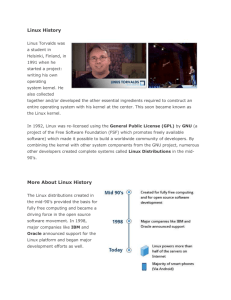
Linux+ - TestOut
advertisement

Lesson Plans LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI (Exam LX0-101 and Exam LX0-102) Version 8.0 Table of Contents Table of Contents ................................................................................................................ 1 Course Overview ................................................................................................................ 3 Section 0.1: Introduction ..................................................................................................... 5 Section 1.1: The Shell ......................................................................................................... 7 Section 1.2: Help ................................................................................................................. 9 Section 1.3: Environment Variables ................................................................................. 11 Section 1.4: Aliases ........................................................................................................... 13 Section 1.5: Text Editors................................................................................................... 14 Section 1.6: Redirection and Piping.................................................................................. 16 Section 1.7: Directories ..................................................................................................... 18 Section 1.8: Files ............................................................................................................... 20 Section 1.9: Links ............................................................................................................. 22 Section 1.11: Locating and Searching Files ...................................................................... 25 Section 2.1: Installation Design ........................................................................................ 27 Section 2.2: Linux Installation .......................................................................................... 29 Section 2.3: Localization .................................................................................................. 31 Section 3.1: Linux Boot Process ....................................................................................... 33 Section 3.2: BootLoaders .................................................................................................. 34 Section 3.3: Runlevels ...................................................................................................... 36 Section 3.4: Init Scripts ..................................................................................................... 38 Section 3.5: System Shutdown ......................................................................................... 40 Section 4.1: X Window System ........................................................................................ 42 Section 4.2: Display Managers ......................................................................................... 44 Section 4.3: Accessibility.................................................................................................. 46 Section 5.1: Red Hat Package Manager (RPM)................................................................ 48 Section 5.2: Debian Package Manager (DPKG) ............................................................... 50 Section 5.3: Shared Libraries ............................................................................................ 52 Section 6.1: User and Group Overview ............................................................................ 54 Section 6.2: User Management ......................................................................................... 56 Section 6.3: Group Management ...................................................................................... 58 Section 7.1: Disk Partitions............................................................................................... 60 Section 7.2: File Systems .................................................................................................. 62 Section 7.3: Mounting File Systems ................................................................................. 64 Section 7.4: File System Maintenance .............................................................................. 66 Section 7.5: Disk Quotas................................................................................................... 68 Section 7.6: Ownership ..................................................................................................... 70 Section 7.7: Permissions ................................................................................................... 72 Section 7.8: Archive and Backup...................................................................................... 74 Section 8.1: Device Drivers .............................................................................................. 76 Section 8.2: Kernel Module Management ........................................................................ 78 Section 8.3: Hotplug and Coldplug Devices ..................................................................... 80 Section 9.1: Processes ....................................................................................................... 82 Section 9.2: Process Management .................................................................................... 84 ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 1 Section 9.3: Task Management ......................................................................................... 86 Section 9.4: Print Management ......................................................................................... 88 Section 9.5: Time Management ........................................................................................ 91 Section 9.6: Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) ......................................................................... 93 Section 9.7: Structured Query Language (SQL) ............................................................... 95 Section 10.1: System Log Files ........................................................................................ 97 Section 10.2: Scripts ......................................................................................................... 99 Section 10.3: Text Stream Processing ............................................................................ 101 Section 11.1: Networking Overview............................................................................... 103 Section 11.2: Network Interface Configuration .............................................................. 105 Section 11.3: Routing Configuration .............................................................................. 107 Section 11.4: Hostname and DNS Configuration ........................................................... 109 Section 11.5: Network Troubleshooting ......................................................................... 111 Section 12.1: Root Usage ................................................................................................ 113 Section 12.2: User Security and Restriction ................................................................... 115 Section 12.3: Network Security ...................................................................................... 116 Section 12.4: File Auditing ............................................................................................. 117 Section 12.5: Login Blocking ......................................................................................... 118 Section 12.6: Xinetd and Inetd Super Daemons ............................................................. 120 Section 12.7: OpenSSH .................................................................................................. 122 Section 12.8: SSH Port Tunneling .................................................................................. 124 Section 12.9: Public Key Authentication ........................................................................ 126 Section 12.10: Gnu Privacy Guard (GnuPG) .................................................................. 128 Practice Exams ................................................................................................................ 129 ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 2 Course Overview This course prepares students for CompTIA’s Linux+ Exams; LX0-101 and LX0-102. It focuses on running GNU and Unix commands from the command line, installing and configuring Linux, and maintaining and securing the Linux system. Module 0 – Introduction This module introduces the students to the Linux+ certification exams; LX0-101 and LX0-102. Module 1 – Using Linux This module introduces the students to using Linux. They will learn about the Linux shell, help options, the role of environment variables, using aliases, text editors, redirection and piping available on a Linux system. Students will also learn about commands to manage files and directories, links, FHS, and how to locate and search files for specific character patterns. Module 2 – Installation and Localization This module examines designing an effective installation, installing a Linux operating system, and configuring country and language-specific settings. Module 3 – Boot and Shutdown In this module students will learn concepts about the Linux boot process, installing bootloaders, managing runlevels, using init scripts, and shutting down the system. Module 4 – User Interfaces and Desktops This module teaches the students about configuring an X Window system and display managers, and providing accessibility to people with impairments. Module 5 – Software Installation This module discusses installing application packages using RPM and Debian, and managing shared libraries. Module 6 – Users and Groups This module examines the fundamentals of managing user and group accounts. Module 7 – Disk and File System Management In this module students will learn concepts about managing disk partitions, managing, monitoring and maintaining file systems, restricting disk space to users, managing file and directory ownership and permissions, and archiving data on a Linux system. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 3 Module 8 – Hardware Installation This module discusses hardware installation. Topics covered include; device drivers, managing kernel modules, and managing Hotplug and Coldplug devices. Module 9 – Processes and System Services In this module students will learn the basics of managing and prioritizing processes, managing tasks, printing, and time. This module also provides an overview of using Structured Query Language (SQL). Module 10 – System Monitoring This module discusses concepts of system monitoring; system logging, using scripts to execute commands and processing a text stream. Module 11 – Networking This module examines the basics of networking, configuring network interfaces, configuring routing, configuring DNS settings, and troubleshooting network communication problems. Module 12 – Security This module examines the fundamentals of security on the Linux system. This includes the root user account, promoting user security and restrictions, increasing network security, file auditing and login blocking. Students will also become familiar with using the xinetd and inetd super daemons, OpenSSH and SSH port tunneling, a public key to authenticate to a computer, and the GnuPG encryption tool. Practice Exams In Practice Exams students will have the opportunity to test themselves and verify that they understand the concepts and are ready to take the certification exams. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 4 Section 0.1: Introduction Summary The Linux+ certification is a vendor neutral certification designed to certify applicants can complete general Linux tasks across many different distributions. In the latest version of the Linux+ certification CompTIA has partnered with the Linux Professional Institute (LPI) to identify what knowledge is necessary to be an effective Linux administrator, thus the CompTIA Linux+ certification is essentially the same as the Linux Professional Institute Level 1 certification. The Linux+ certification certifies that applicants have the skills and knowledge of a junior level Linux administrator, one with about six months to a year’s worth of experience on the job, including the following skills: Managing the system using the command line interface. Performing maintenance tasks such as adding users, backing up the system, shutting down and rebooting the system. Managing your display. Connecting the system to a network. The Linux+ certification has been updated. To obtain the certification, applicants must pass two exams: The LX0-101 exam covers the following: o Basic system architecture o Linux installation and software management o Unix commands o Devices o Linux file systems o Linux file system hierarchy The LX0-102 exam covers details about: o Linux shell o Scripting and managing data o User interfaces and desktops o Administrative tasks o Essential system services o Basic networking fundamentals o Linux security This course covers content for the Linux+ exam. If possible, we recommend that students study for both exams before taking either exam. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 5 Lecture Focus Questions: What exams are required for you to pass to certify for the CompTIA Linux+ Powered by LPI certification? Why do many administrators choose to use a command line interface on a Linux server? What is a Linux distribution? Video/Demo Time 0.1.1 Instructor Introduction 2:12 0.1.2 Linux+ Certification Overview 5:07 0.1.3 Linux Operating System Introduction 13:13 Total 20:32 Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 6 Section 1.1: The Shell Summary This section introduces the student to the shell that administrators use to control a Linux operating system. Students will become familiar with the: Common shell types Common shell characteristics Tips for working in the shell Common commands used from the shell Shell configuration files used when the shell starts Students will learn how to: Navigate through shells and execute shell commands. Use the command history. Use tab completion while executing a shell command. Locate and edit shell configuration files. Use exec to execute a command. Execute common commands such as pwd, whoami, uname, su, and exit. Linux+ Objectives: 103.1 Work on the command line Candidates should be able to interact with shells and commands using the command line. The objective assumes the bash shell. o Use single shell commands and one line command sequences to perform basic tasks on the command line. o Use and edit command history. o Invoke commands inside and outside the defined path. 105.1 Customize and use the shell environment Candidates should be able to customize shell environments to meet users' needs. Candidates should be able to modify global and user profiles. o Set environment variables (e.g. PATH) at login or when spawning a new shell. o Write BASH functions for frequently used sequences of commands. o Maintain skeleton directories for new user accounts. Set command search path with the proper directory. Lecture Focus Questions: What is a shell? What are the basic differences between common shells? