userfiles/202/my files/grade 8 ch 10 notes?id=432486
advertisement

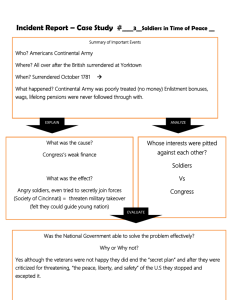
CHAPTER 10: AMERICANS WIN INDEPENDENCE 1776-1787 Section 1: The Early Years MAIN IDEA: DURING THE REVOLUTIONARY WAR THE PATRIOT FORCES STRUGGLED WITH A LACK OF SUPPLIES AND A DIVIDED SOCIETY. SECTION 1. OBJECTIVES: 1. What difficulties did Washington face as head of the American Army? 2. What were the major battles of the war in the North? 3. How did foreign nations affect the war? The Country Divided: 1. Mercy Otis Warren wrote a play called The Blockheads mocking the British because they were stuck in a narrow band of land along the coast and could not go inland without being attacked by the Patriots. 2. The American Revolution was a civil war with only two-fifths of Americans considered themselves PATRIOTS. 3. Most PATRIOTS were from New England and Virginia. Most LOYALIST were from New York State. 4. Many Indians sided with the BRITISH because the CONTINENTAL CONGRESS promised Indian lands to those who ENLISTED in the Army. Americans at War 1. GEORGE WASHINGTON was the Leader of the Continental Army but he had few guns, horses wagons and other supplies. 2. About 5,000 FREE AFRICANS joined the Continental Army. 3. Women also joined the army for several reasons: a. They had no other way to survive so they washed clothes and cooked etc. b. Mary Hays, aka: MOLLY PITCHER served water to soldiers on the battlefield from a nearby well. New York City, 1776 1. General William Howe and 8000 HESSIAN MERCENARIES attack Washington in NY. and after a summer of fighting Washington retreats to Valley Forge Pennsylvania for the winter. New Jersey Victories 1. During the harsh winter in Valley Forge the Continental Army was reduced from 20,000 to 4,000 men. 2. To rally Continental moral THOMAS PAINE writes the first of a series of pamphlets called THE CRISIS 3. Desperate, Washington attacks the Hessians at TRENTON, NJ. On December 25, 1776 killing and capturing over 1,000 and taking supplies, guns and ammunition. 4. One week later the Continental Army won the Battle of Princeton restoring moral and attracting new recruits. Philadelphia, 1777 1. General Howe captures the American Capital of Philadelphia and the Continental Congress moves to York, Penn. The British Strategy: 1. The British wanted to seize the Hudson Valley and cut the Colonies in half. 2. The plan was to have three British armies meet in Albany, NY to cut off New England. a. General John “Gentleman Johnny” Burgoyne would head south from Canada. b. General Barry St. Leger would move east from Lake Ontario. c. General William Howe would move north from NY City. 3. This did not work for several reasons. a. “Gentleman Johnny” Burgoyne traveled slow and threw parties after each battle. b. Howe sent a note to Burgoyne saying he would not RENDEZVOUS him in Albany because he was FOLLOWING WASHINGTON’S ARMY wrecking the plan. c. General Leger was TRICKED by Continental General BENEDICT ARNOLD and his Indians when they FALSELY spread rumors that Arnold had a huge army causing General Leger to retreat so fast they left behind supplies, cannons and tents. Saratoga-A Turning Point 1. Continental General Horatio Gates waited at Freeman’s Farm near Saratoga NY. For Burgoyne. 2. GATES and his men were dug in earthworks put up by Thaddeus Kosciuszko a Polish engineer helping the PATRIOTS. 3. After two battles at Freeman’s Farm, Horatio Gates and Benedict Arnold defeated Burgoyne and drove him back to Saratoga, NY. 4. General “Gentleman Johnny” Burgoyne eventually surrendered at SARATOGA losing 6,000 men. ***IMPORTANT: SARATOGA was a turning point in the war because FRANCE recognized American Independence and formed an alliance in 1778 also convincing Spain to join the war on the American’s side. Help From Abroad: 1. France and Spain gave the Americans much needed money and supplies and troops. 2. In 1779-1780 The Spanish Governor of Louisiana, General Bernardo de Gálvez captured the British strongholds of Natchez and Baton Rouge and Mobile, and in 1781 Pensacola in Florida, this protected America from British invasions from the southwest. Section 2: The Path to Victory MAIN IDEA: After 1777 the war’s focus shifted from the north to other areas: the frontier, the sea, the South. The war’s final battles took place in the South. SECTION 2: OBJECTIVES 1. What strengthened Patriot forces? 2. Why did heavy fighting take place in the South? 3. What events led to the end of the Revolutionary War? Winter at Valley Forge 1777-1778 1. The winter was extremely harsh and about a quarter of the soldiers died from cold, small pox, and typhoid fever. 2. Many soldiers began to DESERT. 3. Several Europeans would join Washington and help the Patriots: a. Marquis de Lafayette; a 19 year old FRENCH nobleman arrived in 1777. Very Popular b. Baron Von Steuben; A German General Trained the Patriots in European tactics like the BAYONET CHARGE. Very Strict. Within a couple of months the Patriots were well-trained and ready to fight. War on the Western Frontier 1. In 1778 George Rogers Clark walked into the office of Virginia’s Governor PATRICK HENRY and asked to lead men to fight the British in the West. 2. HENRY Hired him and he quickly captured Forts at Kaskaskia in Illinois and Vincennes in Indiana with 175 men. 3. Fort Vincennes was recaptured by the British General Henry “Hair Buyer” Hamilton that winter. 