Chemistry 1 Syllabus
advertisement

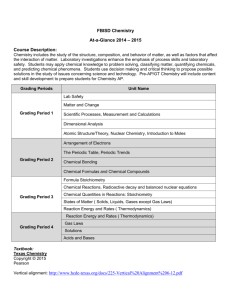
Chemistry I Syllabus Mrs. Carson Book: World of Chemistry by Zumdahl (2002) Chemistry I is the first level of chemistry in which students will learn the language of chemistry and fundamental concepts, how to solve problems, how chemistry applies to our daily lives, and important laboratory skills. Knowledge of these concepts is necessary to enter many professions such as engineering, medicine, biology, forensics, geology, and of course, chemistry. It is a course that will prepare you for college chemistry. Accordingly, you will have to study on your own, do your homework, and ask for help when the going gets tough. But in addition to learning chemistry, I hope that you also enjoy chemistry, see that it can be fun, and experience the wonderment that I have every time something goes pop, fizz, or boom! The following is a general outline of the chapters involved in this course. Notice the order doesn’t follow the book as we initially visit topics and then later revisit them to add more details. Tests are at the end of each unit. UNIT 1A Ch. 1 Chemistry: An Introduction What is Chemistry and why learn it? Solving problems by the scientific method, importance of theories, laws, and models Ch. 5 Measurements and Calculations Measurements, uncertainty in measurements, significant figures UNIT 1B Ch. 5 Measurements and Calculations Density, scientific notation, graphing, techniques for solving problems – algebra or factor label (dimensional analysis) UNIT 2 Ch. 10 Energy Ch. 2 Matter Ch. 13 Gases Temperature and heat States of matter Effects of pressure, volume, temperature, number of particles – Gas Laws; Kinetic Molecular Theory UNIT 3 Ch. 10 Energy Energy, endothermic and exothermic processes (during change of state), energy changes during change of states (thermodynamics) Ch. 2 Matter Changes in state of matter, graphs of changes in states UNIT 4 Ch. 2 Matter Elements and compounds, properties of matter, physical and chemical changes Ch. 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions Early atomic theories, element symbols UNIT 5 Ch. 6 Chemical Composition The mole, molar mass, percent composition, empirical formulas, molecular formulas UNIT 6 Ch. 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions Basic atomic structure, isotopes, ions, periodic table organization Ch. 4 Nomenclature Chemical names and formulas UNIT 7 Ch. 7 Chemical Reactions: An Introduction Signs of a chemical reaction, writing a balanced chemical equation Ch. 8 Reactions and Aqueous Solutions Driving forces of chemical reactions, types of chemical reactions, predicting products of a reaction and writing equations for such reactions Ch. 10 Energy Energy, endothermic and exothermic reactions, energy changes during chemical change (thermochemistry) UNIT 8 Ch. 9 Chemical Quantities Stoichiometry - Using the mole and equations to determine quantities of reactants and/or products in a reaction, limiting reagents, theoretical yields Ch. 10 Energy Energy, endothermic and exothermic reactions, energy changes during chemical change (thermochemistry) UNIT 9 Ch. 13 Gases Partial pressures, Ideal gas law, molar volume, gas stoichiometry Ch. 15 Solutions Molarity, solution stoichiometry UNIT 10 Ch. 16 Acid-Base Reactions Definitions and properties of acids and bases, indicators, pH and pOH, titrations Ch. 15 Solutions Molarity, solution stoichiometry UNIT 11 Ch. 11 Modern Atomic Theory Quantum mechanical model of the atom, electrons and light, electron arrangement in the atom and the periodic table, atomic properties and the periodic table Ch. 12 Chemical Bonding Electronegativity UNIT 12 Ch. 12 Chemical Bonding Types of chemical bonds, bond polarity, Lewis structures of molecules, molecule geometry (VSEPR)