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 7 What is the difference between how executable programs are run by a Linux shell as compared to a DOS environment? What is the difference between how a Linux shell recognizes the path to executable programs compared to how a DOS environment recognizes the path? What common commands are used to navigate through shells? What types of items can Tab complete be used to complete once you start typing the entities' name? What does the tilde symbol (~) in the prompt indicate? Video/Demo Time 1.1.1 Shell Overview 4:23 1.1.3 Shell Commands 19:16 1.1.4 Using Shell Commands 12:47 1.1.6 Shell Configuration Files 9:29 1.1.7 Viewing Shell Configuration Files 7:19 Total 53:14 Time About 65 minutes Number of Exam Questions 14 questions ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 8 Section 1.2: Help Summary This section provides information about sources that can be used to find syntax, options available, and uses for the commands that are available on a Linux computer. Students will become familiar with help options available for a Linux system: Manual (man) pages Info pages On-screen help Whatis database Students will learn how to: Access documentation about a specified command. Search for information about a command. Use on-screen help to display the syntax and available options of a command. Linux+ Objectives: 103.1 Work on the command line Candidates should be able to interact with shells and commands using the command line. The objective assumes the bash shell. o Use single shell commands and one-line command sequences to perform basic tasks on the command line. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the differences between the man utility and info utility? What types of files are stored in the /usr/share/doc directory? How can you access on-screen help for each command? Video/Demo Time 1.2.1 Help 9:30 1.2.2 Accessing Help 9:18 Total 18:48 Lab/Activity Get Help 1 Get Help 2 Get Help 3 ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 9 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 10 Section 1.3: Environment Variables Summary This section discusses the role of environment variables. Concepts discussed include: User-defined variables Common environment variables Common environment variable commands Students will learn how to: Display the value of currently set environment variables. Set the value of an environment variable. Linux+ Objectives: 103.1 Work on the command line Candidates should be able to interact with shells and commands using the command line. The objective assumes the bash shell. o Use and modify the shell environment including defining, referencing and exporting environment variables. 105.1 Customize and use the shell environment Candidates should be able to customize shell environments to meet users' needs. Candidates should be able to modify global and user profiles. o Set environment variables (e.g. PATH) at login or when spawning a new shell. o Write BASH functions for frequently used sequences of commands. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of environment variables? What is the standard syntax for environment variable identifiers? How do you preserve the current values of the PATH environment variable when adding a new value to it? How do you make a new value assigned to an environment variable persistent across all shell sessions? Video/Demo Time 1.3.1 Environment Variables 16:18 1.3.2 Managing Environment Variables 10:14 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 26:32 11 Lab/Activity View Environment Variables Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 12 Section 1.4: Aliases Summary In this section students will learn how to use aliases to perform a specific action invoked at startup or from the shell. Students will learn how to: Display a list of the currently defined aliases on the system. Create a custom command using an alias. Create a single alias that includes multiple commands. Remove an alias. Linux+ Objectives: 105.1 Customize and use the shell environment Candidates should be able to customize shell environments to meet users' needs. Candidates should be able to modify global and user profiles. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the purpose of an alias? What happens if you create a new alias with an alias name that already exists? When would it be important to make an alias persistent? Video/Demo Time 1.4.1 Aliases 6:43 1.4.2 Using Aliases 6:50 Total 13:33 Number of Exam Questions 1 question Time About 15 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 13 Section 1.5: Text Editors Summary This section examines using text editors to create and modify text files. Concepts covered include: Vim (vi improved) modes: o Command mode o Command line mode o Edit modes Common vi commands Students will learn how to: Navigate a text file using vi. Open and edit an existing text file using the vi editor. Create a new file using vim. Linux+ Objectives: 103.8 Perform basic file editing operations using vi Candidates should be able to edit text files using vi. This objective includes vi navigation, basic vi modes, inserting, editing, deleting, copying and finding text. o Navigate a document using vi. o Use basic vi modes. o Insert, edit, delete, copy and find text. Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to know how to run a text editor on a Linux system? What are the four different modes available in vim, and how can you tell the current mode? Which vi mode would you use to overwrite existing text? Video/Demo Time 1.5.1 Text Editors 15:21 1.5.2 Using vim 12:05 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 27:26 14 Lab/Activity Create a New File Modify an Existing File Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 15 Section 1.6: Redirection and Piping Summary This section provides information about using redirection and piping to create, send, or gather information on a Linux system. Concepts covered include: The role of redirection The role of piping Redirection and piping commands The xargs command Students will learn how to: Redirect the standard output from the screen to a file. Redirect and append new content to an existing file. Redirect a standard error from a command to a file. Redirect the standard input to a command. Pipe the output of a command to the input of another command. Use the pipe command to search a file for specified text. Use the pipe command to create a text stream. Linux+ Objectives: 103.4 Use streams, pipes and redirects Candidates should be able to redirect streams and connect them in order to efficiently process textual data. Tasks include redirecting standard input, standard output and standard error, piping the output of one command to the input of another command, using the output of one command as arguments to another command and sending output to both stdout and a file. o Redirecting standard input, standard output and standard error. o Pipe the output of one command to the input of another command. o Use the output of one command as arguments to another command. o Send output to both stdout and a file. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between redirection and piping? When might you choose to redirect the input of a command? What are the three default file descriptors that Linux uses to classify information for a command? How can you overcome the 128 KB shell command size restriction? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 16 Video/Demo Time 1.6.1 Redirection 10:21 1.6.2 Piping 7:12 1.6.3 Using Redirection and Piping 9:19 1.6.5 Xargs 2:50 Total 29:42 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 17 Section 1.7: Directories Summary This section discusses basic commands used to manage directories: pwd cd ls mkdir cp –r cp –R mv rmdir rm Students will learn how to: Navigate directories using the cd command. Display the current working directory using the pwd command. Display a list of the contents of a directory including hidden files. Create a new directory using the mkdir command. Delete an empty directory and also a directory with existing files. Copy the entire directory including files and subdirectories to a new location. Move directories to a new location using the mv command. Linux+ Objectives: 103.3 Perform basic file management Candidates should be able to use the basic Linux commands to manage files and directories. o Copy, move and remove files and directories individually. o Copy multiple files and directories recursively. o Remove files and directories recursively. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the shortcut to move directly to the home directory when using the cd command? What is the difference in function between the rm command and the rmdir command? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 18 Video/Demo Time 1.7.1 Directory Management 15:15 1.7.2 Manage Directories 11:52 Total 27:07 Lab/Activity Find the Working Directory View Directory Information Find a Hidden Directory Create Directories Delete Directories Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 19 Section 1.8: Files Summary This section examines basic commands that are used to manage files on a Linux system: touch cat less head tail file cp mv rm shred lsattr Students will learn how to: Create and view files from the command line. Use cat, less, head, and tail to view the contents of a text file. Delete and move files from one directory to another. Delete an existing directory including all subdirectories and files. Linux+ Objectives: 103.3 Perform basic file management Candidates should be able to use the basic Linux commands to manage files and directories. o Copy, move and remove files and directories individually. o Copy multiple files and directories recursively. o Remove files and directories recursively. Lecture Focus Questions: How can you display only the first few lines of a file? Why is it more common to use the tail command than the head command? How can you use the tail command to monitor a specified file when troubleshooting the system? What is different about file extensions in Linux compared to file extensions in a DOS environment? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 20 Video/Demo Time 1.8.1 File Management 19:08 1.8.2 Managing Files 15:37 Total 34:45 Lab/Activity View the Contents of a File View a List of Available Shells Delete Files Move Files Delete Files and Directories Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 60 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 21 Section 1.9: Links Summary This section discusses using links to point to another file. Concepts covered include: Link types: o Hard link o Symbolic link Commands for creating hard links and symbolic links: o ln source link_name o cp source link_name Students will learn how to: Determine where a link points to. Create a hard link to share access to data. Create a symbolic link to a specified directory. Linux+ Objectives: 104.6 Create and change hard and symbolic links Candidates should be able to create and manage hard and symbolic links to a file. o Create links. o Identify hard and/or softlinks. o Copying versus linking files. o Use links to support system administration tasks. Lecture Focus Questions: What is an inode? What is the difference between a hard link and a symbolic link? How can you identify a symbolic link when using the ls -l command? Which type of link is similar to shortcuts in Windows? Which utilities can you use to create links? Video/Demo Time 1.9.1 Links 6:50 1.9.2 Creating Links 7:54 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 14:44 22 Lab/Activity Create a Hard Link Create a Symbolic Link Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 23 Section 1.10: Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) Summary In this section students will explore the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) which is a subset of the Linux Standards Base (LSB). Students will become familiar with the standard set of directories defined by the FHS. Students will learn how to: Determine the correct location for files under the FHS. Linux+ Objectives: 104.7 Find system files and place files in the correct location Candidates should be thoroughly familiar with the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS), including typical file locations and directory classifications. o Understand the correct locations of files under the FHS. o Find files and commands on a Linux system. o Know the location and purpose of important files and directories as defined in the FHS. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the benefits to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS)? Why does a Linux system use a more structured file system than the Windows OS? What should you be aware of when saving files in the /temp directory? Which directory is specified by Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) to hold temporarily mounted filesystems? Video/Demo 1.10.1 Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) Time 18:54 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 25 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 24 Section 1.11: Locating and Searching Files Summary This section discusses the details about locating and searching files. Concepts covered include: Commands to find file locations o find o locate o which o whereis o type Commands to search file text for specific words or character patterns: o grep o egrep o fgrep Students will learn how to: Determine the location of a command and view detailed information about it. Linux+ Objectives: 103.7 Search text files using regular expressions Candidates should be able to manipulate files and text data using regular expressions. This objective includes creating simple regular expressions containing several notational elements. It also includes using regular expression tools to perform searches through a filesystem or file content. o Create simple regular expressions containing several notational elements. o Use regular expression tools to perform searches through a filesystem or file content 104.7 Find system files and place files in the correct location Candidates should be thoroughly familiar with the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS), including typical file locations and directory classifications. o Understand the correct locations of files under the FHS. o Find files and commands on a Linux system. o Know the location and purpose of important files and directories as defined in the FHS. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the advantage of using the locate utility over the find utility? What are the disadvantages? When would you use the which command to locate a file? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 25 Which utilities can you use to locate a file? Which utilities can you use to locate and get information about a command? What does it mean when a command is hashed? How can you discover the category of a command? What commands can you use to search for text within files? Video/Demo Time 1.11.1 File Location Utilities 10:51 1.11.2 Finding Files 12:41 1.11.4 Content Search Utilities 10:03 1.11.5 Finding File Content 4:49 Total 38:24 Time About 60 minutes Number of Exam Questions 19 questions ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 26 Section 2.1: Installation Design Summary This section examines the general steps to design an effective installation: Perform a needs assessment Pick a distribution Determine the hardware requirements Plan the file system Plan the partitions Identify software Identify the users Gather network information Select an installation source Students will learn how to: Design and gather information to plan a Linux installation. Linux+ Objectives: 102.1 Design hard disk layout Candidates should be able to design a disk partitioning scheme for a Linux system. o Allocate filesystems and swap space to separate partitions or disks. o Tailor the design to the intended use of the system. o Ensure the /boot partition conforms to the hardware architecture requirements for booting. Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to create a detailed plan prior to deploying a Linux installation? What elements should you consider when performing a needs assessment? What factors should you consider when selecting a Linux distribution? How can you ensure that specific hardware is compatible with the Linux distribution you have selected? Why must the /etc, /bin, /sbin, /lib, and /dev directories all be on the same partition? Which user account is automatically created when Linux is installed? What types of installation sources are available for Linux? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 27 Video/Demo 2.1.1 Installation Design Time 24:08 Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 28 Section 2.2: Linux Installation Summary In this section students will learn the general steps necessary to install a Linux operating system: Start the install Select a language Set the system time Format partitions Select applications and services Set the root password Specify a host name Configure network connections Configure services Add new users and groups Configure the hardware settings Students will learn how to: Install a Linux operating system. Linux+ Objectives: 102.1 Design hard disk layout Candidates should be able to design a disk partitioning scheme for a Linux system. o Allocate filesystems and swap space to separate partitions or disks. o Tailor the design to the intended use of the system. o Ensure the /boot partition conforms to the hardware architecture requirements for booting. Lecture Focus Questions: What might you have to do to ensure that the system will boot from the correct installation media? Under what conditions should you select the UTC for the system time? How can you create more than four partitions on a Linux system? What are the characteristics of a secure password? What is the purpose of the bootloader? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 29 Video/Demo Time 2.2.1 Linux Installation 2:41 2.2.2 Installing Linux 20:55 Total 23:36 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Time About 30 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 30 Section 2.3: Localization Summary This section examines how to configure country and language-specific settings for various applications. Concepts covered include: Configurable environment variables Commands to configure local settings: o locate o iconv Students will learn how to: Localize a system with the appropriate country, monetary and language-specific settings. Linux+ Objectives: 107.3 Localisation and internationalisation Candidates should be able to localize a system in a different language than English. As well, an understanding of why LANG=C is useful when scripting. o Locale settings. o Timezone settings. Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to configure locale settings? What type of elements can be configured using the locale settings? What is the syntax of the locale settings? Which environment variable overrides all other locale settings? Video/Demo Time 2.3.1 Locale Settings 9:38 2.3.2 Configuring Locale Settings 5:20 Total 14:58 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 31 Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 32 Section 3.1: Linux Boot Process Summary This section examines the general stages of the Linux boot process: BIOS Boot loader OS Kernel Init Students will learn how to: Direct the system through the boot process. Linux+ Objectives: 101.2 Boot the system Candidates should be able to guide the system through the booting process. o Provide common commands to the boot loader and options to the kernel at boot time o Demonstrate knowledge of the boot sequence from BIOS to boot completion o Check boot events in the log file Lecture Focus Questions: What are the four general stages for the boot process? When is the initrd image loaded into memory? What is the default initial program? Which component mounts the root partition? What is the process ID of the initial program? Where is the primary boot loader located? Video/Demo 3.1.1 Linux Boot Process Time 7:36 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 33 Section 3.2: BootLoaders Summary This section discusses bootloaders. Concepts covered include: The Grand Unified Boot Loader (GRUB) utility Linux Loader Students will learn how to: View the grub configuration file and gather pertinent information about the system. Configure the GRUB configuration file to boot as required by your setup. Install the LILO bootloader. Linux+ Objectives: 102.2 Install a boot manager Candidates should be able to select, install and configure a boot manager. o Providing alternative boot locations and backup boot options. o Install and configure a boot loader such as GRUB. o Interact with the boot loader. Lecture Focus Questions: What do you have to do to apply the changes you have made to the LILO configuration file? What is the path to the GRUB configuration file? How do you change the default operating system when using GRUB? Which setting displays the available operating systems during system boot up? What is the syntax used to identify the root file system for each operating system in the GRUB menu? How can you require authentication for the options in the GRUB menu? Video/Demo Time 3.2.1 GRUB 9:23 3.2.2 Using GRUB 10:24 3.2.6 LILO 8:52 3.2.7 Using LILO 5:56 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 34:35 34 Lab/Activity Read the Boot File Configure the Boot File Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Time About 60 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 35 Section 3.3: Runlevels Summary In this section students will learn about managing runlevels. Concepts covered include: Runlevels 0-6 The role of the /etc/inittab file The contents of the /etc/inittab file Commands to determine and change the current runlevel Kernel options to customize Linux boot parameters. Students will learn how to: Identify the current runlevel and change it as required by your system circumstances. Change the default runlevel. Supply kernel options at boot time to customize how the system boots. Linux+ Objectives: 101.2 Boot the system Candidates should be able to guide the system through the booting process. o Provide common commands to the boot loader and options to the kernel at boot time 101.3 Change runlevels and shutdown or reboot system Candidates should be able to manage the runlevel of the system. This objective includes changing to single user mode, shutdown or rebooting the system. Candidates should be able to alert users before switching runlevel and properly terminate processes. This objective also includes setting the default runlevel. o Set the default runlevel. o Change between run levels including single user mode. Lecture Focus Questions: Which file affects the default runlevels? Why would you set the runlevel to 1? What is the difference in functionality between a runlevel 1 and runlevel 3? Which runlevel reboots the system, and which runlevel shuts the system down? What commands can be used to change the runlevel? How can you enter kernel options during the system boot up? How can you identify the current and previous runlevels? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 36 Video/Demo Time 3.3.1 Runlevels 8:17 3.3.2 Managing Runlevels 6:34 3.3.7 Using Kernel Options 6:05 Total 20:56 Lab/Activity Find the Runlevel Change the Runlevel Change the Default Runlevel Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 37 Section 3.4: Init Scripts Summary This section examines the basics of using init scripts. Concepts covered include: The role of init scripts Init script directories o rc (BSD and System V) o halt (BSD and System V) o boot (BSDF) or rc.sysinit (System V) o boot.local (BSD) Commands to manage daemons and the init scripts o service o insserv o chkconfig Students will learn how to: Use init scripts to start and stop services on the system. Determine the default runlevels for init scripts. Linux+ Objectives: 101.3 Change runlevels and shutdown or reboot system Candidates should be able to manage the runlevel of the system. This objective includes changing to single user mode, shutdown or rebooting the system. Candidates should be able to alert users before switching runlevel and properly terminate processes. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role and function of init scripts? Which distribution stores the init scripts in the /etc/rc.d/init.d directory? What does the /etc/init.d/rc5.d directory contain? How would you view what init scripts are available in your distribution? What command runs an init script? What identifier kills or starts an init script? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 38 Video/Demo Time 3.4.1 Init Scripts 17:16 3.4.2 Using Init Scripts 19:36 Total 36:52 Lab/Activity Change a Service Runlevel Determine Service Status Restart a Service Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Time About 60 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 39 Section 3.5: System Shutdown Summary This section discusses commands for shutting down the system. Students will learn how to: Use the shutdown, halt, and init commands at the shell prompt to properly shutdown or reboot the system. Linux+ Objectives: 101.3 Change runlevels and shutdown or reboot system Candidates should be able to manage the runlevel of the system. This objective includes changing to single user mode, shutdown or rebooting the system. Candidates should be able to alert users before switching runlevel and properly terminate processes. This objective also includes setting the default runlevel. o Set the default runlevel. o Change between run levels including single user mode. o Shutdown and reboot from the command line. o Alert users before switching runlevels or other major system event. o Properly terminate processes. Lecture Focus Questions: What happens when you run init 0 at the shell? How would you send a message to all users on the system without shutting down the system? Which commands shut the system down immediately? What command will reboot the system after 15 minutes? What is the purpose of the /etc/shutdown.allow? How can you terminate the shutdown process after it is already running? Video/Demo Time 3.5.1 System Shutdown 4:12 3.5.2 Shutting Down the System 5:11 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 9:23 40 Lab/Activity Shut Down Immediately Shut Down with Notification Shut Down and Reboot Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 41 Section 4.1: X Window System Summary This section discusses configuring an X Window system. Concepts covered include: X Window components: o X server o Window manager o Desktop environment o X font server Configuring the X server o Required information o Configuration files o Sections in configuration files o Utilities used with X server Configuring a window manager or desktop environment on a System V distribution Commands to start a specific application if the system does not have a graphical interface enabled Students will learn how to: Configure the X server settings. Linux+ Objectives: 106.1 Install and configure X11 Candidates should be able to install and configure X11. o Verify that the video card and monitor are supported by an X server. o Awareness of the X font server. o Basic understanding and knowledge of the X Window configuration file. Lecture Focus Questions: What three components make up the X Windows System? What is the additional optional component? Why does the xorg.conf file contain a warning about editing the file? What is the function of the module section in the xorg.conf or XF86Config file? What types of information do you need to gather before configuring the X server? What are the two popular desktop managers? Which utilities can you use to configure XFree86 X server? How can you launch a desktop manager if the system does not have a graphical interface enabled? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 42 Video/Demo Time 4.1.1 X Window System 9:15 4.1.3 X Window System Configuration 19:20 4.1.4 Configuring X Window System 7:50 Total 36:25 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 43 Section 4.2: Display Managers Summary This section discusses details about configuring display managers. Concepts covered include: Main display manager types for Linux: o X Display Manger (XDM) o Gnome Display Manager (GDM) o KDE Display Manager (KDM) Tasks to complete when configuring the display manager Paths to XDM configuration files: o /etc/X11/xdm o /usr/X11R6/lib/x11/xdm XDM configuration files o Xresources o Xservers o xdm-config o Xaccess KDM configuration files o /etc/kde/kdm/kdmrc o /etc/x11/ksm/kdmrc General sections of the kdmrc configuration file o General o XDMCP o Xgreeter The GDM configuration file is /etc/X11/gdm/gdm.conf Sections of the /etc/X11/gdm/gdm.conf file o Xserver definitions o Servers o Security options o XDMCP support o XDMCP chooser o Greeter Students will learn how to: Enable or disable an XDM display manager. Use the Xresources and Xserver files to configure the display manager. Configure the display manager to use X terminals. