Evaluating and Serving Students with Medical Issues
advertisement

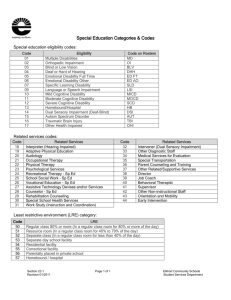
1 Revised - July 2015 Evaluating and Serving Students with Medical Needs and Physical Impairments Under Section 504 In its simplest language, Section 504 is an anti-discrimination policy. Originally designed for people in the workplace to avoid discrimination based on disability, Section 504 also has implications for public schools. To be eligible under Section 504, a student must be both “qualified” (the student is within the age range in which services are provided to disabled and nondisabled students under state law), and “handicapped.” Pursuant to 34 CFR §104.3(j)(l), “Handicapped persons means any person who; (i) Has a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life activities **(ii) Has a record of such an impairment, or; **(iii) Is regarded as having such an impairment.” **(ii) and (iii)of the above determination are not used in the educational setting. The last two prongs of that definition are meant to be used in situations where individuals either never were or are not currently handicapped, but are treated as if they were. These are most often used in the workplace. It is exceedingly rare for them to be used in elementary or secondary education, since the student is not, in fact, mentally or physically handicapped, and therefore has no need for special education or related services. They CANNOT be the basis upon which the requirement of FAPE is triggered. While Lincoln County Schools has a clearly defined Section 504 disability determination process, making determinations regarding potential accommodations with respect to medical needs is more complicated. There are a number of variables which must be taken into consideration, and each student must be looked at on an individual basis. Depending on the severity of the impairment, that process can be very simple or quite complex. The Office of Civil Rights (hereby referred to as OCR), sees safety of the school environment as part of the school’s duty under Section 504. The OCR indicates that school districts take steps necessary to ensure that the school environment for students with disabilities is as safe as the environment for students without disabilities. “As the vast majority of district students without a disability do not face a significant possibility of experiencing serious and/or life threatening reactions to their environment while they attend district schools, Section 504 requires that the district provide the disabled student with an environment in which he also does not face such a significant possibility.” Saluda (SC) School District one, 47 IDELR 22 (OCR 2006) © 2015 –Mary Moren 2 That said, it is unrealistic (and not legally required) to expect a school to be able to eliminate “ALL” risk; however, the school should be diligent in its efforts to eliminate any significant risk. An important distinction when determining appropriate services is, “parent-desired” vs. “doctorrequired.” Evaluation data is key to resolving these types of issues. A parent demand for an accommodation or service does not create a school duty to provide the same under Section 504. Again, the duty of the school is to provide services that are necessary for the disabled student to have equal access to FAPE (Free and Appropriate Public Education) as their non-disabled peers. This should also include equal access or consideration related to issues of safety. Health Care Plans: A health care plan generally focuses solely on addressing a student’s medical needs. It is typically not developed in accordance with formal procedures, such as those required for the development of a Section 504 plan. The OCR has concluded that a school system may not broadly exclude students with health plans from being considered for a Section 504 evaluation. In determining whether a student’s medical condition is substantially limiting, a school district must decide whether the condition would substantially limit a major life activity if the student did not have a health care plan. It is safe to assume that a health care plan alone may not be enough. In some cases it will be necessary to consider a Section 504 evaluation, even if a health care plan exists. This will be based on the individual student and his/her needs. More information on Health Care Plans and the school systems process relative to HCP’s can be found in the pages following this document. Concussions: Post-concussion Syndrome: If a child is still symptomatic at the 3-4 week mark, evaluate for Section 504. If injury is much more severe, evaluate sooner. Food Allergies: We must be extremely diligent when making Section 504 decisions regarding students with food allergies. While many students with food allergies will have Health Care Plans, often that is not sufficient, especially if the particular student’s allergies could present a life threatening situation. When the Office of Civil Rights receives a complaint, they are typically looking for procedural compliance, for example, procedures by which a school system identifies and evaluates students with disabilities and the procedural safeguards which are provided to those students. The OCR will also examine incidents in which students with disabilities are subjected to treatment that is different from the treatment of their non-disabled peers. There is an exception to this generality which would be considered an “extraordinary circumstance.” The risk of serious illness or death of a student from a decision on Section 504 eligibility and/or accommodation plan would constitute an “extraordinary circumstance.” If a student has a food allergy that has the potential to be life threatening, it would be judicious to consider a Section 504 referral. Even if a school is “informally addressing” issues surrounding a food allergy, it is likely that will not be enough. Informality, especially when needs are complex will not get things done consistently. Conventional wisdom and “Child Find” obligations would suggest that serious consideration regarding 504 evaluation be given to students with significant food allergies. © 2015 –Mary Moren 3 Homebound Instruction: If a student is being considered for Homebound Instruction, and he/she has not already been identified under IDEA or Section 504, the homebound request should prompt a Section 504 evaluation. The Office of Civil Rights has determined that because “Homebound Instruction” would constitute a “significant change of placement” for a student with a physical or mental impairment, a Section 504 evaluation would be required prior to that placement. In essence, the belief is that the school had/has knowledge of the impairment and the resulting need for services, so they had/have a duty to evaluate. As a general rule, educating a student at home is a disfavored placement under federal disability law, as education occurs in a setting that generally does not allow access to non-disabled peers. The 9th Circuit summarized the rule by saying, “hospitalized and homebound care should be considered to be among the least advantageous educational arrangements and are to be utilized only when a more normalized process of education is unsuitable for the student who has severe health restrictions.” Additionally, “homebound instruction is never intended to be an open-ended placement on the least restrictive environment continuum: to the contrary, on the least restrictive environment continuum, homebound is more restrictive than instruction received in a detention center or hospital.” In North Carolina, the state homebound definition is: “if a student is confined at home or in a hospital, is unable to attend school, and is receiving homebound instruction from his/her home school/LEA, he/she is to be considered Hospital/Homebound.” Further the state eligibility standard indicates, “if it is determined that the homebound instruction is the least restrictive alternative environment for the student, the student’s IEP (or 504) team shall meet to determine the nature of the homebound educational services to be provided. In addition, the appropriateness of the homebound instruction shall be evaluated monthly by the designee of the student’s IEP (or 504) team.” NC Code Article 9 §115C-107.7 In OCR complaints regarding homebound instruction, the hearing officer routinely takes into consideration the extent to which the student truly is “homebound.” If homebound services are requested for a student, there should be a medical necessity that the child be confined to the home. A student who attends social functions, and engages in other activities outside the home makes qualification for homebound service questionable. Questions concerning the Hospital/Homebound process in Lincoln County should be directed to: DeAnna Finger Lincoln County Schools 353 N. Generals Blvd. Lincolnton, NC 28092 Phone: (704) 732-2261 Email: dfinger3@lincoln.k12.nc.us © 2015 –Mary Moren