Year 1 skills coverage - Thorpedene Primary School
advertisement

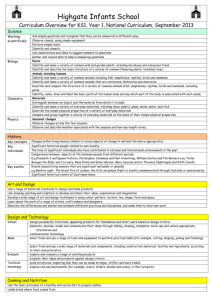
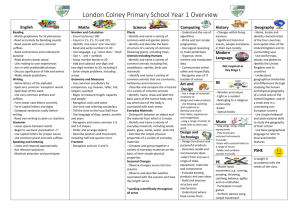
Year Group Skills Ladders – Foundation Subjects Year One Art DT History Drawing To represent objects To draw an enclosed space Painting Mix colours for a reason/that are appropriate for a purpose Sculpture Explore modelling materials to develop fine motor skills Analysis Make comments about their own work, likes and dislikes. New Curric. Requirements Use a range of materials Use drawing, painting and sculpture Develop techniques of colour, pattern, texture, line, shape, form and space Learn about a range of Artists, crafts persons and designers. Design Make Evaluate Technical Knowledge Design purposeful, Use a range of tools and Evaluate existing products and Food: Use measuring When approaching the functional and appealing materials to complete own ideas spoons and bowls investigate and disassemble products. Generate, model practical tasks. Understand where food comes appropriately. part of design please try to and communicate ideas Build and improve structure from. To see the changes in identify and use real life 3d construction and and mechanisms Food: Have an awareness of properties of food examples which can be deconstruction: Use Cutting and joining hygiene (freezing). broken down with the construction kits to build materials: Children need to To classify foods (meat,veg) group. shapes up in stages in be able to: Cut, join, score To discuss full and empty. The NC requires every year order to form a solid shape. and hole punch. Design and evaluate group to look at real existing Lego, Duplo, Clixi Make things by selecting Describe and draw what you products. Investigate and appropriate materials. plan to do. Your topic/subject of study disassemble: Identify materials. What do you like and dislike? should steer you towards To recognise the Mechanism and control: To professional makers, characteristics of products make a simple electrical designers and artists of and to gather ideas from circuit. products. experiences. Skills to cover New curriculum requirements Topics Suggestions Use everyday terms about the passing of time (e.g. yesterday, Changes linked in living memory. Linked to aspects of national Bonfire night today, tomorrow, past, present). life where appropriate. Events of local Place a few events or objects in chronological order – e.g. Lives of significant figures, including those from different importance sequencing photographs and artefacts from their own life. periods. Recognise the distinction between past and present in their Significant local people. own and other’ lives. Know and recount episodes from stories about the past. Use stories to distinguish fact and fiction. Geography Find answers to simple questions about the past from sources of information e.g. artefacts. Local Knowledge Place Knowledge Progression Use globes to Progression Through discussion Name and locate UK Understand use geographical locate four Use world and geographical vocabulary to countries and Europe maps to similarities and describe local and capital cities of locate UK Use differences familiar features (eg UK. UK map to through visit to the beach, Use atlases and locate countries studying the park, Broadway) globes and capital human and Describe where cities of UK physical they are, using Name UK geography of a everyday terms and countries and small area of follow capital cities the United directions.Introduce and record on a Kingdom, and of N.S.E.W blank map a small area in a Draw a simple map contrasting nonEuropean country Find information from a map and be aware of compass directions. Physical Geography Progression Keep a weather Identify chart for a time seasonal and during each daily weather season to patterns in the compare later in United the year. Kingdom and Look at weather the location of charts for rest of hot and cold UK discuss how areas of the it changes from world in north to south relation to the Identify North Equator and and South poles the North and and equator and South Poles how Use basic temperature geographical changes from vocabulary to equator to the refer to: poles. Hot and key physical cold regions/ features, countries of the including: world. beach, cliff, Use coast, forest, geographical hill, mountain, vocabulary sea, ocean, relevant to local river, soil, area valley, vegetation, season and weather key human features, including: city, town, Skills & Fieldwork Progression Use globes and identify the maps to identify United places studied Kingdom and Use simple its compass countries, as directions and well as the simple countries, directional continents and language to oceans studied move around the at this key school stage environment. Use simple Begin to compass recognize the directions location of (North, South, familiar places. East and West) Draw simple and locational local and environmental directional features language [for observed. example, near Use simple and far; left measurements and right], to With help ask describe the some simple location of questions. features and Make simple routes on a observations map indoors and outdoors. Use simple Find answers to fieldwork and simple questions observational about places skills to study using resources the geography provided. of their Draw simple school and its maps adding grounds and pictorial features the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key PSHE MFL Skills to cover New curriculum requirements Toipc Ideas Take and share responsibility, for example, for their own Approximately 45 minutes per week. People who keep us behaviour. Modelling, circle time and reflection. safe. Recognise why we have rules and expectations. Children need to discuss situations to develop language to Recognise what they like and dislike, what is fair and unfair. communicate how they feel. Begin to make simple choices that improve their health and Actions and responses need to be discussed too. well-being. Somebody hurts us we… Begin to maintain personal hygiene. Before we eat we… Recognise how to keep themselves safe in school. Role-play and stories are another effective way of discussing Develop positive relationships through work and play. challenging situations. Listen to other people, and play and work co-operatively. To read To write To speak To understand the culture of the fluently imaginatively confidently countries of lang. spoken Read out loud everyday words and To write of copy everyday words Understand spoken phrases Identify countries which speak the phrases (greetings) (greetings) (greetings, classroom instructions). language. Read and understand short written Label item Be able to ask for a word to be Show an awareness of the customs RE (See Medium Term plan for ideas/details) phrases (greetings) repeated. Read out loud familiar words and phrases (greetings, colours, family members, classroom objects) Special Times/ Belonging Christmas Understand what it Understand how and means to belong. why people -Belonging to a family celebrate. and groups in and -How and why do we outside school celebrate? What do Understand why people wear, eat? religion is important -Focus on a religious for others. festival and explore -Welcoming the story linked to ceremonies, for that festival. example: Celebrating Christmas: focus on gifts and giving. Correct pronunciation. Worship Learn about some of the features of worship in Christianity and another religion -Explore why and how places of worship are special. - Make links with their own experiences of worship in school. - Reflect on and talk about places that are special for them. Who is special? Identify people who are special and explain why -Learn about people who lead religious communities and what they do. -Learn that such people often wear special clothes and that these may have special meanings. of countries that speak the language. (songs and festivals) Special Books Identify the significance of special texts both to themselves and others -Identify the importance of the Bible for Christians and other sacred texts in the religions studied. -Make links between religious language and stories and the beliefs which lie behind them. -Reflect on what is of value in their own lives Who cares for the World? Identify people who are special and explain why -Learn about people who lead religious communities and what they do. -Learn that such people often wear special clothes and that these may have special meanings. Year Group Skills Ladders – SCIENCE Science Topics – statutory units to be covered in each year group During years 1 and 2, pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme of study content: asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying using their observations and ideas to suggest answers to questions gathering and recording data to help in answering questions. Year 1 Units to be covered in school year Everyday Materials Plants Animals identify and name a variety of common wild and garden plants, including deciduous and evergreen trees identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of common flowering plants, including trees. identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals identify and name a variety of common animals that are carnivores, herbivores and omnivores describe and compare the structure of a variety of common animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, including pets) identify, name, draw and label the basic parts of the human body and say which part of the body is associated with each sense. distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, metal, water, and rock describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties. Seasonal Changes observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies.