The Elbow and Forearm - Special Tests Notes Special tests
advertisement

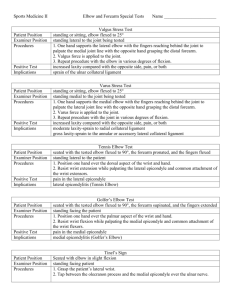
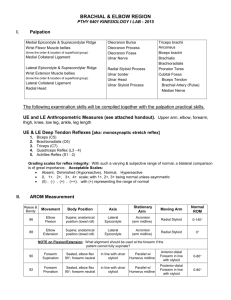
The Elbow and Forearm - Special Tests Special tests Categories Ligamentous Provocation Neurological Ligamentous stress tests Valgus stress test Varus stress test Valgus stress test Patient: sitting or standing, forearm , elbow flexed at 20-30˚ Examiner: lateral to patient One hand supports lateral elbow w/fingers passing behind joint to medial joint line One hand grasps distal forearm Action: valgus force applied to joint Perform at various degrees of flexion (30o, 60o) Positive: ↑ laxity, , or both Pathology: Sprain of (anterior portion) Laxity beyond 60˚, may involve posterior fibers Varus stress test Patient: sitting or standing, forearm supinated, elbow flexed at ˚ Examiner: medial to joint line being tested One hand supports medial elbow w/fingers passing behind joint to palpate lateral joint line One hand grasping distal forearm Action: varus force applied to joint Perform at various degrees of flexion (30o, 60o) Positive: ↑ laxity, pain, or both Pathology: Sprain of radial collateral ligament Laxity may also indicate damage to ligament or other lateral ligaments Moving valgus Patient: sitting, shoulder to 90o, elbow maximally flexed Examiner: lateral to patient One hand supports distal humerus One hand grasps of distal forearm Notes Action: valgus force applied to joint while and humerus is externally rotated Return elbow to full flexion Positive: reproduction of pain between o of flexion Pathology: Sprain of ulnar collateral ligament (anterior portion) Shoulder pathology may also elicit pain Milking maneuver Action: Patient crosses arms and pulls involved arm’s , creating a valgus force on the elbow Positive: ↑ laxity, pain, or both Pathology: Sprain of ulnar collateral ligament (anterior portion) Provocation tests Cozan’s Test (active) Mill’s Test (passive) Medial Epicondylitis Test (active) Medial Epicondylitis Test (passive) Cozan’s test (active) Patient: elbow @ 90°, forearm fingers flexed Examiner: lateral or anterior to patient One hand proximal forearm while palpating lateral epicondyle One hand on dorsal aspect of hand (metacarpals) Action: patient actively wrist Positive: reproduction of Sx & Sy at lateral epicondyle Pathology: (“Tennis elbow”) Mill’s test (passive) Patient: elbow @ 90°, forearm pronated, fingers flexed Examiner: lateral or anterior to patient One hand proximal forearm while palpating lateral epicondyle One hand one dorsal aspect of hand (metacarpals) Action: passive forced wrist & finger and elbow Positive: reproduction of Sx & Sy at lateral epicondyle Pathology: lateral epicondylitis (“ ”) , The Elbow and Forearm - Special Tests Medial epicondyle test (active) Patient: elbow @ 90°, forearm fingers flexed Examiner: lateral or anterior to patient One hand proximal forearm while palpating medial epicondyle One hand one palmar aspect of hand (metacarpals) Action: patient actively and wrist Positive: reproduction of Sx & Sy at , Pathology: medial epicondylitis (“Thrower’s or Golfer’s elbow”) Medial epicondyle test (passive) Patient: elbow @ 90°, forearm fingers flexed Examiner: lateral or anterior to patient One hand proximal forearm while palpating medial epicondyle One hand one palmar aspect of hand (metacarpals) Action: passive forced wrist , finger and elbow Positive: reproduction of Sx & Sy at medial epicondyle Pathology: (“Thrower’s or Golfer’s elbow”) Neurological tests Stretch reflexes Tinel’s sign Stretch reflexes Strike the tendon with a reflex hammer Use your thumb to protect the tendon and focalize the force of the hammer Observe for the stretch reflex Repeat 3-6 times for consistency 1. reflex 2. reflex 3. reflex , Notes Tinel’s sign Patient: relaxed and comfortable w/forearm supination Examiner: lateral or anterior to patient One hand supporting forearm, wrist and hand One hand free to administer test Action: firm tapping of cubital tunnel Positive: reproduction of Sx & Sy to nerve sensory distribution Pathology: