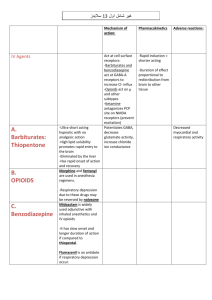
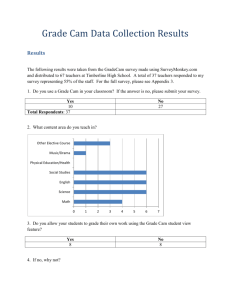
File - Terry Gill E
advertisement

Computer Technology Terminology Types Of Computers: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Desktop or Personal Computer -A PC is in a form for regular use at a base. Workstation -Is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Laptop or Notebook - A computer for mobile use. Supercomputer -A computer for processing capacity, particularly speed of calculation. Mainframe -Powerful computers used mostly by corporate and government organizations. Server -Is a physical computer used for running many services. PDA/Handheld - Is a personal digital assistant. Viruses: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Boot sector virus - It is a virus that infects the first sector, the book sector, or a hard drive. File virus - It is a virus that infects executable type files. Macro virus -It is a virus that infects a Microsoft Word and causes a sequence of actions to be performed automatically when the application is started. Trojan Horse -is a type of malware that seems like a normal file but it’s real purpose is to grant a hacker unauthorized access to a computer. Time bomb -Is a virus that is in effect at a certain time or date and the computer blacks out. Worm -They are a special form of virus that uses the internet email address book to spread to other computers. Logic bomb - Is a piece of code intentionally inserted into a software system that will set off a malicious function. Attachments - Is a computer file sent along with an email message or anything else. Virus Prevention -Computer systems that prevent viruses. Networks: ● ● ● ● ● Network - Is a group of computers and other hardware components interconnected. File server - Is a computer attached to a network that has the function of providing a location for shared disk access. LAN -Local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a small area. WAN -A Wide Area Network is a network that covers a huge area. IP address -An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device. Word Processing: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Ruler Bar -It allows you to format the vertical alignment of text. Grammar vs. Spell Check -It’s a tool that checks your Grammar or Spelling in a text. Line Spacing -It’s the distance between the baselines of successive lines of type. Graphics - The representation of a image. Clipboard - Is a software that can be used for short-term data storage.. Tabs -Used for multi-tasking. Letterhead -Is the heading at the top of a sheet. Signature Block -Area provided for one’s signature. Memo -A note or document used for reminders Fax - Is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material Letter -Is a form of communication. Computer Components, Hardware: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● System unit - It includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus and ports. CPU -Central processing unit is the central processor unit. Silicon chip - It is a chip that contains millions of transistors. Hertz -The SI unit of frequency Ram -A type of computer memory. ROM -A class of storage medium. Bit - The basic capacity of information in a computer. Byte -Unit of digital information in computing. Kilobyte -Is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information Megabyte - Is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information Gigabyte -Is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage Terabyte - Is a multiple of the unit byte digital information Storage devices -For storing or recording information. Medium/media -They are the storage and transmission channels. Hard drive -Used to store data. Input devices -Devices you put into your computer for use of data or syncing, etc. Output devices -Devices you use with your computer like printers or scaners, etc. Resolution -A measurement of digital audio quality. Pixels - Is a physical point in a raster image. Peripheral devices -Things such as a computer mouse, keyboard, hard drive, etc. Computer Performance And Processing: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Boot process -It is a group of steps that a computer uses to reboot when electricity is gone. Input -It’s the entrance or exit of a certain device that is inserted into a system. Output -It’s the term used for an exit device which actives and modifies a process. Storage -It’s technology that, of a computer components, records media used to retain digital data. Processing -Is an electronic sketchbook. Base 2 binary code - It represents numeric values using 0 and 1. Spreadsheet -Is a computer application program for organization and to analysis information. Formula -Is an entity that uses the symbols and formation rules of a logical language. Functions - Is a relation between a set of inputs and a set of outputs. Order of Operation -It is the order of which procedures should be performed. Column Heading -It is the coloured row of letters, used to show each column. Number Formatting -The arrangement of date for storage. Active Cell -The cell that continues the value being used. Different type of Charts -Is a graphical representation of data. Legend -Things to be read. Mathematical Operators -A computer performs mathematical operators, which is a procedure where it produces something new from one or more input values. Rows vs. Columns - A row is a horizontal set of date or components and a column is a vertical line of characters from top to the bottom of the screen. Computer Components, Software: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Program -It is a number of instructions written to perform a specific task with a computer. Operating system -Is a software that manages computer hardware resources and gives normal services for programs. Folder -A virtual container within a digital file system. Multitasking -Doing more than one thing at a time GUI (Graphical interface) -User interface that allows people to interact with electronic devices using images. Platform -Where the combination allows software to run. Icons -They are pictograms on a computer screen that are used to go through a computer system. Menus - ????? Application software -Is computer software designed to help the person to perform certain tasks. Internet: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● WWW -Is the World Wide Web. Internet -It is a global system of interconnected computer networks. URL -It is a uniform resource locator, which is a specific character string. Browser -It is an application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. Domain (list examples) -It’s a common network name, like Facebook and Google. Internet Service Provider -Companies that provide you your internet, like Teles and Shaw. Search Engine -They are engines used to search the World Wide We. Freeware -Is a software sold for no cost, it’s free. Shareware -It’s a software that is provided to users for no cost and on a trial basis. Public Domain -any program that is not copyrighted. Keyword -Words that are used to reveal the internal structure. Boolean Operators (And, Or, +, -, Not, “ “) -Describes how to determine a Boolean value. Hyperlink - It is a reference to data that the reader can directly follow. SPAM -It sends unsolicited bulk messages. Phishing -A try to get information like usernames, passwords, and credit card details by looking like a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) - They are a set of rules that are put there by the owner or the manager or a network. Presentations: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Slide Layout - They contain formatting, positioning, and placeholders for all the stuff that appears in a slide. Transition -It is an mainl part of a smooth flowing presentation. Slide sorter view - Is a window that displays thumbnail versions of all your slides. Animations -They used to make reveal new texts in a unique way. Custom Animation -Customized to your standards to reveal new texts. Handouts -Pamphlets that are given to the audience containing information about the presentation. Slide Design -The customized view of a slide. Action Button -It makes your presentation simpler to navigate. Hyperlink -It’s a reference to data that the reader can directly follow. Speaker Notes -Are notes that you can to the presentation slides to use as a reference. Rehearse Timing -The amount of time you give to each slide.