DNA Study Guide CP2015
advertisement

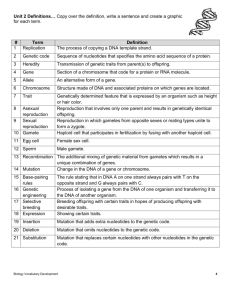
Name ______________________________ DNA Test Study Guide Complete the following multiple-choice questions. As we go over the correct responses, make notes for yourself about the question below it. ______1. The cells that make up the skin of an individual have some functions different from the cells that make up the liver because a. all cells have a common ancestor. b. different cells have different genetic material. c. environment and past history have no influence on cell function. d. different parts of genetic instructions are used in different types of cells. Notes: ______2. Notes: ______3. Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different chromosomes. b. type of genes present in the fruit fly is dependent upon environmental temperature. c. environment affects the expression of the genes for this trait. d. higher temperature produces a gene mutation. The production of certain human hormones by genetically engineered bacteria results from a. inserting a specific group of amino acids into the bacteria. b. combining a portion of the human DNA with the bacterial DNA and inserting this into bacteria. c. crossing two different species of bacteria. d. deleting a specific amino acid from human DNA and inserting it into bacterial DNA. Notes: ______4. Notes: ______5. Which phrase does not describe cells cloned from a carrot? a. They are genetically identical. c. They have the same DNA codes. b. They are produced sexually. d. They have identical chromosomes. Genes involved in the production of abnormal red blood cells have an abnormal sequence of a. ATP molecules. c. sugars. b. amino acids. d. bases. Notes: ______6. Klinefelter’s syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome in the body cells of humans. This extra chromosome occurs in the gamete as a result of a. an error in the process of cloning. c. a gene mutation. b. an error in meiotic cell division. d. replication of a single chromosome during mitosis. Notes: Name the individual subunits on the left and the name of the structure they make on the right. Answer the following. 1. Transcribe the provided DNA strand, and then translate it into a protein using your amino acid chart from your notes. DNA strand: TACCCGTTACCTGGCAACGATCACATC MRNA: Protein: Show the following mutations of the above DNA strand and discuss how they would or would not affect the amino acids found within the protein: A. Point (Substitution): Effect on protein: B. Silent (Point) Effect on protein: C. Nonsense (Point) Effect on protein: D. Frame shift (insertion) Effect on protein: E. Frame shift (deletion) Effect on protein: 2. Arrange the following structures from largest to smallest. Explain how they are related. A chromosome A nucleus A gene Largest ____________________________ ____________________________ Smallest 3. ____________________________ Fill in the blank to show the proper flow of information from DNA to expressing a gene (showing the phenotype of the gene) DNA changes to ______________, the codons on mRNA are read to figure out the chain of ____________ ___________, amino acids are then linked to form a ___________, this protein is made from a ____________ or segment of DNA. 4. Complete the chart to show the building blocks and the product they build. Monomers (separate single units) monosaccharides Polymer (one large unit) phospholipid protein nucleotides 5. What is a mutation? 6. What is the difference between a gene mutation and a chromosomal mutation? 7. Match the chromosomal mutation to its proper definition, then draw an example of the mutation (using the original chromosome as ABCDEF which are the genes on the chromosome) under the title of each type of mutation. a. 1. This type of chromosomal mutation occurs when there is an unequal exchange between homologous sets and some genes are doubled. b. Inversion _____ 2. This type of chromosomal mutation occurs when non-homologous sets exchange pieces. EX: genes from set 17 are on set one. c. Duplication: _____ 3. This type of chromosomal mutation occurs when a piece of the chromosome breaks off and is missing. d. Nondisjunction: ____ 4. This type of chromosomal mutation occurs when a piece breaks off and reinserts backwards so that the genes are not out of order. e. Translocation: _____ 5. This chromosomal mutation occurs when chromosomes fail to separate equally during meiosis and some gametes (sex cells) get too many chromosomes. (Trisomy like Down Syndrome) 8. Deletion _______ Describe DNA replication. What is replication (purpose): What main molecule is involved: Where does it take place in eukaryotes: Quick summary of the steps involved: How is the information in DNA conserved (kept the same): 9. Describe Transcription. What is transcription (purpose): What main molecules are involved (what do you start with and what do you end with): Where does it take place in eukaryotes: Where does it take place in prokaryotes: Quick summary of the steps? 10. Describe translation. What is translation/purpose (aka protein synthesis): What main molecules are involved: Where does it take place in eukaryotes: Where does it take place in prokaryotes: Quick summary of the steps: 11. How are transcription and translation similar in all living things? 12. Trace the path of a membrane or secretory protein beginning with the instructions in the nucleus to the final destination of the product at the cell membrane (trace the flow of the information from beginning to end)? Nucleus - ____________ - ____________ - ___________ - __________ - Cell Membrane 13. What is cloning? How can something be cloned? How might cloning be useful? 14. Use the picture to answer the following questions 15. Circle the band(s) on the gel electrophoresis that would be considered the smallest bands based on their travel time. 16. Which 2 organisms would be most closely related? 17. Describe how scientists can genetically engineer something. What are some benefits of genetic engineering/gene splicing? What are some negative aspects of genetic engineering? 18. What is a GMO? What are the pros and cons to creating GMO’s? 19. What is gene therapy? How does it help someone to survive a genetic disorder?