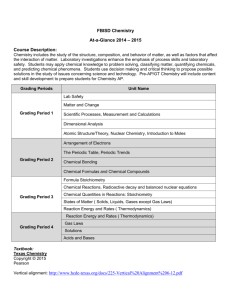
Unit 2 Timetable
advertisement

Suggested Units 1 and 2 Timetables These are only suggestions as different schools and different teachers may decide to teach the material in different orders. However, these timetables will give an indication of the time to spend on various topics. The references are the Pearson/Heinemann Chemistry One and Chemistry Two text books and the accompanying Student Workbooks for Units 1 and 2 and Units 3 and 4. These text books have accompanying Work programs online that are also very useful. With regard to the new 2013 – 2016 Study Design: Most text books have not made any changes yet for the 2013-2016 Study Design. There are changes for Units 1 and 2 so there is no need for change to Chemistry One; There are changes for Units 3 and 4, but the present 4th edition (enhanced) of Chemistry Two has not been changed for the 2013 Study Design. The Heinemann Chemistry 2 Student Workbook Units 3 and 4, Edition 2, has been updated specifically for the 2013 Study Design. In the Units 3 and 4 timetable the following notes apply. **Text reference: Chemistry Two Edition 4 *Workbook reference: Heinemann Chemistry 2 Student workbook Units 3 and 4 Edition 2 Possible UNIT 1 TIMETABLE Week Concepts Text chapt Minimum Chapter Questions Term 1 Area of Study 1: THE PERIODIC TABLE 1 Elements 1 15, 17, 20, 23 Periodic table Compounds 2 3 4 5 Development of atomic theory Nuclear atom Electronic configuration 2 19, 20, 21, 22, 23a,c, 24, 26, 29, ace, 30, 31, 34 The modern periodic table Periodic properties Trends in properties Compounds Masses of particles The mole 3 16, 18, 19, 20, 22, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 Practice mole concept calculations and complete all questions form chapters in text book 6 Molar mass Empirical and molecular formulas percentage composition Term 1 Area of Study 2: MATERIALS 7 Metals 8 SAC Dates & Details TRB1 p. 13 Changes in chemical reactions Video: World of Chemistry, Periodic Table. (parts) P16 worksheet activity 5 - Organising elements Revision – Worksheets 3 &4 SW1 p. 81 Flame colours of selected metals (an experiment for the summary report) Video: Bohr atom (parts) SW1 p. 28 Period 3 elements P17 worksheet activity 6 - Tracking Trends TRB1 p. 26 Mole simulation and applications Video: World of Chemistry, The Mole 21, 22, 23, 24 Worksheets 7-11 (Homework or class revision) 4 26aceg, 27, 28, 29, 31, 32, 36, 37, 38, 40, 32, 45, 48, 50, 51 SW1 p. 31 Chemical composition of a compound Prac: Empirical formula determination 5 10, 14, 15, 17, 20, 21, 23 Ionic compounds – properties & model Electron transfer diagrams Chemical formulas 6 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 29 Covalent molecular substances 7 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 SW1 p. 72 Testing materials TRB1 p. 33 Growing metal crystals Prac: Modifying the properties of metals SW1 p. 82 Solubility of compounds in water (an experiment for the summary report) SW1 p. 84 Conductivity of common materials (an experiment for the summary report) SW1 p. 75 Making molecular models 9 4 Practical work including Worksheets from W/book and videos SW1 p. 34 Periodic variation of properties – analysis of 2nd hand data Shapes of molecules Polarity of molecules 7 23, 24, 25, 26, 29, 31, 34, 36 Forces between molecules Covalent lattices 11 Carbon Hydrocarbons Naming hydrocarbons 8 18, 21, 22, 23, 24 12 8 Properties of alkenes and alkenes Polymers 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 32, 34, 40 An overview of bonding Surfaces Nan particles 9 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17 Holiday – move as needed 10 13 14 15 16 17 Semester 1 2 Worksheets No 12, 17 Revision Revision Exams Exams 2: Unit 2: Area of Study 1 Water The water cycle 10 Properties of water Water as a solvent Measuring solubility Concentration of solutions 11 13, 14, 19, 23, 24, 31, 32, 34, 35 14. 15, 17, 19, 22ace, 23ace, 26, 28, 32, 35, 37 TRB1 p. 41 Comparing the physical properties of different covalent lattices Worksheet No 18, 19 SW1 p. 78 Investigating hydrocarbons Worksheet No 21 Worksheet No 23 Demo: Thermosetting and Thermoplastic polymers TRB1 p. 50 Making ghost buster slime TRB1 p. 53 Making an Eastover Prac: Wetting Demo: Flotation of Mothballs TRB1 p. 43 Bucky balls, annotates and other allotropes of carbon No. 22 worksheet, p69 Selections from TRB1 p. 61 Properties of water WS25: Wonderful water—structure and properties TRB134: Effect of polarity on solubility TRB135: Supersaturation TRB136: Stalagmite from a supersaturated solution TRB137: Concentrations of solutions SW1 p. 81 A summary report of three practical activities SW1 p. 86 Nanotechnolo gy and new materials – a poster presentation (optional for you not the students!) Possible UNIT 2 TIMETABLE Term 3 Area of