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 44 Linux+ Objectives: 106.2 Setup a display manager Candidates should be able setup and customize a display manager. This objective covers the display managers XDM (X Display Manger), GDM (Gnome Display Manager) and KDM (KDE Display Manager). o Turn the display manager on or off. o Change the display manager greeting. o Change default color depth for the display manager. o Configure display managers for use by X-stations. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of a display manager? What are the three main display manager types? Which display manager uses the same configuration files as the XDM display manager? What two different commands can you use to start the display manager? How can you change the color depth of the display manager? Video/Demo Time 4.2.1 Display Managers 15:44 4.2.2 Configuring Display Managers 10:10 Total 25:54 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 45 Section 4.3: Accessibility Summary This section explores providing accessibility to Linux systems to people with tactile, audible, and visual impairments. Concepts covered include: Keyboard accessibility options: o Sticky keys o Mouse keys o Slow keys o Toggle keys o Repeat rate o Bounce keys Visual accessibility options: o Onscreen keyboard o Mouse gesture o Screen reader o Screen magnifier o Braille devices o Desktop themes Students will learn how to: Configure the Assistive Technologies options for people with impairments. Use the GOK onscreen keyboard to send characters to an application. Configure Orca for use by visually impaired users. Configure High Contrast Large Desktop Themes for visually impaired users. Linux+ Objectives: 106.3 Accessibility Demonstrate knowledge and awareness of accessibility technologies. o Keyboard Accessibility Settings (AccessX?) o Visual Settings and Themes o Assistive Technology (ATs) Lecture Focus Questions: What types of disabilities does the accessibility option support? Which accessibility option can be set to assist users who have trouble pressing multiple keys at the same time? What feature can you use to compensate for a user who has Parkinson's disease and accidentally presses a single key multiple times? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 46 What accessibility options are available for the visually impaired user? Which types of alternative input methods are supported by GOK? Video/Demo Time 4.3.1 Accessibility 8:22 4.3.2 Configuring Accessibility Settings 13:05 Total 21:27 Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Time About 30 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 47 Section 5.1: Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) Summary This section examines using the RPM utility to install application packages. Concepts covered include: Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) o The role of RPM o RPM naming conventions o Commands for managing RPM packages rpm rpm2cpio Yellowdog Updater Modified (YUM) o The role of YUM o Uses /etc/yum.conf as the configuration file o Uses /etc/yum.repos.d to keep a .repo file o Uses /var/usr.yum.log as a log file o Commands for managing RPM packages: yum yumdownloader createrepo Students will learn how to: Use rpm to test dependencies before installing a package. Install a package using the rpm -ihv options to install and view the progress of the installation. Uninstall a package using rpm. Determine if a package has been installed. Use yum install a package and all the required dependencies. Linux+ Objectives: 102.5 Use RPM and YUM package management Candidates should be able to perform package management using RPM and YUM tools. o Install, re-install, upgrade and remove packages using RPM and YUM. o Obtain information on RPM packages such as version, status, dependencies, integrity and signatures. o Determine what files a package provides, as well as find which package a specific file comes from. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 48 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of a package manager? How does the RPM naming convention help you to quickly select a package with a specific version? How would you check the authenticity of a package? What sources are available for obtaining packages? What utility will extract files from an RPM package without installing the package? What is the difference between how RPM handles dependencies and how YUM handles dependencies? How would you verify if a package has been installed? What is the main configuration file for the YUM package? Video/Demo Time 5.1.1 RPM Part 1 16:56 5.1.2 RPM Part 2 9:49 5.1.3 Managing RPM Packages 12:32 5.1.5 Yellowdog Update Manager (YUM) 6:25 5.1.6 Installing RPM Packages with YUM 5:12 Total 50:54 Number of Exam Questions 22 questions Time About 80 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 49 Section 5.2: Debian Package Manager (DPKG) Summary This section explores using Debian packages to install packages. Details include: Commands used to manage Debian packages: o dpkg o apt-cache o apt-get o aptitude Students will learn how to: Install and uninstall a new package using the dpkg command. Use the apt-cache command to view information about installed packages. Download and install a package using the apt-get command. Linux+ Objectives: 102.4 Use Debian package management Candidates should be able to perform package management using the Debian package tools. o Install, upgrade and uninstall Debian binary packages. o Find packages containing specific files or libraries which may or may not be installed. o Obtain package information like version, content, dependencies, package integrity and installation status (whether or not the package is installed). Lecture Focus Questions: When would you use Debian packages instead of RPM packages? How can you identify a Debian package from an RPM package? What dpkg option prevents a package from being installed if a newer version of the package already exists on the computer? What command would you use to display all of the package’s dependencies? What command for Debian is similar to the YUM tool for RPM packages? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 50 Video/Demo Time 5.2.1 Debian Package Manager (DPKG) 10:12 5.2.2 Managing Debian Packages 7:27 Total 17:39 Number of Exam Questions 16 questions Time About 30 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 51 Section 5.3: Shared Libraries Summary This section provides information about managing shared libraries. Concepts covered include: The role of shared libraries Types of shared libraries: o Dynamic o Static Commands to manage libraries o ldd o ldconfig Students will learn how to: Identify a daemon's required shared libraries. Recognize a broken library link. Linux+ Objectives: 102.3 Manage shared libraries Candidates should be able to determine the shared libraries that executable programs depend on and install them when necessary. o Identify shared libraries. o Identify the typical locations of system libraries. o Load shared libraries. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the purpose of a shared library? What is the difference between a dynamic shared library and a static shared library? What does it mean if a library file name contains .so in the name? What command would you use to identify library dependencies? What are the management complications for shared libraries? Which file contains a cached list of dynamic shared libraries? What are the methods to configure additional dynamic libraries on a Linux system? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 52 Video/Demo Time 5.3.1 Shared Libraries 7:00 5.3.2 Managing Shared Libraries 2:22 Total 9:22 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 53 Section 6.1: User and Group Overview Summary This section provides the following information about user and group accounts: Types of users and groups: o Standard user o System user o Primary group o Secondary groups Files the user and group databases are stored in: o /etc/passwd o /etc/shadow o /etc/group o /etc/gshadow Students will learn how to: View the user account information in the /etc/passwd file. View the group membership information in the /etc/group file. Linux+ Objectives: 107.1 Manage user and group accounts and related system files Candidates should be able to add, remove, suspend and change user accounts. o Add, modify and remove users and groups. o Manage user/group info in password/group databases. o Create and manage special purpose and limited accounts. Lecture Focus Questions: Which file stores user accounts? Which file contains the passwords for each user account? What are the differences between standard user accounts and system user accounts? What is default primary group for each user? How can you determine if a user account is locked? How is the GECOS field typically used? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 54 Video/Demo Time 6.1.1 User and Group Overview 19:14 6.1.2 User and Group File Review 9:44 Total 28:58 Lab/Activity View User Account Information View Group Membership Information Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 50 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 55 Section 6.2: User Management Summary This section provides information about managing user accounts. Details include: Configuration files used when managing user accounts: o /etc/default/useradd o /etc/login.defs o /etc/skel Commands to manage user accounts: o useradd o passwd o usermod o userdel Students will learn how to: Create, rename, lock and unlock a user account. Change a user's password. Rename or remove a user account. Linux+ Objectives: 107.1 Manage user and group accounts and related system files Candidates should be able to add, remove, suspend and change user accounts. o Add, modify and remove users and groups. o Manage user/group info in password/group databases. o Create and manage special purpose and limited accounts. Lecture Focus Questions: Which directory contains configuration file templates that are copied into a new user's home directory? When using useradd to create a new user account, what types of default values create the user account? How can you view all the default values in the /etc/default/useradd file? What is the purpose of the /etc/login.defs file? How would you create a user using useradd without using the default values in /etc/default/useradd file? At the shell prompt, how do you create a password for a user? What does it mean if a user account is locked? Which command deletes a user and their home directory at the same time? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 56 Video/Demo Time 6.2.1 Useradd Command 9:59 6.2.2 Passwd Command 3:27 6.2.3 Usermod and Userdel Commands 5:38 6.2.4 Managing Users 9:29 Total 28:33 Lab/Activity Create a User Account Rename a User Account Delete a User Change Your Password Change a User's Password Lock and Unlock User Accounts Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Time About 75 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 57 Section 6.3: Group Management Summary In this section students will learn about the following commands used to manage group accounts and group membership: groupadd groupmod groupdel gpasswd newgrp usermod groups Students will learn how to: Create groups and define the group ID. Change secondary group membership for specific user accounts. Enable a group password. Linux+ Objectives: 107.1 Manage user and group accounts and related system files Candidates should be able to add, remove, suspend and change user accounts. o Add, modify and remove users and groups. o Manage user/group info in password/group databases. o Create and manage special purpose and limited accounts. Lecture Focus Questions: Which usermod option changes the secondary group membership? Which command removes all secondary group memberships for specific user accounts? How can you display the primary and secondary group membership for a single user? Which groupmod option changes the name of a group? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 58 Video/Demo Time 6.3.1 Group Management Commands 4:52 6.3.2 Managing Groups 3:17 Total 8:09 Lab/Activity Rename and Create Groups Add Users to a Group Add a User to Additional Groups Delete a Group and Users Remove a User from a Group Remove a User from All Groups Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 59 Section 7.1: Disk Partitions Summary This section examines details about managing disk partitions. Concepts covered include: Partition types: o Primary o Extended Tools to create and manage partitions: o fdisk o partprobe The role of device files Common device files: o /dev/sdxn o /dev/cdrom o /dev/fdn o /dev/ttyn o /dev/ttySn o /dev/lpn o /dev/usb/file_name o /dev/psaux o /dev/stn Students will learn how to: Use fdisk to view the partition information on the system. Linux+ Objectives: 102.1 Design hard disk layout Candidates should be able to design a disk partitioning scheme for a Linux system. o Allocate filesystems and swap space to separate partitions or disks. o Tailor the design to the intended use of the system. o Ensure the /boot partition conforms to the hardware architecture requirements for booting. 104.1 Create partitions and filesystems Candidates should be able to configure disk partitions and then create filesystems on media such as hard disks. This includes the handling of swap partitions. Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to plan disk partitioning before installing Linux? What is the difference between a primary and an extended partition? