complete sentences
advertisement

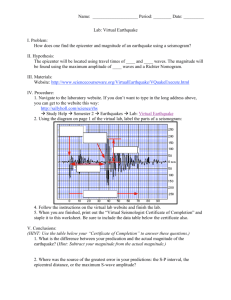
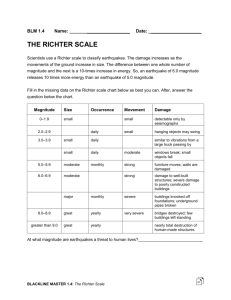
10.2 RSG Locating and Measuring Earthquakes pgs. 217 – 221 Name Date Score Before you read define the Key terms from the section NOT from glossary: 1. Seismograph – 2. Seismogram – 3. Magnitude – After you read answer these key concept questions in COMPLETE SENTENCES: 4. – 5. Create a Venn diagram that explains the difference between a seismograph and a seismogram using the following phrases: the instrument, the record sheet, used to detect earthquakes, indicates arrival times of each type of wave, consist of a weight, pen and rotating drum. 6. – 7. If the difference in the time of arrival of P and S waves increases, the distance to the epicenter of the earthquake is (increasing / decreasing). Explain why? 8. Why is it essential to have data from more than 1 seismograph station to locate an earthquakes epicenter? 9. – 10. Use the graph on page 218 to answer the following. (A) If the difference between P and S wave arrival times is 3 minutes and 45 seconds, what is the distance to the Collinsville station to the epicenter. (B) A station in Chapel Hill, North Carolina records data from the same earthquake. Chapel hill is 3000 km from the epicenter. What is the difference in P and S wave arrival times for this station? A. ________________________ B._________________________ 11. Explain what is meant by magnitude of an earthquake. 12. List and describe two scales used to measure an earthquakes magnitude. (Bonus 2pts) Suppose an earthquake has a Richter magnitude of 3 and a second earthquake a Richter magnitude of 7. How many times more powerful is the magnitude 7 than the magnitude 3. Show all math work!!!