salinity affect water’s freezing point? 21. Which factor is most important in determining water’s density? 22. What is a Halocline? What is a good example we looked at in class (it was cool)? 23. How do temperature and pressure affect water’s ability to dissolve gasses (like CO2 and O2)? 24. What are the reactants (things that go into a chem. reaction), and the products (things that come out of a chemical reaction) of photosynthesis and respiration? 25. If I mentioned a rule that stated that major ions in seawater are in constant proportions, what rule would I be referring to? 26. What are the most abundant dissolved ions in the ocean? 27. Why do lakes “turn over” in the fall? 28. What is the average ppt (parts per thousand) concentration of dissolved substances in the ocean? What is the word for this?