Quarter 2 Review - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement

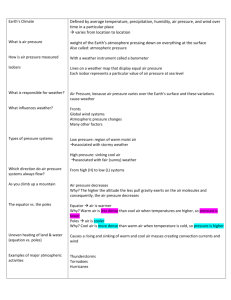
Meteorology-REVIEW QUARTER 2 TEST FOCUS STUDIES ON AIR MASSES, FRONTS, LOW and HIGH pressure Systems Atmosphere- layers of gasses surrounding earth Layers of atmosphere Satellite Comets Supersonic planes Weather Air pressure- as you go up the air pressure decreases Greenhouse Gases: Cause Global warming, melt icecaps. Methane, CO2, Water Vapor Earth heated unevenly- hot land and cool land creates warm air and cool air- creates air masses **Air masses- pushed by prevailing winds and upper air currents (Jet streams). Ex- mT, mP, cP, cT Temperature and Humidity used to describe characteristics: humid form over water (m: maritime), dry form over land (c: continenetal), warm form in lower latitudes (T: tropical) , cool form over higher latitudes ( P: polar) Front- leading edge of air masses- changes in weather, moves west to east/northeast, moved by prevalling winds, upper air currents (Jet streams). FRONTS ALWAYS BRING RAIN Cold front-cold air mass pushes (like a bully) into and under warm air mass causes storms. Brief, heavy down pours. Following a cold front will be usually be a cP airmass (cooler, dry, clear, stable weather Warm front- warm air mass pushes over cool air mass. Light precipitation, warmer temps. After front passes, usually mT air. Warmer, unstable High pressure system- H- center of air masses, fair, sunny “Happy” weather . HOCA: High, outward, clockwise, anticyclone Low pressure system- L- edges of air masses, rainy, not so nice “ Lowsy” weather LICCC: Low, inward, counter-clockwise,cyclone Weather- conditions at a given location for a short period of time Climate- long term average weather conditions Relative Humidity: percentage. Comparison of amount of water vapor in the air compared with how much water vapor the air can hold. RH rises to 100% (saturated) before precipitation Wind- caused by horizontal air movement. Uneven heating of Earth’s surface Specificic Heat- amount of energy needed to raise one gram of a substance one degree. Water has high specific heat so it heats/cools more slowly. Sea Breeze and Land Breeze Factors that determine climate- latitude, altitude, ocean currents, mountains, volcanic eruptions, green house gasses. Temperature Range increases as you increase in latitude!!! Storms: Falling air pressure (a storm is coming!... remember low means “Lowsy” weather) thunder storms- stay indoors. Usually only a few hours long. Lightning hazard. hurricane- evacuate or stay @ high level indoors. Form in tropics (Atlantic by equater, Gulf of Mexico). Must form over warm water. Fueled by ocean water!!!! VERY LARGE STORM!!! tornado- go underground. Cannot predict accurately!!! Stay away from windows. Very small in diameter. Extremely fast wind speeds… up to 300mph cyclones. Created by extreme differences in pressure from cP and mT airmasses when they meet blizzard- stay indoors. Lot’s of Snow!!!! Usually lasts less than 2 days Preparation: have flashlights, batteries, non-perishable food, first aid kit