Quiz
advertisement

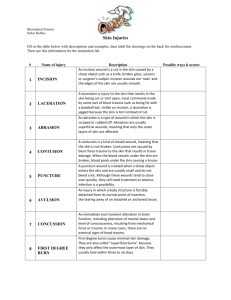
Wounds & Hemostasis Quiz by C. Kohn Name: Hour Date: Score: 1. These thin the blood and keep it flowing under normal circumstances a. Coagulants b Anticoagulants c Viscosity d Platelets 2. This type of wound is characterized by long smooth edges usually caused by a sharp object a. Abrasion b. Incision c. Puncture Wound d. Laceration 3. This type of wound is usually known as a ‘scrape’ a. Abrasion b. Incision c. Puncture Wound d. Laceration 4. This type of wound could be a combination of many kinds of wounds and has irregularly torn edges a. Abrasion b. Incision c. Puncture Wound d. Laceration 5. Hemostasis is… a. The term for the body’s ability to regulate itself b. The term for keeping the blood at a specific viscosity c. The term for the body’s chemical reactions that stop bleeding d. The blood vessels that lead away from the heart 6. Vasoconstriction occurs when… a. Platelets are released b. Blood vessels constrict c. A fibrin clot forms d. White blood cells cause inflammation 7. How do platelets know to stick to the site of any injury to form a clot? a. They stick to collagen fibers sticking out from the wound b. They sense signals being sent by nerves in the wound c. They change as a result of injury d. They stick to everything, including injuries 8. How are platelets different from other cells a. Platelets divide more quickly b. Platelets lack proteins, making them very flexible c. Platelets lack a nucleus, have a sticky protein coat, and have contractile proteins d. All of the above 9. What is responsible for the closing of a wound? a. Red Blood Cells b. White Blood Cells c. Fibrin d. Platelets Page | 1 Copyright 2011 by Craig Kohn, Agricultural Sciences, Waterford WI. This source may be freely used provided the author is cited. /20 10. The process in which platelets release chemicals that cause the release of more platelets is an example of a… a. Feed-forward mechanism b. Negative feedback mechanism c. Forward passing mechanism. 11. Where does the new skin come from after the wound is closed? a. Red Blood Cells b. Fibrin c. Mitosis of existing skin d. Collagen 12. A scab is made from a. Fibrin b. Red Blood Cells c. White Blood Cells d. All of the above 13. Blood vessels a. Dilate b. Constrict once bleeding has been controlled to bring more white blood cells to the injury c. Close d. Pulse 14. Which of the following is responsible for destroying germs that enter an open wound? a. Red Blood Cells b. White Blood Cells c. Fibrin d. Platelets e. Fibrinolysis 15. Which of the following is a term for the disassembly of a scab after the wound has healed? a. Red Blood Cells b. White Blood Cells c. Fibrin d. Platelets e. Fibrinolysis 16. Warfarin is a… a. Rat Poison b. Blood Thinner c. Anticoagulant d. All of the above 17. Warfarin is named for… a. WARF, the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation of UW-Madison b. WARF, the Wisconsin Area Research Federation c. A Warf, or ship harbor, where the rats first killed by this drug were tested d. James Warf, the chemist who developed the drug 18. What world leader is Warfarin credited with for saving? a. Stalin b. Roosevelt c. Khrushchev d. Eisenhower 19. Why does a wound swell while it is healing? a. Because of vasoconstriction b. Because of vasodilation c. Because of the destruction of germs by white blood cells d. Because of platelets 20. Where do platelets come from? a. Cell division of other existing platelets b. White blood cells c. Bone marrow d. The liver Page | 2 Copyright 2011 by Craig Kohn, Agricultural Sciences, Waterford WI. This source may be freely used provided the author is cited.