4. Clark then set out through miles of swamp called the “Drowned Lands” in February of 1779 and recaptured Fort Vincennes. 5. This gave the Americans all the land between the OHIO RIVER and the GREAT LAKES, half the size of the 13 states. The War at Sea 1. By 1777 the British had 100 warship along the coast of America. 2. The Patriots used privateering to capture British ships and the crews would split the “Prize”. 3. A Privateer JOHN PAUL JONES, from Scotland in his ship the BONHOMME RICHARD, attacked the British ship SERAPIS, along the coast of England and sank it forcing a surrender. -4. With the Bonhomme Richard badly damaged Jones famously says “I have not yet begun to fight”. Setbacks in the South: -1. After getting nowhere for three years in the north the British look to the South. -2. 50,000 African Americans joined the British because of promises of freedom by the British, British officers instead made fortunes by selling them to the West Indies. -3. In 1778 the British captured Savanna, Ga. And in 1780 Charleston, SC. -4. Now General Gates and Baron de Kalb headed south to fight British General Lord Cornwallis. The “Swamp Fox”: -1. FRANCIS MARION, Known as the “Swamp Fox” because of his knowledge of the Southern Swamps and forests. -2. The “Swamp Fox” helps Gates by cutting off British supplies near Camden, SC. -3. The British defeat the Patriots at Camden but the Swamp Fox then attacks the British and rescues the Patriot Prisoners and Captures the British soldiers. Guerrilla Fighting: -1. The Swamp Fox and other PATRIOTS AND LOYALISTS both formed GUERRILLA BANDS. -2. The “Swamp Fox and his Guerrilla’s cut off the British supply lines to Charleston and the interior of SC. -3. OCTOBER 1780, A Patriot force of frontier GUERILLAS defeated the British at the Battle of Kings Mountain, slaughtering over 1,000 British soldiers. The Tide Turns in the South -1.1780 Washington puts Nathaniel Greene in charge of the Southern Continental Army. -2. He commits hit and run Guerrilla attacks on the British and lets them chase him all over the South, wearing themselves out and wasting supplies. -3. Even when the Patriots lost a battle they made sure the British suffered heavy losses. The End of the War -1. After 6 years of war even British leaders in England began to feel American Independence might not be so bad. -2. British General Cornwallis set up a base in YORKTOWN, Virginia so he could get supplies from NY. -3. French troops under General ROCHAMBEAU (ro-sham-BO) and joined WASHINGTON. -4. The FRENCH NAVY had arrived in the WEST INDIES who sailed north and cut off YORKTOWN from the sea. -5. WASHINGTON and ROCHAMBEAU attacked YORKTOWN and CORNWALLIS from the land. -6. CORNWALLIS trapped between WASHINGTONS Troops on land and the FRENCH NAVY by sea -7. On OCTOBER 19 1781, at the BATTLE OF YORKTOWN, CORWALLIS SURRENDERED and the WAR WAS OVER! Section 3: Independence Won MAIN IDEA: THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION ESTABLISHED THE UNITED STATES AS AN INDEPENDENT NATION AND GAVE IT NEW POWER AND TERRITORY. Section 3: Objectives 1.What were the reasons for the American victory over Britain? 2. How was a new national government established? 3. How did the American Revolution affect other countries? Why the Americans won 1. Better Leadership, a.Washington had experience from the French and Indian war and this gave him better judgment. b. British Generals got their jobs through personal connections and were less experienced leading to bad judgment as in Saratoga and Yorktown. 2. Foreign Aid: a. Britain’s RIVALS, France and Spain, helped the PATRIOTS with Loans and Military aid. 3. Knowledge of the Land: a. The AMERICANS knew the land and controlled the INTERIOR on the country. b. The BRITISH only controlled cities on the coast NOT the Interior. 4. Motivation: a. The PATRIOTS were fighting for their PROPERTY and their LIBERTY. b. The BRITISH were far from home and lacked motivation. The Cost of War: 1. About 25,000 Americans and 10,000 British were killed in the war many died as prisoners. 2. Many Patriots left the war penniless and had to sell land the government had given them in the west, just to eat. 3. The United States was deeply in DEBT, they began taxing American trade to pay off debt. The Treaty of Paris 1783: THESE ARE THE MAIN POINTS OF THE TREATY 1. The United States was INDEPENDENT. 2. U.S. Boundaries were now the Miss. River to the west, Canada to the North and Florida to the South. 3. The U.S was given fishing rights in the Atlantic off Nova Scotia and Newfoundland. 4. Each side must repay debts they owed each other before the war. 5. The BRITISH would return any slaves they captured. 6. Congress would RECOMMEND any property taken from Loyalists be returned. Not Everyone was Happy or obeyed the Treaty 1. Virginia tobacco planters were angry they had to pay back debts. 2. The U.S did not repay its debts to Britain or return Loyalist’s property. 3. Britain did not return slaves and they still occupied forts like Detroit, near the Great Lakes. The Fate of Loyalists 1. Between 80,000 and 100,000 loyalists left the U.S. after the War. 2. They went to British lands in Canada, Great Britain, The Caribbean and The Bahamas. New State Governments: 1. The original 13 colonies, after the Declaration of independence, had written CHARTERS stating how each was to be governed. 2. Now each state formed a new Governments each with 3 Branches of Government. a. The most powerful branch the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH, makes laws. b. The EXECUTIVE BRANCH enforces the laws. c. The JUDICIAL BRANCH interprets laws and punishes lawbreakers. Forming a Republic: The States began to decide how to set up a national government. 1. Most Americans agreed the U.S. should be a REPUBLIC were VOTERS choose representatives to make laws. NO KING EVER. 2. Congress decided to join the states together in a loose confederation, like the Iroquois. 3. The Plan was called THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION. a. The United States would have a National Government. b. The STATES would have MOST of the POWER. 4. MARCH 1781 the ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION was RATIFIED by all 13 States. THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: *** Different than our Government today 1. Americans did not trust central government and Congress had limited Power. 2. only the STATES had the Power to TAX or ENFORCE LAWS. 3. Congress controlled FOREIGN AFFAIRS and Indian negotiations. 4. 9 of the 13 States had to agree to make a law and ALL 13 had to vote for a change to the Articles of Confederation. 5. The EXECUTIVE Branch had a 3 person committee chosen by Congress. *** The STATES had the most power. Thus The National Government was a weak union of Independent States*** Section 4: The Confederation, Successes and Problems MAIN IDEA: UNDER THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION, CONGRESS PASSED LAWS TO DEAL WITH WESTERN LANDS BUT IT LACKED THE POWER TO DEAL WITH OTHER PROBLEMS. Section 4: Objectives: 1. How did the Confederation Congress organize lands north of the Ohio River? 2. What kinds of problems faced the Confederation Congress? Moving Westward: 1. Virginia wanted to build a road to Kentucky, they hired DANIEL BOONE, a famous Woodsman and Scout. 2. 1775 BOONE built the WILDERNESS ROAD to Kentucky (meadowland). 3. Many people began to settle lands in Kentucky south of the Ohio River but few north of it. 4. The were several reasons people did not settle the NORTHWEST TERRITORY. a. The Indians still remained very strong their and were determined to keep their land. b. The land also had NO GOVERNMENT, it was in the hands of the National Gov. 5. THOMAS JEFFERSON proposed dividing the NW Territory into 14 territories. PROBLEMS: a. WESTERNERS did like this because they wanted the boundaries based on natural features like rivers and mountains not Jefferson’s proposed rectangles. b. EASTERNERS Objected because there might be too many new states in the west and they would soon control congress, and they doubted settlers could rule themselves. The Ordinance of 1785: 1. 1785 Congress passes a law stating the NW territory to be SURVEYED, in order to sell it off to the highest bidder. The Northwest Ordinance: 1. 1787 the Northwest Ordinance was passed allowing congress to choose a Governor and three judges to rule over the territory. 2. The Ordinance would create no less than 3 states but no more than 5, and that a territory could become a states in two steps. a. when the territory had 5,000 FREE MEN settled there they could work towards statehood. b. When they had 60,000 FREE CITIZENS it could apply and be voted in as a state. 3. The Ordinance also set 3 other IMPORTANT points. a. All citizens in those lands had freedom of religion, speech, the right to trial by jury and freedom from unfair punishment. b. Settlers had to treat Indians fairly. c. Slavery was banned in the territory. A Troubled Government: 1. The Confederation Congress did not have the power to tax, and it did not receive money from the states as it was supposed to be. 2. Congress had borrowed huge amounts of money from France, Spain, Holland and other European banks. They also owed soldiers back pay from the war. 3. Former Soldiers resorted to violence attacking the Congress in Philadelphia forcing them to flee and showing that Congress had no Power. International Problems: 1. Britain made it hard for American ships to trade in the West Indies 2. The British refused to give up forts in the west and America could do nothing about it. 3. Spain and the U.S. Argued over Florida and Spain blocked American shipping in the West Indies also. 4. Spain also threatened to restrict U.S. access to the Mississippi River, which would hurt development of western lands. The Not-So United States: 1. It was hard for the Confederation Congress to gather representatives or get them to agree on anything. 2. Different States argued over land, some almost going to war. 3. Some northern states imposed duties on imported goods southern states did not. 4. States placed heavy taxes on others state’s goods. 4. As time went one many Americans agreed the Articles of Confederation and the Confederation Congress needed more power. 5. If this did not happen the States might all become separate tiny nations and become prey for Britain and Spain.