Long Term Plan 2014-2015 page 1 Y4
advertisement

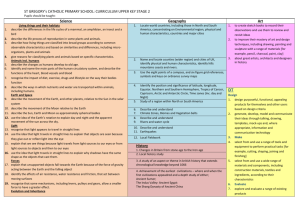
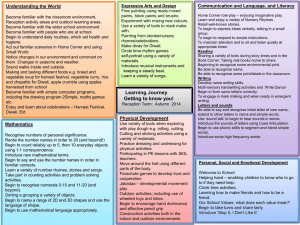
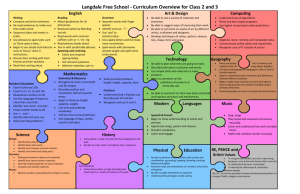
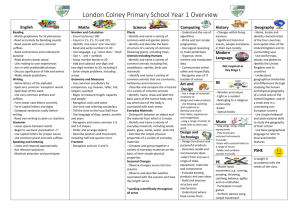
Long Term Plan 2014-2015: Year__4____ Theme: The Past Theme: The World Around Us Theme: The Here and Now History Across KS2 Changes in Britain from the Stone Age to the Iron Age. The Roman Empire and its Impact on Britain. Britain’s settlement by Anglo Saxons and Scots. The Viking and Anglo Saxon struggle for the Kingdom of England. A local history study. A study of a theme in British history. Early Civilizations achievements and an in-depth study of one of the following: Ancient Sumer; The Indus Valley; Ancient Egypt; The Shang Dynasty. Ancient Greece. A non- European society that contrasts with British history chosen from: Early Islamic Civilization • Mayan Civilization • Benin. To investigate and interpret the past Use evidence to ask questions and find answers to questions about the past. Suggest suitable sources of evidence for historical enquiries. Use more than one source of evidence for historical enquiry in order to gain a more accurate understanding of history. Describe different accounts of a historical event, explaining some of the reasons why the accounts may differ. Suggest causes and consequences of some of the main events and changes in history. To build an overview of world history Describe changes that have happened in the locality of the school throughout history. Describe the social, ethnic, cultural or religious diversity of past society. Describe the characteristic features of the past, including ideas, beliefs, attitudes and experiences of men, women and children. To understand chronology Place events, artefacts and historical figures on a time line using dates. Understand the concept of change over time, representing this, along with evidence, on a time line. Use dates and terms to describe events. To communicate historically Use appropriate historical vocabulary to communicate, including: Dates, time period era, change, chronology. Use literacy, numeracy and computing skills to a good standard in order to communicate information about the past. Religious Education Christianity/generic- What religions are represented in our neighbourhood/Sheffield Possible links to philosophy Christianity- How do Christians find meaning in the accounts and stories of Jesus’ birth? Hinduism- How does worship help Hindus? Links to India topic Christianity- Why is Easter so important for Christians?) Judaism- What is one of the most important events in Jewish history and how do Jewish people celebrate Passover? Islam- What are the 5 Pillars of Faith? Geography To investigate places Science Working Scientifically To ask relevant questions and use different types of scientific enquiries to answer them To set up simple practical enquiries, comparative and fair tests To make systematic and careful observations and, where appropriate, taking accurate measurements using standard units, using a range of equipment, including thermometers and data loggers To gather, record, classify and present data in a variety of ways to help in answering questions To record findings using simple scientific language, drawings, labelled diagrams, keys, bar charts, and tables To report on findings from enquiries, including oral and written explanations, displays or presentations of results and conclusions To use results to draw simple conclusions, make predictions for new values, suggest improvements and raise further questions To identify differences, similarities or changes related to simple scientific ideas and processes To use straightforward scientific evidence to answer questions or to support their findings. Living Things and their Habitats To recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways To explore and use classification keys to help group, identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment To recognise that environments can change and that this can sometimes pose dangers to living things. Animals Including Humans To describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans To identify the different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions To construct and interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey. States of Matter To compare and group materials together, according to whether they are solids, liquids or gases To observe that some materials change state when they are heated or cooled, and measure or research the temperature at which this happens in degrees Celsius (°C) To identify the part played by evaporation and condensation in the water cycle and associate the rate of evaporation with temperature. Sound To identify how sounds are made, associating some of them with something vibrating To recognise that vibrations from sounds travel through a medium to the ear To find patterns between the pitch of a sound and features of the object that produced it To find patterns between the volume of a sound and the strength of the vibrations that produced it. To recognise that sounds get fainter as the distance from the sound source increases Electricity To identify common appliances that run on electricity To construct a simple series electrical circuit, identifying and naming its basic parts, including cells, wires, bulbs, switches and buzzers To identify whether or not a lamp will light in a simple series circuit, based on whether or not the lamp is part of a complete loop with a battery To recognise some common conductors and insulators, and associate metal with being good conductors Ask and answer geographical questions about the physical and human characteristics of a location. Explain own views about locations, giving reasons. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features. Use fieldwork to observe and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies. Use a range of resources to identify the key physical and human features of a location. Name and locate the countries of Europe and identify their main physical and human characteristics. To investigate patterns Describe geographical similarities and differences between countries. Describe how the locality of the school has changed over time. To communicate geographically Describe key aspects of: • physical geography, including: rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes and the water cycle. • human geography, including: settlements and land use. Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, symbols and key to communicate knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world. MFL (Target language: Spanish) Listen attentively to spoken language and show understanding by joining in and responding Explore the patterns and sounds of language through songs and rhymes and the link the spelling, sound and meaning of words. Engage in conversations; ask and answer questions; express opinions and respond to those of others; seek clarification and help. Speak in sentences using familiar vocabulary, phrases and basic language structures. Develop accurate pronunciation and intonation so that others understand when they are reading aloud or using familiar words and phrases. Present ideas and information orally to a range of audiences. Read carefully and show understanding of words, phrases and simple writing. Appreciate stories, songs, poems and rhymes in the language. Broaden their vocabulary and develop their ability to understand new words that are introduced into familiar written material, including through using a dictionary. Write phrases from memory, and adapt these to create new sentences, to express ideas clearly. Describe people, places, things and actions orally and in writing. Understand basic grammar appropriate to the language being studied, including (where relevant): feminine, masculine and neuter forms and the conjugation of high-frequency verbs; key features and patterns of the language; how to apply these, for instance, to build sentences; and how these differ from or are similar to English.