Students Notes
advertisement
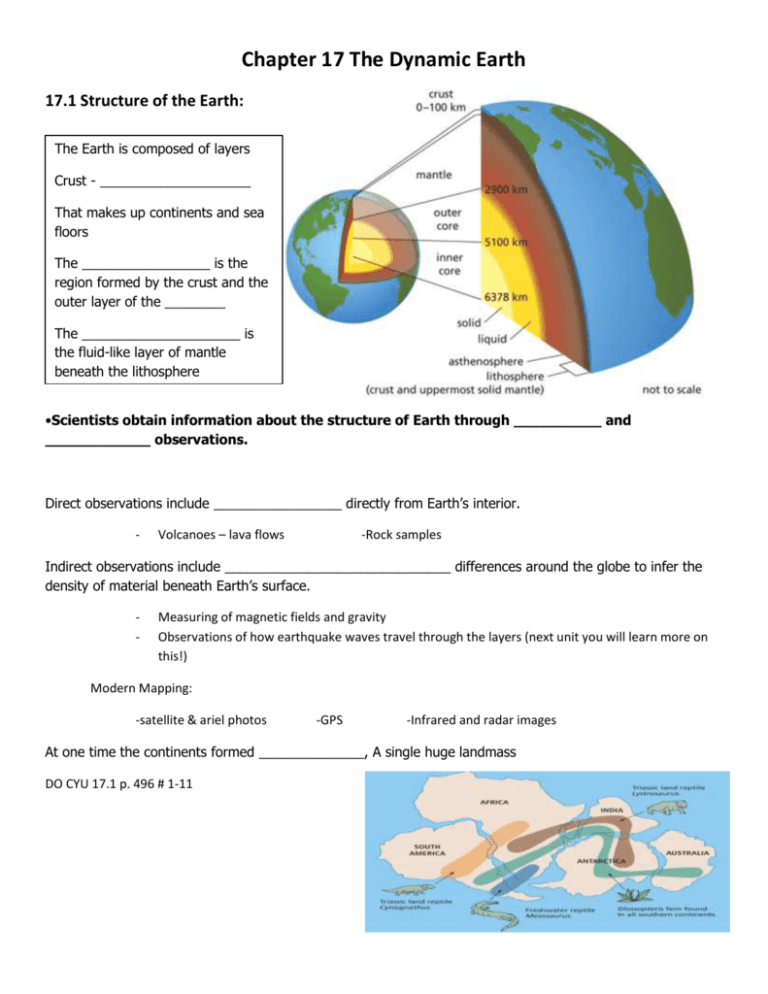
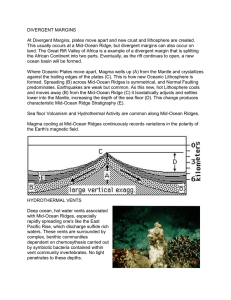
Chapter 17 The Dynamic Earth 17.1 Structure of the Earth: The Earth is composed of layers Crust - ____________________ That makes up continents and sea floors The _________________ is the region formed by the crust and the outer layer of the ________ The _____________________ is the fluid-like layer of mantle beneath the lithosphere •Scientists obtain information about the structure of Earth through __________ and ____________ observations. Direct observations include _________________ directly from Earth’s interior. - Volcanoes – lava flows -Rock samples Indirect observations include ______________________________ differences around the globe to infer the density of material beneath Earth’s surface. - Measuring of magnetic fields and gravity Observations of how earthquake waves travel through the layers (next unit you will learn more on this!) Modern Mapping: -satellite & ariel photos -GPS -Infrared and radar images At one time the continents formed ______________, A single huge landmass DO CYU 17.1 p. 496 # 1-11 17.2 Evidence of a Dynamic Earth: Continental Drift Theory: - The surface of the Earth the following evidence - Puzzle fit of continents Geological coastline matches Fossil matching First proposed by Wegner based on - Coal deposit matching Equatorial glacial evidence Unfortunately his theory was not accepted until when HOW the continents moved was better understood! DO CYU 17.2 p. 500 #1-7 ______________________ 17.3 New Evidence of a Dynamic Earth: occurs at mid-ocean ridges when magma rises from the mantle and _________ ___ the cracks left by the sea floor moving apart 1. Mid-Ocean Ridges & Maps Mid-oceanic ridges are __________________________________________ The sea floor is cycled back into earth at __________ _______________ The discover of mid-ocean ridges where the sea floor was spreading, as well as trenches where continents and oceanic plates met etc. were mapped along with known locations of high volcanic and earthquake history and this showed the boundaries of the “plates” See Fig 1 p. 501 2. Sea-Floor Spreading Heat within the Earth creates _______________________ in the mantle that help move the plates. Radioactive dating of core samples confirmed that the sea floor is older _____________________________ Radioactive dating When they looked at the mid-ocean ridges closer it was discovered that the rock was youngest at the ridges, and oldest at the trenches where the oceanic plates dip under the continental plates Magnetic Evidence there is also a pattern of magnetic shifts that can be observed moving away from the divergent ocean ridges that show that new plate is forming and moving outward from both sides of this boundary. See Fig 3. P. 503 17.4 Theory of Plate Tectonics: The theory of plate tectonics states that the lithosphere is divided into ________ ________________ and about __________ smaller ones. The lithosphere is divided into 12 sections called plates plus 20 smaller ones. These tectonic plates “float” on top of the dense fluid like asthenosphere which creates a push-and-pull on these plates due to large slow moving convection current within it, causing many different plate boundary phenomena The point where two plates move away from each other is called a ___________ _________________. ________________, _________________, and ____________________ are created at this type o boundary Plates moving towards each other collide at a ____________________________. Plates move past each other in opposite directions at _________________________. ____________________ and __________________ ________________ are created along this type of boundary. Summary of Plate Movement Plate Boundary Description of Movement Geological Formations Associated Picture Convergent Ocean-Ocean Convergent Ocean-Continent Convergent Continent-Continent Divergent Transform Chapter 18 – Plate Tectonics 18.1 Causes and Effects of Plate Movement: Mantle Convection: see Fig 1p. 517 Shaping the Earth: Push: Pull: Convection: CYU 18.1 p. 521 #1-10 DO Worksheet with new seating partners 18.2: Geological Events: Volcanoes: - mark cracks in the lithosphere where magma & gas reach the surface - Found at: Mid-Ocean Ridges Volcanic Belts - Volcanic Island Arcs – Hot Spots – Earthquakes: - mark locations where transform boundaries form faults P OR COMPRESSIONAL WAVES – S OR SHEAR WAVES – ***P waves travel faster (about 1.7x) than s waves What do P-waves and S-Waves provide indirect evidence for? 1 2