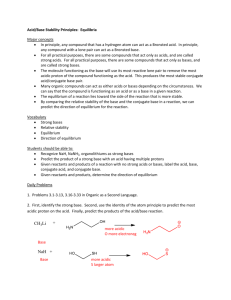
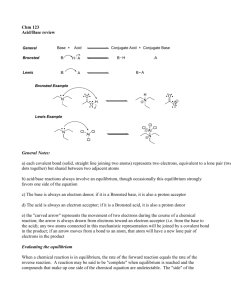
The strengths and weaknesses of acids and bases
advertisement

Name _____________________________________ Period ____ The strengths and weaknesses of acids and bases http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-strengths-and-weaknesses-of-acids-and-bases-george-zaidan-andcharles-morton 1. What’s the difference between a proton and a positively charged hydrogen ion? a. Protons are neutral and hydrogen ions have a positive charge b. Hydrogen ions have one electron and protons don’t have any c. Protons weigh more than hydrogen ions d. They’re the same thing 441498 2. Which of the following statements is true: a. Our stomachs are about as acidic as our blood is basic b. Our stomachs are about as basic as our blood is acidic c. Our stomachs are far more acidic than our blood is basic d. Our stomachs are far more basic than our blood is acidic 3. Which acid is stronger, hydrochloric or acetic? a. Hydrochloric b. Acetic c. They’re the same strength d. Nobody knows 4. A proton deposit customer (an acid) is most similar to ________. a. A proton withdrawal customer b. An electron withdrawal customer c. An electron deposit customer d. None of the above 5. If you were to mix a strong acid with a weak base, would they completely neutralize each other? a. Yes, always b. No, because a weak base cannot neutralize a strong acid c. No, because only acids can neutralize acids d. There’s no way to tell from the information given 6. Two important characteristics of acids and bases are: (1) strength and (2) concentration. We talked about strength in the video, but not concentration. What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid? Vinegar is about 5% acetic acid. Is this a measure of its strength or concentration? If you were given the choice between drinking a solution of 0.1% hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) to 70% acetic acid (a weak acid), which would you choose and why? Is there any additional information you’d need to answer this question? (Note: DON’T DRINK THINGS THAT AREN’T MEANT TO BE DRUNK. THIS IS PURELY A THOUGHT EXPERIMENT.) 7. Suppose you mix hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) with ammonia (a weak base). Would the final mixture be acidic, basic, or neutral? As you might have guessed, there’s not enough information given to answer the question. What other information would you need? 8. Why is donating a proton not very different from accepting an electron? At about 1:20, we show the picture for hydrochloric acid. Draw equivalent pictures for acetic acid and ammonia. In each case, show the donated (or accepted) proton (or electron).