LW106 Business Law Assignment Bob v FreshCo 2010
advertisement

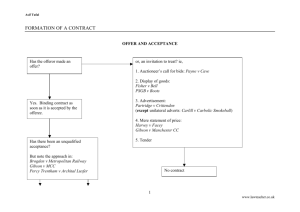
LW106 Business Law Assignment Bob v FreshCo 2010 Requirements for a valid acceptance Clear and unambiguous agreement to offer and acceptance can only be agreed by the offeree only. Acceptance may be oral, written or implied from conduct. Acceptance must be clear and unqualified and must be exactly match the offer. Neale v Merrett (1930). The defendant made an offer to sell land to the plaintiff for £280. The plaintiff replied accepting the offer, enclosing £80 and promising to pay the balance in four monthly instalments. It was held that the proposal for deferred payment was a variation of the terms implicit in the offer. Since the normal term of a contract for the sale of land are that the entire price is payable as a single sum at completion, it was held that there had been no acceptance. The general rule in communication of acceptance is; Acceptance must be communicated to and received by the offeror, or by someone with their authority, to the offeror. Kennedy v London Express Newspapers (1931) the publishers of an English newspaper offered a free insurance scheme to its registered readers. The plaintiff’s wife had registered with the newsagents and on her being killed accidentally by a bus, her husband claimed the sum payable under the insurance scheme. It was held that the offer of the free insurance scheme represented a unilateral offer made to the world at large. Registration by the plaintiff’s wife brought a valid contract into existence, and the publishers were legally bound by it. In this case Bob v FreshCo (2010) the offer was made to the world at large but was meant as “light-hearted fun”. Bob wanted to “purchase” Jenny and made the offer to FreshCo but they communicated that they had no intention of “selling” Jenny. A reasonable man would have understood that Jenny could not be “purchased”. The requirements for valid acceptance had not been met therefore a contract did not exist. Even if Bob had made a valid offer there was one requirement that he had not fulfilled, he was not a FreshCoPoints cardholder therefore he was eligible to apply for the offer. There are certain elements of the offer and acceptance which may be valid but, in this case, are not fulfilled and therefore a contract would not exist.