Google Earth Questions
advertisement

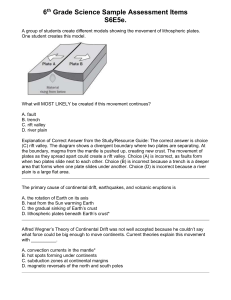
Name: _______________________________ Plate Tectonics Google Earth Tour of Champions Directions: Open the Google Earth Document on my Website under the Geohistory Unit. Click “Tools” in the tool bar at the top, Click “Options”, go towards the bottom and drag the “Terrain Quality” bar to the right, and put in a “3” in the white box called “Vertical Exaggeration” and hit “Apply” and then “OK”. Make sure Borders and Labels, Places, 3-D Buildings, and Oceans, are all checked off on the left hand panel. Follow the locations that are marked for you on Google Earth to answer the questions below. You can click on each location in the toolbar located in the left hand of your screen in Google Earth. Spots are marked with a Yellow Pin. Prelab Questions: 1. What are the 2 types of plates? 2. What are the 3 types of ways plates can move…what are the vocab words we use to describe these motions? 3. What are some of the features created on Earth’s surface due to the movement of the plates? (list as many as you can) Google Earth Tour: Use the key below to determine the plate boundaries and answer the questions. Red- Oceanic Spreading Tan- Continental Transform Fault Green Oceanic Transform Fault Gray- Continental Convergent Boundary Blue- Subduction Zone Pink- Oceanic Convergent Boundary Yellow Continental Divergent Boundary 1. Double-Click on “Puzzle” pin on the lefthand toolbar. What do you notice about the shapes of the opposing land masses? 2. Double-Click on “Puzzle 2” pin. What do you notice here? 3. What does this tell us about tectonic plates on earth? 4. Check the box labeled “Plate Tectonics Reconstruction Model” under “Puzzle 2” and slide the bar on the top of your screen that appears to see how the continents moved over time. Does this confirm what you said in your first 3 answers?\ 5. UNCHECK THE BOX NEXT TO “Plate Tectonics Reconstruction Model” to get rid of the animation before proceeding. 6. Click on “Location 1”. Where is this pin located? 7. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 8. What feature is created by the movement of the plates? 9. What is this movement doing to the ocean here? 10. What is unique about the ocean floor at “Location 1” compared to “Pin A”? 11. Click “Zig Zag” Why is this feature zig zagged? (why isn’t it a smooth or straight line?) 12. Click on “Location 2”. Where is this pin located? 13. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 14. What is unique about the depth of the ocean floor at “Location 2” compared to “Pin B”? 15. What feature is created at the plate boundary? 16. Fill in the blanks below. 17. The ____________________ plate is ______________ under the __________________ plate. 18. What feature is created on the continent? (hint click on the Mt. Rainier Pin) 19. Click on “Location 3”. Where is this pin located? 20. What type of boundary is at the pin (gray line)? (types of plates, and how they move) 21. Click on the “Mt. Everest” icon. What feature is created at the plate boundary? 22. What is the specific name of this range created along the border? 23. Click on the “Mt. Everest Tool” recording. What would be different about this view after another million or so years (assuming the plates continue to move as they are now)? 24. Click on “Appalachian Mountains” pin. These mountain used to be as big as Mt. Everest. This takes you to a place where there was once an active continental, continental convergence zone. Notice the contours of the land where the two land masses collided. Why are these mountains not growing anymore? 25. Click on “Location 4”. Where is this pin located? 26. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 27. Click “Feature A” What feature is created at the plate boundary on Feature A? 28. Click on “Feature B” What feature is created on the continent? 29. Click on “Flow”. What igneous extrusive feature do you see coming off of the volcanoes? 30. Click on “Location 5”. Where is this pin located? 31. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 32. Click “Mariana Trench” What is unique about this spot on Earth? 33. Click on “Location 6”. Where is this pin located? 34. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 35. Click on “Rift Feature” What feature is created by the movement of the plates? 36. Millions of years ago, the Red Sea was not here, but now it is? How did it form, and how did it fill with water? 37. What is this movement of the plates doing to the sea here? 38. Click on “Location 7”. Where is this pin located? 39. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 40. Click on “Fault” What feature is created by the movement of the plates? 41. The western part of California is moving north, while the eastern part is stationary. Based on this information, what will CA look like in millions of years? 42. What do you notice about the fault line (tan) and the actual fault on land? 43. Click on “Wallace Creek”. What happened to the creek here? Why is it this shape..explain… 44. Click on “Location 8”. Where is this pin located? 45. What type of boundary is at the pin? (types of plates, and how they move) 46. Click on “Older Islands” How do you know that these islands are the older ones in the chain? 47. Click on “Newest Islands” How do you know that these islands are the newer ones in the chain? 48. Click on “Mouth of Volcano” What igneous extrusive feature is obvious here? 49. What proof do you have that the island is still growing? 50. Click on “Future Islands” How can you tell there will be more islands? 51. What does the location of these “future islands” say about the direction of the plate movement? 52. Click on “Wini Seamount”. Why is this not official an island yet, even though it is thousands of feet tall?