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 60 What utility do you use to manage disk partitions? Linux allows a maximum of only four primary partitions on a single hard disk drive. What can you do to get around this limitation? What does /dev/sda3 device file name identify? In what directory are the device file names stored? Video/Demo Time 7.1.1 Disk Partitions 13:04 7.1.2 Managing Partitions 7:33 7.1.3 Viewing Partitions 3:03 Total 23:40 Lab/Activity View the Partition Table Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 61 Section 7.2: File Systems Summary This section discusses file systems supported by Linux and how to format a hard disk. Common file systems: o ext2 o ext3 o ext4 o swap o reiserfs o ntfs o vfat o xfs Command used to format a partition: o mkfs o mkreiserfs o mkswap o mke2fs The role of the inode table The role of a superblock Students will learn how to: Format a hard disk with a specified file system. Create and activate a new swap partition. Linux+ Objectives: 104.1 Create partitions and filesystems Candidates should be able to configure disk partitions and then create filesystems on media such as hard disks. This includes the handling of swap partitions. o Use various mkfs commands to set up partitions and create various filesystems such as: ext2 ext3 xfs reiserfs v3 vfat ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 62 Lecture Focus Questions: How would you make mkfs automatically calculate the size of the data blocks for the file system? What two different commands can you use to create the ReiserFS file system type? How would you create and activate a swap partition? Which file systems provide journaling? What is the difference between the ext3 and ext4 file system types? Video/Demo Time 7.2.1 File System Creation 8:59 7.2.2 Creating a File System 4:43 Total 13:42 Lab/Activity Format a Hard Disk with ext3 Format a Hard Disk with reiserfs Create a Swap Area Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 63 Section 7.3: Mounting File Systems Summary This section discusses mounting file systems. Concepts covered include: Files that manage and monitor the mounting of file systems: o /etc./fstab o /etc/mtab o /procs/mounts Commands to manage the mounting of file systems: o mount /dev/device/mountpoint o mount o df o umount Students will learn how to: Mount a volume to a specified directory with a specified file system. Unmount a volume. Mount a DVD drive to a specified directory. Linux+ Objectives: 104.3 Control mounting and unmounting of filesystems Candidates should be able to configure the mounting of a filesystem. o Manually mount and unmount filesystems. o Configure filesystem mounting on bootup. o Configure user mountable removable filesystems. Lecture Focus Questions: What directory contains mount points specifically for external storage devices? What do you need to do to make a USB drive accessible? What happens if you mount a volume to a directory that already contains data? How can you verify that a volume is mounted correctly? What commands can you use to view the devices that are currently mounted? How can you prevent users from mounting an optical media drive? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 64 Video/Demo Time 7.3.1 File System Mounting 15:40 7.3.2 Mounting a File System 4:32 Total 20:12 Lab/Activity Mount a Volume Unmount a Volume Mount a DVD Drive Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Time About 50 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 65 Section 7.4: File System Maintenance Summary This section explores commands to maintain file system integrity: df du lsof fuser fsck e2fsck debugfs dumpe2fs tune2fs xfs_info xfs_metadump Students will learn how to: Use the df and du commands check disk usage. Use the lsof and fuser commands to monitor the file system. Use the fsck command to check and repair the file system Linux+ Objectives: 104.2 Maintain the integrity of filesystems Candidates should be able to maintain a standard filesystem, as well as the extra data associated with a journaling filesystem. o Verify the integrity of filesystems. o Monitor free space and inodes. o Repair simple filesystem problems. Lecture Focus Questions: What utility allows you to view the space available on all mounted file systems? What kinds of information can the lsof utility provide? What action must you perform before using the fsck utility? Which utility converts ext2 file systems to ext3 file systems? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 66 Video/Demo Time 7.4.1 File System Maintenance 8:26 7.4.2 Maintaining File Systems 7:48 Total 16:14 Lab/Activity Determine the Amount of Free Disk Space Determine the Directory Size Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 67 Section 7.5: Disk Quotas Summary In this section students will learn about using disk quotas to limit the amount of disk space a user or group can use. Concepts covered include: Quota types: o Soft limit o Hard limit Steps to implement quotas: o Install quota package o Edit mount option in /etc/fstab o Create quota files o Enable quotas and view a quota report o Edit quotas Commands for working with quotas: o quotacheck –mavug o quotaon o quotaoff o repquota o edquota o quota Students will learn how to: Scan the file system and create quota files. Enable quotas on the file system. Create a quota and set the block and inode quotas. Generate a quota report. Linux+ Objectives: 104.4 Manage disk quotas Candidates should be able to manage disk quotas for users. o Set up a disk quota for a filesystem. o Edit, check and generate user quota reports. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between a soft and hard block limit? What is the difference between block quotas and inode quotas? What tool do you use to create the aquota.user and aquota.group files in the file system? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 68 How would you generate a quota report to display how much space is used by users on the system? Video/Demo Time 7.5.1 Disk Quotas 8:05 7.5.2 Managing Quotas 13:37 Total 21:42 Lab/Activity Find the User Quota Generate a Quota Report Turn Quotas On Turn Quotas Off Edit Quotas 1 Edit Quotas 2 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 65 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 69 Section 7.6: Ownership Summary This section discusses managing file and directory ownership. Concepts covered include: Common commands for managing file ownership: o ls –l o chown o chgrp Students will learn how to: Use the chown command to change file ownership. Change the group ownership of a file. Linux+ Objectives: 104.5 Manage file permissions and ownership Candidates should be able to control file access through the proper use of permissions and ownerships. o Manage access permissions on regular and special files as well as directories. o Use access modes such as suid, sgid and the sticky bit to maintain security. o Know how to change the file creation mask. o Use the group field to grant file access to group members. Lecture Focus Questions: Which user accounts can change file ownership? Which utility will display ownership information for files and directories? What are the two different methods you can use to change group ownership of a file? Video/Demo Time 7.6.1 Ownership 5:23 7.6.2 Managing Ownership 4:52 Total ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 10:15 70 Lab/Activity View Ownership Information Change File Ownership Change Group Ownership for a File Change Directory Ownership Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Time About 30 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 71 Section 7.7: Permissions Summary This section discusses managing file and directory permissions. Concepts covered include: The role of the file inode Mode sections Types of Permissions contained in the mode o Read o Write o Execute Identifying permissions: o Letter Abbreviation o Octal Number Identifying a file vs. a directory in the mode Common commands for managing permissions o ls –l o chmod The role of the umask Commands for managing umask Special permissions o SUID o SGID o Sticky bit Commands to manage special permissions o ls –l o chmod Students will learn how to: Manage permissions by setting the needed file and directory permissions. Change the umask settings to control access. Set or remove special permissions. Linux+ Objectives: 104.5 Manage file permissions and ownership Candidates should be able to control file access through the proper use of permissions and ownerships. o Manage access permissions on regular and special files as well as directories. o Use access modes such as suid, sgid and the sticky bit to maintain security. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 72 o Know how to change the file creation mask. o Use the group field to grant file access to group members. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the 'mode of a file'? Which user accounts can change the mode of a file? What permissions does 764 represent when identifying permissions numerically? What does the first dash represent in -rwxrw-r--? What are the default permissions for files and directories? What is the function of umask? What does the umask value represent? In which file should you set the umask value to make it persistent? On which types of files should you configure the SUID and SGID bits? What is the purpose for setting the sticky bit? Which special permissions would be set using chmod 6421? Video/Demo Time 7.7.1 Permissions 15:36 7.7.2 Managing Permissions 14:18 7.7.8 Umask 9:51 7.7.9 Using Umask 9:39 7.7.12 Special Permissions 4:55 7.7.13 Assigning Special File Permissions 7:58 Total 62:17 Lab/Activity Set Directory Permissions Add File Permissions Set File Permissions Enable Directory Browsing Change the Umask Set the SUID Bit Remove SUID and SGID Permissions Number of Exam Questions 17 questions Time About 110 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 73 Section 7.8: Archive and Backup Summary This section discusses creating archives to backup data. Concepts covered include: The tar (tape archive) utility o tar o gzip o gunzip o bzip2 The cpio utility The dd utility Students will learn how to: Use tar to create a compressed tar file. Use tar to extract files from a tar file. Use cpio to create an archive file and extract files from the cpio file. Use dd to copy information from records. Linux+ Objectives: 103.3 Perform basic file management Candidates should be able to use the basic Linux commands to manage files and directories. o Usage of tar, cpio and dd. Lecture Focus Questions: What type of file would the file marketing.tar.gz represent? Which tar command option decompresses a file? Which utilities can decompress a file with a .bz2 extension? When would you use the dd command over the cp command to copy information? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 74 Video/Demo Time 7.8.1 Tar Utility 10:22 7.8.2 Using Tar 4:26 7.8.6 cpio and dd Utility 10:23 7.8.7 Using cpio and dd 8:48 Total 33:59 Lab/Activity Create a Compressed tar File Extract from tar Files Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 75 Section 8.1: Device Drivers Summary In this section students will learn the basics of device drivers. Concepts covered include: Methods Linux uses to implement device drivers: o Loaded as a kernel module o Compiled into the kernel Directories that contain hardware information: o /proc o /sys Utilities that provide information about hardware configuration: o lsusb o hwinfo o lspci Students will learn how to: View hardware information by viewing the contents of the /proc and /sys directories. View hardware information using the lsusb, hwinfo and lspci utilities. Linux+ Objectives: 101.1 Determine and configure hardware settings Candidates should be able to determine and configure fundamental system hardware. o Enable and disable integrated peripherals o Configure systems with or without external peripherals such as keyboards o Differentiate between the various types of mass storage devices o Set the correct hardware ID for different devices, especially the boot device o Determine hardware resources for devices o Tools and utilities to list various hardware information (e.g., lsusb, lspci, etc.) o Tools and utilities to manipulate USB devices Lecture Focus Questions: How are device drivers implemented on a Linux system? Why are some device drivers not compiled into the kernel? Which directories contain information about the hardware that is installed on the computer? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 76 How would you use the hwinfo utility to display information about all the hardware in the computer? What extension identifies a kernel module? What type of information is stored in /proc/cmdline? Which utility will display information about the PCI devices on the system? o Tools and utilities to list various hardware information (e.g., lsusb, lspci, etc.) o Tools and utilities to manipulate USB devices Video/Demo Time 8.1.1 Device Drivers 12:36 8.1.2 Viewing Hardware Information 10:21 Total 22:57 Lab/Activity View /proc Information Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 77 Section 8.2: Kernel Module Management Summary This section examines managing kernel modules. Concepts covered include: Files to automatically load kernel modules when the system boots: o /etc/modprobe.conf o /etc/modprobe.d Commands to manage kernel modules manually: o lsmod o modinfo o depmod o insmod o modprobe o rmmod Students will learn how to: View a list of currently loaded modules using lsmod. Create a list of module dependencies using depmod. Use modprobe to load a kernel module. Remove a module using rmmod. Linux+ Objectives: 101.1 Determine and configure hardware settings Candidates should be able to determine and configure fundamental system hardware. o Enable and disable integrated peripherals o Configure systems with or without external peripherals such as keyboards o Differentiate between the various types of mass storage devices o Set the correct hardware ID for different devices, especially the boot device o Determine hardware resources for devices Lecture Focus Questions: Which commands can you use to view modules that are currently loaded? How would you generate a list of module dependencies? What is the advantage of using modprobe over insmod to load a module into the kernel? How do you unload a kernel module with its dependencies? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 78 Video/Demo Time 8.2.1 Kernel Module Management 13:45 8.2.2 Managing Kernel Modules 4:29 Total 18:14 Lab/Activity Insert a Module into the Kernel Remove a Module from the Kernel Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 79 Section 8.3: Hotplug and Coldplug Devices Summary This section provides information about managing Hotplug and Coldplug devices. Concepts covered include: Device categories: o Coldplug o Hotplug Components to manage devices: o sysfs o Hardware Abstraction layer (HAL) daemon o Desktop Bus (D-Bus) daemon o /udev Students will learn how to: View the rules file in /udev/rules. Modify and save a rule. Linux+ Objectives: 101.1 Determine and configure hardware settings Candidates should be able to determine and configure fundamental system hardware. o Know the differences between coldplug and hotplug devices o Conceptual understanding of sysfs, udev, hald, dbus Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between a hotplug and a coldplug device? Which types of devices are usually coldplug devices? What is the function of the sysfs virtual file? Where is sysfs located? How does the system recognize when a device is added or removed? Which utility dynamically creates device files as devices are added to the system? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 80 Video/Demo Time 8.3.1 Hotplug and Coldplug Devices 6:47 8.3.2 Managing udev Rules 3:01 Total 9:48 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Time About 15 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 81 Section 9.1: Processes Summary This section discusses the basics of processes. Concepts covered include: File types that create processes on a Linux system: o Binary executable o Internal shell commands o Shell scripts Types of processes: o User o Daemon Process identifiers: o Process ID (PID) o Parent Process ID (PPID) Commands to view processes: o top o ps Students will learn how to: Use top to monitor Linux processes. Use ps to troubleshoot a Linux system. Linux+ Objectives: 103.5 Create, monitor and kill processes Candidates should be able to perform basic process management. o Monitor active processes. o Select and sort processes for display. o Send signals to processes. 103.6 Modify process execution priorities Candidates should be able to manage process execution priorities. o Know the default priority of a job that is created. Lecture Focus Questions: Which types of files can create processes on a Linux system? What is the difference between user process and daemon processes? How are system processes usually identified? Which process is always assigned the same process ID number? What is the major difference between how top and ps display system processes? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 82 Video/Demo Time 9.1.1 Processes 14:16 9.1.3 Process Display 9:38 9.1.4 Viewing Processes 9:22 Total 33:16 Lab/Activity View process Information Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 50 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 83 Section 9.2: Process Management Summary This section discusses managing and prioritizing processes. Concepts covered include: Commands to move processes between the foreground and background, and adjust process priorities: o command & o jobs o bg o fg o Ctrl+z o nice o renice o nohup & Commands to terminate running processes: o kill o killall o xkill Students will learn how to: Switch a process between the foreground and background. Set and change the priority of a process. Terminate a process using either kill or killall. Scan and kill zombie processes on the system. Linux+ Objectives: 103.5 Create, monitor and kill processes Candidates should be able to perform basic process management. o Run jobs in the foreground and background. o Signal a program to continue running after logout. o Monitor active processes. o Select and sort processes for display. o Send signals to processes. 103.6 Modify process execution priorities Candidates should be able to manage process execution priorities. o Know the default priority of a job that is created. o Run a program with higher or lower priority than the default. o Change the priority of a running process. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 84 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between a process running in the foreground and a process running in the background? Which commands can be used to move processes between the foreground and the background? How can you change the priority of a process? What is the range for nice values? What number would be the highest priority for a nice value? Which termination signal is sent by the Ctrl+c key combination? Which utility changes the cursor to an X to terminate GUI applications? Video/Demo Time 9.2.1 Process Management 12:04 9.2.2 Switching Foreground and Background Processes 4:54 9.2.3 Prioritizing Processes 6:54 9.2.5 Process Termination 5:57 9.2.2 Terminating Processes 3:55 Total 33:44 Lab/Activity Stop a Zombie Process Number of Exam Questions 19 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 85 Section 9.3: Task Management Summary This section discusses task management. Details include: The role of the at daemon o Steps to use the at utility o Commands to manage tasks with the at command at time date at time_of_day at now at now + number time_period at –f filename time at -1 atq at –d jobnumber atrm jobnumber The role of the cron daemon The configuration files that cron uses: o /etc/crontab o /etc/cron.timeparameter o /var/spool/cron/username o /etc/cron.allow o /etc/cron.deny Commands to manage cron task scheduling: o crontab o vi /etc/crontab o crontab file o which Students will learn how to: Verify that the atd daemon is running. Schedule a job to run in the future using the at command. View a list of pending jobs using the atq command. Removing a pending job using the atrm command. Linux+ Objectives: 107.2 Automate system administration tasks by scheduling jobs Candidates should be able to use cron or anacron to run jobs at regular intervals and to use at to run jobs at a specific time. o Manage cron and at jobs. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 86 o Configure user access to cron and at services. Lecture Focus Questions: Which script controls the at daemon? Which files control access to the at command? What is the main difference between using at and cron to schedule a job? Which files control access to the cron command? Where is the system wide crontab file located? How can you edit personal crontab files? Video/Demo Time 9.3.1 At Task Scheduling 7:11 9.3.2 Scheduling Tasks with at 4:35 9.3.4 Cron Task Scheduling 12:04 9.3.5 Scheduling Tasks with cron 7:12 Total 31:02 Number of Exam Questions 16 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 87 Section 9.4: Print Management Summary This section examines managing printers and printing on Linux systems. Concepts covered include: CUPS components: o Client o Server o Scheduler o Queue o Filter o Backend o Postscript Printer Descriptions (PPD) The steps CUPS uses to process print jobs Common parameters in /etc/cups/cupsd.conf configuration file: o ServerName o ServerAdmin o DocumentRoot o LogLevel o Listen o MaxCopies o MaxJobsPerUser o User o Group o MaxClients o Browsing o BrowseAddress o BrowseInterval o BrowseOrder o BrowseAllow o BrowseDeny Utilities used to configure CUPS: o cupsctl o lppasswd –g sys –a root Commands associated with LPD and CUPS: o lpr o lpc o lpq o lprm o lpstat o cancel o lpoptions o accept o reject ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 88 o disable o cupsdisable o enable o cupsenable Parameters commonly found in the LPD configuration file, /etc/lpd.perms. o DEFAULT o HOST o REMOTEHOST o REMOTIP o REMOTEUSER o SAMEHOST o SAMEUSER o SERVER o SERVICE o USER Students will learn how to: Verify CUPS is installed and running. Configure the CUPS daemon parameters to provide network printing on a Linux system. Enable the printer to allow printer sharing. Use lp commands to manage print jobs at the shell prompt. Linux+ Objectives: 108.4 Manage printers and printing Candidates should be able to manage print queues and user print jobs using CUPS and the LPD compatibility interface. o Basic CUPS configuration (for local and remote printers). o Manage user print queues. o Troubleshoot general printing problems. o Add and remove jobs from configured printer queues. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of the cupsd daemon on the server? How can you access the Web-based administration tool for the CUPS server? What is the file used to configure CUPS? Which commands can you use to remove print jobs from the queue? What command is necessary to activate a printer queue? How can you display all the printer queues on the system? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 89 Video/Demo Time 9.4.1 Common Unix Print System (CUPS) Operation 8:29 9.4.2 CUPS Installation and Configuration 12:57 9.4.3 Configuring a CUPS Printer 11:15 9.4.5 Print Management Commands 5:45 9.4.6 Managing Print Jobs 4:31 Total 42:57 Lab/Activity Print a File Remove a Print Job Number of Exam Questions 17 questions Time About 75 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 90 Section 9.5: Time Management Summary This section discusses the basics of time management. Details include: Time zones Linux clocks: o Hardware clock o System time Local time or Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time Calculating the UTC offset Tools and files to determine and change time zone settings: o /usr/share/zoneinfo o /etc/localtime o /etc/timezone o /etc/sysconfig/clock o date o tzselect o TZ=time-zone export TZ Files and utilities to manage the hardware clock and system time: o cat /proc/driver/rtc o hwclock o /etc/sysconfig/clock o netdate o date The role of the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Files and utilities to manage time using the NTP: o /etc/ntp.conf o ntpdate o ntpd o rcntp start or service ntpd start o insserv ntp o ntpq o ntptrace Students will learn how to: Change time zone settings and make them permanent. Setting the hardware clock. Create a time synchronization solution using public NTP time providers. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 91 Linux+ Objectives: 107.3 Localisation and internationalisation Candidates should be able to localize a system in a different language than English. As well, an understanding of why LANG=C is useful when scripting. o Locale settings. o Timezone settings. 108.1 Maintain system time Candidates should be able to properly maintain the system time and synchronize the clock via NTP. o Set the system date and time. o Set the hardware clock to the correct time in UTC. o Configure the correct timezone. o Basic NTP configuration. o Knowledge of using the pool.ntp.org service Lecture Focus Questions: How can you view the current hardware clock time? What does it mean for 'time to drift'? How do you synchronize time on a Linux network? How does stratum help to provide accurate time? What is the difference between stepping and slewing? What happens when the time provider and the time consumer are more than 17 minutes off from each other? Video/Demo Time 9.5.1 Time Zone Settings 10:20 9.5.2 Configuring Time Zone Settings 4:34 9.5.4 Time Maintenance 7:02 9.5.5 Setting the Hardware Clock 8:08 9.5.7 Network Time Protocol (NTP) 15:03 9.5.8 Synchronizing Time with NTP 10:57 Total 56:04 Number of Exam Questions 21 questions Time About 90 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 92 Section 9.6: Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) Summary In this section students will explore using Mail Transfer Agents (MTA). Details include: Common MTA types on a Linux system: o Sendmail o Postfix o qmail o Exim To manage messages use: o mail o /etc/aliases.db o ~/.forward o /var/spool/mail Students will learn how to: Send mail to a local user from the command line. Configure an alias for long term redirection of mail. Configure forwarding to another user for a temporary redirection of mail. Linux+ Objectives: 108.3 Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) basics Candidates should be aware of the commonly available MTA programs and be able to perform basic forward and alias configuration on a client host. Other configuration files are not covered. o Create e-mail aliases. o Configure e-mail forwarding. o Knowledge of commonly available MTA programs (postfix, sendmail, qmail, exim) (no configuration) Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role and function of a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)? What are the most common types of MTAs on a Linux system? How do you read mail for local user accounts from the command line? Why would you configure an alias for the MTA running on a local system? What file do you use to configure forwarding of e-mail messages? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 93 Video/Demo Time 9.6.1 MTA Overview 11:29 9.6.2 MTA Configuration 8:26 9.6.3 Configuring MTA Settings 8:44 Total 28:39 Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 94 Section 9.7: Structured Query Language (SQL) Summary This section provides an overview of using Structured Query Language (SQL) in database applications. Details include: Commands used to access and control a MySQL server: o mysql_install_db o mysqladmin o mysql o service mysqld start rcmysql start Database objects: o Database o Table o Record o Attributes o Integers o Primary key Common SQL data types: o Character o Varchar o Decimal o Float o Time o Date o Enum Commands to create, modify and extract data from databases: o CREATE DATABASE o USE o SHOW TABLES o CREATE TABLE o INSERT INTO o DESCRIBE o SELECT o UPDATE o DELETE FROM o ALTER TABLE o DROP TABLE Students will learn how to: Use SQL commands to create a new database and a table within the database. Add data to the table using SQL commands. Use the SELECT command to print data from the database. Use the DELETE command to delete data from the table. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 95 Linux+ Objectives: 105.3 SQL data management Candidates should be able to query databases and manipulate data using basic SQL commands. This objective includes performing queries involving joining of 2 tables and/or subselects. o Use of basic SQL commands. o Perform basic data manipulation. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the components that make up a database? What is the difference between a table record and an attribute? What SQL command would you use to view the data in a database? How can you ensure that you do not delete the wrong data from the database? When would you combine the SELECT and SORT BY commands? Video/Demo Time 9.7.1 SQL Data Management 10:03 9.7.2 Manipulating SQL Data 12:31 Total 22:34 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Time About 35 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 96 Section 10.1: System Log Files Summary This section examines system logging. Concepts covered include: The role of log files Entry options in the /etc/syslog.conf Common log files The role of the logrotate utility: Commands found in the /etc/logrotate.conf or scripts in /etc/logrotate.d: o compress o maxage o dateext o rotate o size o notifyempty o missingok o create o postrotate Commands to view and manage text-based log files: o cat o grep o tail o head o less o more o vi o gedit Commands to view and manage binary log files: o dmesg o dmesg –n # o last o faillog o lastb o lastlog o logger o logrotate o sar Students will learn how to: Configure a syslog daemon to log to a remote host. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 97 Linux+ Objectives: 108.2 System logging Candidates should be able to configure the syslog daemon. This objective also includes configuring the logging daemon to send log output to a central log server or accept log output as a central log server. o syslog configuration files o syslog o standard facilities, priorities and actions Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of the syslog daemon? Why is it a good idea to send log message to a remote server? What actions are necessary to configure a server to receive messages from a client? What is the syntax for the entries in the /etc/syslog.conf file? How can you send messages to a virtual console? What is the function of logrotate utility? Where are the entries for the logrotate configuration file stored? What commands can be used to view text-based log files? What command will show all failed login attempts on the system? Video/Demo Time 10.1.1 Log Files 14:23 10.1.2 Configuring Remote Logging 8:24 10.1.5 Logrotate 7:06 10.1.7 Log File Display 9:53 10.1.8 Displaying Log Files 5:18 Total 45:04 Number of Exam Questions 20 questions Time About 65 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 98 Section 10.2: Scripts Summary In this section students will learn about using scripts to execute commands. Details include: The role of scripts Methods to run scripts Simple scripting functions: o Specify the shell that runs the script o Add comments o Add commands o Use variables o Display information on the screen o Get user input o Declare integers or function in the text Script control structures: o Branching structures o Looping structures Commands and statements to create control structures: o Sequences o Testing conditions o If, then, else statements o Case statements o While loops o Until loops o For loops Students will learn how to: Create a simple script to echo text on the screen and run a command. Create a script that will read input from a user. Create a script that will use declared variables as integers to allow math to be performed by the script. Create a script using control structures. Linux+ Objectives: 105.2 Customize or write simple scripts Candidates should be able to customize existing scripts, or write simple new BASH scripts. o Use standard sh syntax (loops, tests). o Use command substitution. o Test return values for success or failure or other information provided by a command. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 99 o Perform conditional mailing to the superuser. o Correctly select the script interpreter through the shebang (#!) line. o Manage the location, ownership, execution and suid-rights of scripts. Lecture Focus Questions: What lines are required within a shell script? How can you comment out lines in a shell script? Why do you need to assign the execute permission to a script? What methods can you use to run a script from the command line? What command do you use to obtain user input during the execution of a script? Why might you need to use the declare command in a script? Under which conditions would you use an until loop in place of a while loop? How should you end the script containing the if, then, else control structure? Video/Demo Time 10.2.1 Scripts Overview 15:17 10.2.2 Creating Simple Scripts 9:45 10.2.4 Script Control Structure 11:27 10.2.5 Creating Script Control Structures 5:33 Total 42:02 Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Time About 60 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 100 Section 10.3: Text Stream Processing Summary This section discusses the processing of a text stream. Details include: Commands to intercept and process the text stream: o cut o expand o fmt o join o nl o od o paste o pr o sed o awk o sort o split o tr o unexpand o uniq o wc Students will learn how to: Use text stream processing to manipulate text using commands that filter and modify the output. Linux+ Objectives: 103.2 Process text streams using filters Candidates should be able to apply filters to text streams. o Send text files and output streams through text utility filters to modify the output using standard UNIX commands found in the GNU textutils package. Lecture Focus Questions: How can text stream processing be used to modify the output of text? What command would you use to remove characters from lines of text in a text stream? How could you format files with long lines to display properly on the monitor? What command would you use to format a text file for printing? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 101 Which commands replace a tab character with a specified number of spaces and vice versa? How can you display a text stream with numbers preceding each line? Video/Demo Time 10.3.1 Text Stream Processing 24:37 10.3.2 Processing Text Streams 17:32 Total 42:09 Number of Exam Questions 20 questions Time About 60 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 102 Section 11.1: Networking Overview Summary This section provides students with an overview of networking. Details include: The role of a protocol Protocols in the IP protocol suite IPv4 address details o 32-bit binary number represented in four octets (four 8-bit numbers) o Subnet mask o Default class o Address classes A B C D E Network Address Translation (NAT) router Subnetting Network address Broadcast address IPv6 address details: o 32 hexadecimal numbers, organized into 8 quartets o 128-bit address contains two parts: Prefix Interface ID The role of ports ICANN specifies three categories for port: o Well known o Registered o Dynamic Ports that correspond to common Internet services Linux+ Objectives: 109.1 Fundamentals of internet protocols Candidates should demonstrate a proper understanding of TCP/IP network fundamentals. o Demonstrate an understanding network masks. o Knowledge of the differences between private and public "dotted quad" IP-Addresses. o Setting a default route. o Knowledge about common TCP and UDP ports (20, 21, 22, 23, 25, 53, 80, 110, 119, 139, 143, 161, 443, 465, 993, 995). ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 103 o Knowledge about the differences and major features of UDP, TCP and ICMP. o Knowledge of the major differences between IPv4 and IPV6. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of the IP protocol? What is the difference between a connectionless and a connection-oriented protocol? What is the main role of the ICMP protocol? What is the difference between a private and public IP address? How does the subnet mask identify the network address and network node? What are the differences between IP version 4 and IP version 6 addresses? Which file lists all network services and their ports on the Linux system? Video/Demo Time 11.1.1 IP Protocols 7:33 11.1.3 IP Addresses 8:32 11.1.4 Subnet Masks 6:50 11.1.6 Common Ports 4:03 Total 26:58 Number of Exam Questions 24 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 104 Section 11.2: Network Interface Configuration Summary This section discusses configuring network interfaces. Topics covered include: Options for assigning IP addresses o Static (manual assignment) o Dynamic Host Configuration protocol (DHCP) assignment Files used for network configuration: o /etc/init.d/network o /etc/rc.d/init.d/network o /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts o /var/lib/dhcpcd/dhcpclientn o /var/lib/dhcpcd/dhclient.leases Commands for configuring network settings o service network o ifconfig interface parameters o ifup o ifdown o ifconfig o ifconfig interface Students will learn how to: View information about the current network interfaces. Use the interface configuration file to manually assign a static address for the network interface. Disable and enable a network interface. Linux+ Objectives: 109.2 Basic network configuration Candidates should be able to view, change and verify configuration settings on client hosts. o Manually and automatically configure network interfaces o Basic TCP/IP host configuration. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the advantage of using dynamic addressing over static addressing? Where is the interface configuration file located on the system? What is the purpose of the lo network interface? How can you view the current status of the network interfaces from the shell prompt? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 105 What utilities can disable and enable the network interfaces? Video/Demo Time 11.2.1 Address Configuration 11:57 11.2.2 Viewing and Managing Addresses with ifconfig 5:33 11.2.3 Configuring DHCP and Static Addressing 5:57 Total 23:27 Lab/Activity Start a NIC Stop a NIC Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 106 Section 11.3: Routing Configuration Summary In this section students will learn about configuring routing. Details include: The role of a router The role of a routing table The role of a default router Commands for configuring routing o route add o route del o route Students will learn how to: Configure a persistent default gateway route in the proper configuration file (dependent upon your Linux distribution). Set the default gateway address. Manually add a route to another network. Delete a route. Linux+ Objectives: 109.1 Fundamentals of internet protocols Candidates should demonstrate a proper understanding of TCP/IP network fundamentals. o Setting a default route. 109.2 Basic network configuration Candidates should be able to view, change and verify configuration settings on client hosts. o Manually and automatically configure network interfaces o Basic TCP/IP host configuration. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of a router? What file contains the complete routing table on the system? How would you make the default gateway persistent? Which command sets the default route on the system? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 107 Video/Demo Time 11.3.1 Routing Configuration 6:02 11.3.2 Configuring the Default Route 7:06 Total 13:08 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 108 Section 11.4: Hostname and DNS Configuration Summary This section discusses the files that administrators use to configure DNS settings on Linux: /etc/hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf /etc/HOSTNAME /etc/sysconfig/network host hostname Students will learn how to: Configure the settings in the hosts file to resolve name resolution on a system. Configure name resolution using the settings in the /etc/resolv.conf file to access a DNS server. Configure the /etc/nsswitch.conf file to define the order in which the name resolution should be completed. Linux+ Objectives: 109.4 Configure client side DNS Candidates should be able to configure DNS on a client host. o Demonstrate the use of DNS on the local system. o Modify the order in which name resolution is done. Lecture Focus Questions: When configuring the DNS, what is the purpose for having multiple nameservers? Which file provides the system with domain names mapped to IP addresses? What function does the /etc/nsswitch.conf file provide? What are the advantages of using a DNS server for name resolution? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 109 Video/Demo Time 11.4.1 Hostname and DNS Configuration 7:24 11.4.2 Configuring DNS Settings 9:14 Total 16:38 Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Time About 25 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 110 Section 11.5: Network Troubleshooting Summary This section provides the guidelines for troubleshooting network communication problems. Details include: Troubleshooting methodology 1. Identify the symptoms and potential causes. 2. Establish what has changed. 3. Create a hypothesis. 4. Create an action plan and account for side effects of the proposed plan. 5. Implement the fix to the problem, verifying the solution has fixed the problem and not caused any other problems. 6. Ensure user satisfaction. 7. Document the solution and process. Considerations when troubleshooting communications: o Physical issues o Interference o Network issues Tools for troubleshooting network communication problems: o ping o netstat o traceroute o tracepath o nslookup o dig Students will learn how to: Troubleshoot the network by verifying connectivity between hosts within the network. Test the connectivity and show the path between the two devices. Test for name resolution and obtain in-depth information about a domain name. Linux+ Objectives: 109.3 Basic network troubleshooting Candidates should be able to troubleshoot networking issues on client hosts. o Manually and automatically configure network interfaces and routing tables to include adding, starting, stopping, restarting, deleting or reconfiguring network interfaces. o Change, view, or configure the routing table and correct an improperly set default route manually. o Debug problems associated with the network configuration. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 111 Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to completely identify the source of a problem before starting to fix it? What are good sources to research when creating a hypothesis and determining a resolution? After you fix the problem what actions should you still complete? How can you verify the connectivity of hosts within a network? Which utility can display the round trip time of an ICMP echo request? Which utilities send name resolution requests? Which utility will provide the most information about the hostname or IP address? Video/Demo Time 11.5.1 Troubleshooting Methodology 11:11 11.5.3 Network Troubleshooting Tools 13:16 11.5.4 Using Network Troubleshooting Tools 7:36 Total 32:03 Number of Exam Questions 16 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 112 Section 12.1: Root Usage Summary This section discusses using the root user account to perform tasks. Details include: The role of the root user account Guidelines to protect the root user account The sudo command and /etc/sudoers file Sections used to configure the /etc/sudoers file: o User_Alias o Cmnd_Alias o Host_Alias o Runas_Alias Commands for using the superuser account and switching user: o su o exit o gnomesu o logout o sudo o visudo Students will learn how to: Use su to switch to another user. Start a graphical application from the desktop as a standard user, but gain privileged access. Configure sudo to allow a specific user to complete specific commands with privileged access. Linux+ Objectives: 110.1 Perform security administration tasks Candidates should know how to review system configuration to ensure host security in accordance with local security policies. o Basic sudo configuration and usage. Lecture Focus Questions: Why should you protect the root user password? What utility should you use to the launch the /etc/sudoers file? What is the syntax for the /etc/sudoers file? How can you use su to execute a command without switching into another login console? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 113 What su option will switch to another user and include the user's environment variables? How does the command prompt appear for a standard user account versus the root user account? Video/Demo Time 12.1.1 Appropriate Root Usage 14:11 12.1.2 Using su 4:09 12.1.3 Configuring sudo 10:00 Total 28:20 Lab/Activity Switch Users for a Command Log Out of the System Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Time About 40 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 114 Section 12.2: User Security and Restriction Summary This section discusses commands used to promote user security and restrictions: chage ulimit Students will learn how to: Configure user password aging limits. Configure the user login restrictions in the /etc/security/limits.conf file. Set limits for programs launched from the shell prompt. Linux+ Objectives: 110.1 Perform security administration tasks Candidates should know how to review system configuration to ensure host security in accordance with local security policies. o Set or change user passwords and password aging information. o Set up limits on user logins, processes and memory usage. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the characteristics of a secure or strong password? Which chage option sets the minimum number of days a user must keep a password? What types of resources are affected by the ulimit utility? When would you need to configure the /etc/security/limits.conf file? What is the syntax of the /etc/security/limits.conf file? Video/Demo Time 12.2.1 User Security and Restriction 9:54 12.2.2 Configuring User Security and Restrictions 6:40 Total 16:34 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Time About 30 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 115 Section 12.3: Network Security Summary This section explores general procedures for increasing network security on a Linux system: Remove unneeded software Check for unneeded network services Locate open ports Check network connections Students will learn how to: Scan for open ports on Linux. Identify open network connections on Linux. Linux+ Objectives: 110.1 Perform security administration tasks Candidates should know how to review system configuration to ensure host security in accordance with local security policies. o Being able to use nmap and netstat to discover open ports on a system. Lecture Focus Questions: What is a socket? Which utility will scan for all listening and non-listening sockets? Which utility will identify open ports on the Linux system? Which commands should you use to disable unneeded daemons? Video/Demo Time 12.3.1 Network Security 7:10 12.3.2 Removing Unneeded Services and Scanning Ports 6:30 Total 13:40 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 116 Section 12.4: File Auditing Summary This section examines using file auditing to secure the computer by looking for files that pose a security risk. Details include: Types of files that file auditing identifies: o Files that have the SUID (Set User ID) permission. o Files that have the write and execute permissions for others. File auditing commands: o find / type f –perm o crontab Students will learn how to: Audit a system to identify files that are owned by root and have the SUID permission set. Linux+ Objectives: 110.1 Perform security administration tasks Candidates should know how to review system configuration to ensure host security in accordance with local security policies. o Audit a system to find files with the suid/sgid bit set. Lecture Focus Questions: How do files with the SUID bit pose a security risk? Which command should you use to audit for files with the SUID bit set? How can you schedule file auditing? Video/Demo Time 12.4.1 File Auditing 5:00 12.4.2 Auditing Files 3:07 Total 8:07 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Time About 10 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 117 Section 12.5: Login Blocking Summary This section provides information about blocking users from logging in while resolving serious issues. Concepts covered include: Login blocking is enabled using the Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) Steps to configure login blocking: o Force all user to log out of the system o Disable the ability to login to the system o Configure the PAM module to verify whether the file /etc/nologin exists Students will learn how to: Disable logins and optionally display a message if a user tries to login. Linux+ Objectives: 110.2 Setup host security Candidates should know how to set up a basic level of host security. o Awareness of shadow passwords and how they work. o Turn off network services not in use. o Understand the role of TCP wrappers. Lecture Focus Questions: What command displays all active users on the Linux system/? What utility should you use to remove active users? Which file configures login blocking? How can you display a message to users when logins are blocked? Which PAM module file configures login blocking? Video/Demo Time 12.5.1 Login Blocking 5:11 12.5.2 Disabling Login 3:08 Total 8:19 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 118 Time About 15 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 119 Section 12.6: Xinetd and Inetd Super Daemons Summary This section provides an overview of the Xinetd and Inetd super daemons. Concepts covered include: The role of Xinetd Files to configure the xinetd super daemon: o /etc/xinetd.conf o /etc/xinetd.d The role of TCP wrappers To use TCP wrapper with xinetd: o Install/Verify the TCP wrappers package is installed o Edit the daemon files in /etc/xinet.d o Restart xinetd o Modify tcpd control files o Confirm TCP wrapper configuration The role of inetd Configuration parameters in the /etc/inetd.conf configuration file: o Daemon o Socket o Protocol o Flag o User o Executable o Arguments Students will learn how to: Configure the superdaemon, xinetd, to manage network and Internet services. Configure access control to daemons using TCP wrappers. Linux+ Objectives: 110.2 Setup host security Candidates should know how to set up a basic level of host security. o Awareness of shadow passwords and how they work. o Turn off network services not in use. o Understand the role of TCP wrappers. Lecture Focus Questions: Why is xinetd called a super daemon? When should you use TCP wrappers? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 120 Which types of files are stored in the /etc/xinetd.d directory? Which file configures the xinetd daemon? When should you use the /etc/host.allow or /etc/host.deny files? Which utility confirms the TCP wrapper configuration? Why is inetd no longer a commonly-used super daemon? How do you configure the inetd daemon? What is the syntax of the /etc/inetd.conf configuration file? Video/Demo Time 12.6.1 Xinetd and Inetd Super Daemons 12:38 12.6.2 Configuring xinetd and TCP Wrappers 8:04 12.6.4 Inetd 6:57 Total 27:39 Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Time About 45 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 121 Section 12.7: OpenSSH Summary This section discusses configuring OpenSSH to encrypt network traffic over a subnet or Internet. Details include: Encryption types: o Symmetric o Asymmetric Standards for symmetric encryption: o Data Encryption Standard (DES) o Triple DES (3DES) o Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) o Blowfish Standards for asymmetric encryption: o Rivest, Shamir Adleman (RSA) o Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) o Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange The role of OpenSSH Types of SSH o SSH1 is an older, less secure version of SSH. o SSH2 is the current standard SSH implementation. Steps to establish a session using SSH Using OpenSSH configuration files to configure o SSH server o SSH clients o Firewall Configuration files that OpenSSH uses: o /etc/ssh/sshd_config o /etc/ssh/ssh_config o ~/.ssh/config Commands used in conjunction with SSH: o which o service sshd o ssh o scp o sftp o slogin Students will learn how to: Create an encrypted connection between two Linux systems. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 122 Linux+ Objectives: 110.3 Securing data with encryption The candidate should be able to use public key techniques to secure data and communication. o Perform basic OpenSSH 2 client configuration and usage. o Understand the role of OpenSSH 2 server host keys o Perform basic GnuPG configuration and usage. o Understand SSH port tunnels (including X11 tunnels). Lecture Focus Questions: What are the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption? When would you use the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange encryption standard? Which encryption standards are supported by SSH1 versus SSH2? Where does a client store public keys it has received from SSH servers? Which keys are sent to the client when establishing an SSH session? Which file should you edit to configure the SSH daemon on the server? Which file overrides the client's SSH configuration on a per-user basis? What ssh command would you use to log in to a server, execute a command, and return to the local system's shell prompt? Which utility secure copies files and encryption keys? Video/Demo Time 12.7.1 OpenSSH 12:08 12.7.2 OpenSSH Configuration 15:22 12.7.5 Configuring OpenSSH 9:38 Total 37:08 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Time About 55 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 123 Section 12.8: SSH Port Tunneling Summary This section provides an overview of using SSH port tunneling to encrypt data from nonsecure protocols before sending the data over a network. Details include: The role of Secure Shell (SSH) port tunneling Commonly-needed options in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file used for configuring an SSH server: o AllowTcpForwarding o ForwardX11 o ForwardX11Trusted o X11Forwarding Commands to create an SSH port tunnel: o ssh o ss –X Commands to send unencrypted X server traffic between a client and server: o xhost +servername o DISPLAY=hotst_name:0.0 o Export DISPLAY Students will learn how to: Configure SSH port tunneling to send unencrypted network traffic through an encrypted SSH connection. Linux+ Objectives: 110.3 Securing data with encryption The candidate should be able to use public key techniques to secure data and communication. o Understand SSH port tunnels (including X11 tunnels). Lecture Focus Questions: What is the benefit to tunneling traffic through an SSH connection? Which file on the server configures SSH port tunneling? Which ssh command should you use to tunnel X server traffic? How can you send unencrypted X server traffic between a client and server? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 124 Video/Demo Time 12.8.1 SSH Port Tunneling 11:46 12.8.2 Configuring SSH Port Tunneling 2:30 Total 14:16 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Time About 20 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 125 Section 12.9: Public Key Authentication Summary In this section students will learn about using a public key to authenticate to a computer. Concepts covered include: The public key authentication process Commands and files for public key management: o /etc/ssh/sshd_config o ssh-keygen o scp o ssh o cat o ssh-agent bash o ssh-add Students will learn how to: Configure public key authentication between two systems. Linux+ Objectives: 110.3 Securing data with encryption The candidate should be able to use public key techniques to secure data and communication. o Perform basic OpenSSH 2 client configuration and usage. o Understand the role of OpenSSH 2 server host keys o Understand SSH port tunnels (including X11 tunnels). Lecture Focus Questions: What is an MD5 checksum, and how is it used in public key authentication? Which file configures the server to accept public key authentication? Which keys are generated by the ssh-keygen command when no options are specified? Which utility should you use to copy encryption keys between Linux systems? When is the ~/authorized_keys file used? How can you configure a client to automatically provide the private key passphrase when establishing an SSH session? ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 126 Video/Demo Time 12.9.1 Public Key Authentication 11:47 12.9.2 Configuring Public Key Authentication 5:49 Total 17:36 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Time About 25 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 127 Section 12.10: Gnu Privacy Guard (GnuPG) Summary This section examines information about using the Gnu Privacy Guard (GPG) encryption tool. Details include: Commands and files to be aware of when using GPG: o which gpg o gpg Students will learn how to: Use gpg to create a key pair and use the public key to encrypt and decrypt a file. Linux+ Objectives: 110.3 Securing data with encryption The candidate should be able to use public key techniques to secure data and communication. o Perform basic GnuPG configuration and usage. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the benefit of using Gnu Privacy Guard (GPG)? What command should you use to determine if GPG is installed on the Linux system? What gpg option will digitally sign a file? How can you display all the GPG keys on the key ring? Video/Demo Time 12.10.1 GnuPG 7:22 12.10.2 Configuring GnuPG 4:48 Total 12:10 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Time About 25 minutes ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 128 Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the following exams and to register for the exams. LX0-101 LX0-102 Students will also have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exams. For example, all questions that apply to Objective 101: System Architecture are grouped together and presented in practice exam Domain 1: System Architecture, All Questions. Students will typically take about 60-90 minutes to complete each of the following practice exams. The domains included in the LX0-101exam are: Domain 1: System Architecture, All Questions (52 questions) Domain 2: Linux Installation and Package Management, All Questions (75 questions) Domain 3: GNU and Unix Commands, All Questions (129 questions) Domain 4: Devices, Linux Filesystems, Filesystem Hierarchy Standard, All Questions (89 questions) The domains included in the LX0-102 exam are: Domain 5: Shells, Scripting and Data Management, All Questions (36 questions) Domain 6: User Interfaces and Desktops, All Questions (28 questions) Domain 7: Administrative Tasks, All Questions (52 questions) Domain 8: Essential System Services, All Questions (62 questions) Domain 9: Networking Fundamentals, All Questions (83 questions) Domain 10: Security, All Questions (60 questions) The LX0-101 Certification Practice Exam and LX0-102 Certification Practice Exam each consist of 60 questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time a Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. Each Certification Practice Exam has a time limit of 90 minutes -- just like the real certification exam. A passing score of 95% should verify that the student has mastered the concepts and is ready to take the real certification exams. ©2010 TestOut Corporation (Rev 1/11) LabSim for CompTIA’s Linux+ Powered by LPI 129