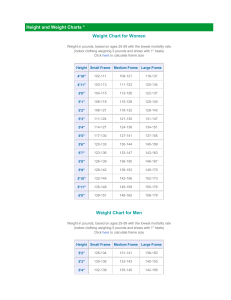
Elbow Anatomy
Medial
Epicondyle
Lateral Epicondyle
Trochlea and Capitulum
Olecranon Process
Ulna and Radius
Radial Head
Interosseus Membrane
http://www.courses.vcu.edu/DANC291003/elbow_jt.jpg - Pic of Bony Anatomy
© 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Elbow Anatomy
http://images.main.uab.edu/healthsys/ei_0153.jpg
Elbow Anatomy (2)
Humeroulnar joint
______________
Trochlea of humerus
_______________
Flexion (0 – 150)
Extension (0)-some hyperextension(-5 to -15)
Ligaments:
_________________________
_________________________
Elbow Anatomy (3)
Radioulnar
Not
joint
part of elbow but associated with
__________________________
Supported by the annular ligament which
binds the head of the radius to the radial
notch of the ulna forming the joint
___________________________
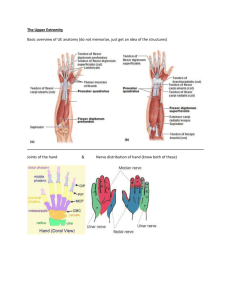
Muscular Anatomy
______________________
Brachioradialis
(flexion with arm neutral)
Brachialis (flexion w/ pronation)
______________________
Pronator Group (pronation)
______________________
http://images.main.uab.edu/healthsys/ei
_0153.jpg - biceps attachment
Bursa, Blood and Nerve
Supply
Bursa-
_____________________
Blood supply
Brachial
artery
___________
___________
Nerve
supply
Brachial
plexus extends into the radial and
ulna nerve***
Prevention of Injuries
General
muscular condition
Restrict pitching/ teach proper form
Make sure equipment is proper (ie:
racquet)- grip size, racquet weight
Teach shoulder roll method of fallingexample volleyball players rolling after a
dig
Contusions
MOI: Direct contact
HOPS
__________________________________
Limited range of motion
TX
Rule out fracture first
Ice, wrap and pad area
Avoid aggressive stretching and strengthening
Watch for ectopic bone formation
________________________________
Olecranon Bursitis
Olecranon
bursa is largest in elbow
MOI: fall on bent arm, leaning on elbow
for long periods, infection
HOPS
____________________________
Tx:
ice, compression, pad area
If associated with fever: refer
_____________________________
http://www.aafp.org/afp/971101
ap/salzfig3.jpg
http://www.physsportsmed.
com/issues/2000/03_00/mcf
arland4.gif
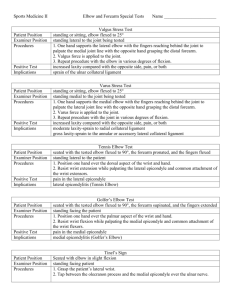
Elbow Sprains (1 – UCL)
MOI: valgus force, repetitive stress
HOPS:
Pain over medial joint especially in cocking phase
or acceleration phase of throwing
Point tenderness over joint line
____________________________________
____________________________
Tx: rest, general strengthening of flexors/
pronators; _________________________
________________________________
Elbow Dislocations
MOI: ____________________________
______________________________, falling
on outstretched hand
HOPS
Obvious deformity
Snapping or cracking sensation
Severe pain
Forearm in flexion and appears shortened
Tx:
immobilize and refer MED EMERGENCY
Check neurovascular status
-http://www.worldortho.com/database/introtrauma/pics/img0123.jpg
http://www.angelfire.com/sc2/seahawksportsmed/injpi
x.html
Medial Epicondylitis
______________________________
MOI: repetitive tension or valgus forces on
the arm
HOPS
Swelling, ecchymosis over medial epicondyle
Pain aggravated by pronation and resisted flexion
of wrist
_________________________________
Tx: RICE, Strengthening/Stretching, look at
technique
http://www.esportmed.com/smrn/figures/Golfer
ElbowInjury.gif
Lateral Epicondylitis
__________________
Most
common overuse injury in the
adult elbow
MOI: _______________________
______________________
Precursor: too large tennis racquet,
gripping racket too tightly, excessive
string tension, faulty mechanics
Lateral Epicondylitis (2)
HOPS
Pain over lateral epicondyle
Pain with resisted wrist extension
+ tennis elbow test
Tx
RICE
__________________________________
_________________________
Counter force brace
Impingement of Ulnar nerve
Ulnar nerve passes behind humerus in ulnar
groove
_______________
HOPS
_________________
Can be caused from a medial elbow injury
“crazy bone” or “funny bone”
Tingling and numbness in ring and little finger
__________________
Refer if chronic
Strength Testing
Elbow
flexion
Elbow extension
Wrist flexion and extension
Pronation
Supination
Stress Tests
(UCL)/Varus (RCL) stress test –
Positive Sign is laxity
Tennis Elbow test-(Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Positive Sign is increased pain
Tinel’s sign (Ulnar nerve) – Numbness,
Tinkling into Ulnar nerve region.
Valgus