Study 1: WATER Wk Concepts Text chapt Minimum Chapter Questions 3 Precipitation reactions Ionic equations Maintaining water quality 12 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17 4 Introducing Acids & bases Reactions involving acids and bases 13 2, 5, 8, 9 5 Brønsted - Lowry definition Acid and base strength pH scale 14 15, 16, 17, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 31, 32 6 Stoichiometry 15 14, 15, 17, 19, 23, 24, 28, 30, 32, 33, 7 Excess reactants Volumetric analysis 15 35, 36, 39, 40, 41, 43, 45 More practice of stoichiometry and catch up 15 8 Practical work including Worksheets from W/book and videos SW1 p. 115 Precipitation reactions WS26: Solving solubility—predicting precipitation reactions TRB1 p. 77 Purification of polluted water TRB1 p. 80 reactions of hydrochloric acid eei- Use some of the activities from Experimental investigation of the properties and behaviour of acids only use as a prac WS27: Recording equations—Full and ionic chemical equations; WS28: Concentration and strength—picturing acids and bases; T49: Strong and weak acids TRB1 p. 82 Amphiprotic substances in water WS31: Acidity of solutions—calculating pH WS24: Crossword— acids and bases SW1 pp. 119 Products of a decomposition reaction WS29: Stoichiometry 1: Mass–mass calculations TRB1 p. 90 Determination of the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution WS30: Stoichiometry 2: Excess reagent calculations WS32: Solving complex calculations—using School-assessed Coursework An extended experimental investigation could be developed using acids and bases and pH pracs and making the links (It could be good to do this at this early stage of the semester) 9 Oxidation and reduction Redox reactions Oxidation numbers 16 22, 25, 27, 29, 30, 31, 32 10 Galvanic cells The electrochemical series Corrosion 16 36, 38, 40, 42, 43, 46, 47, 50 11 Green Chemistry: Some of the following-Applications of green chemistry; The CFC story; replacement of halogenated solvents with supercritical CO2 in industrial processes or in plant protection. Area of study review 17 3, 4, 5 18 19 11, 12, 14, 16, 20 12, 14, 15, 21, 22, 24 12 The atmosphere Essential gases Acid rain Depletion of the ozone layer Smog Green house effect Term 4 Area of Study 2 - THE ATMOSPHERE 13 Laboratory and industrial 20 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, preparation of a gas of 20 significance to the quality of the atmosphere – carbon dioxide 14 Kinetic molecular theory Pressure, volume relationships Gas laws General gas equation Gas stoichiometry 21 33, 34, 36, 40, 41, 43, 45, 47, 48, 49, 51, 57, 59, 61, 64, 66, 67 more than one formula SW1 p. 121 Corrosion WS33: Matchmaker— redox reactions; WS34: Metals and their cations—writing half equations TRB1 p. 98 Electrochemical cells and corrosion WS35: From chemicals to electricity—galvanic cells TRB1 p. 102 Investigating galvanic cells WS36: Sorting statements—principles of green chemistry WS37: Conserving atoms—the green chemistry principle of atom economy SW1 p. 155 Preparation and properties of oxygen WS41: Gases of the atmosphere—concept maps WS38: Crossword—the atmosphere WS39: Humans doing damage—the greenhouse effect and the ozone layer SW1 p. 155 Preparation and properties of oxygen WS40: Cycling matter—carbon and nitrogen SW1 p. 157 Volumepressure relationships of gases SW1 p. 160 Molar volume of hydrogen WS42: Explaining gas behaviour—kinetic molecular theory WS44: How humans breathe—Boyle’s Law WS45: Charles Law WS47: Different but SW1 p. 163 Greenhouse and global warming – a response to stimulus material (optional for you if time permits) SW1 p. 164 Preparation and properties of carbon dioxide – an extended experimental investigation (could be done here but it is very late in the year) 15 Revision 16 17 Revision Exams /Year 12 exams for those doing a ¾ subject the same—molar volume of gases WS43: Equivalent measures—converting units WS46: Changing conditions—effects of temperature, volume and amount on pressure. WS48: Putting it all together—the general gas equation WS49: Stoichiometry 3: mass–volume It is worth remembering that many Year 11 students are doing Year 12 subjects and once Week 3 of Term 4 arrives they are thinking mainly of their Year 12 subject. I always tried to complete the Year 11 course by the end of Week 2, Term 4 and only be doing revision in the Weeks 3, 4, 5 leading up to Year 11 exams. Many of your students will be missing at different times. For this reason I would not recommend doing the eei or summary report in Term 4 on the material in The Atmosphere. It will be treated more seriously if it is done in Term 3 and therefore on the Area of Study 1, Water. There are plenty of pracs that could be appropriate – stoichiometry (titrations etc) redox reactions as well as my suggestion of acids and bases.