Author year
advertisement
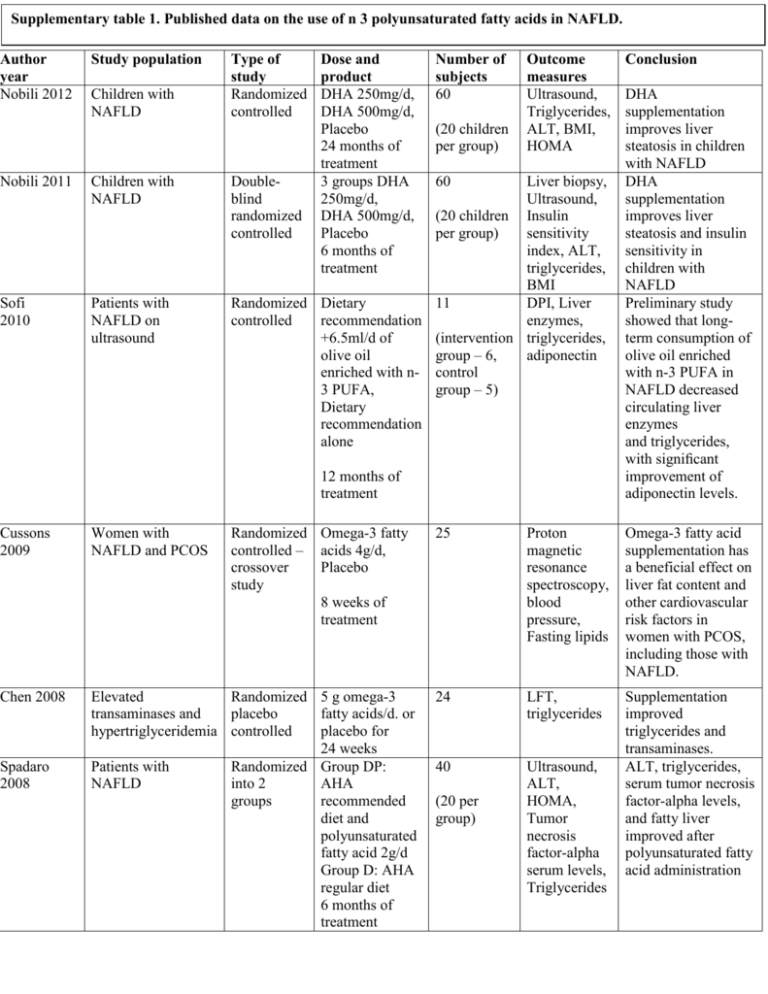
Supplementary table 1. Published data on the use of n 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in NAFLD. Author year Nobili 2012 Study population Children with NAFLD Nobili 2011 Children with NAFLD Sofi 2010 Patients with NAFLD on ultrasound Type of study Randomized controlled Doubleblind randomized controlled Dose and product DHA 250mg/d, DHA 500mg/d, Placebo 24 months of treatment 3 groups DHA 250mg/d, DHA 500mg/d, Placebo 6 months of treatment (20 children per group) Outcome measures Ultrasound, Triglycerides, ALT, BMI, HOMA Liver biopsy, Ultrasound, (20 children Insulin per group) sensitivity index, ALT, triglycerides, BMI Randomized Dietary 11 DPI, Liver controlled recommendation enzymes, +6.5ml/d of (intervention triglycerides, olive oil group – 6, adiponectin enriched with n- control 3 PUFA, group – 5) Dietary recommendation alone 60 12 months of treatment Cussons 2009 Women with NAFLD and PCOS Chen 2008 Elevated Randomized 5 g omega-3 transaminases and placebo fatty acids/d. or hypertriglyceridemia controlled placebo for 24 weeks Patients with Randomized Group DP: NAFLD into 2 AHA groups recommended diet and polyunsaturated fatty acid 2g/d Group D: AHA regular diet 6 months of treatment Spadaro 2008 Number of subjects 60 Randomized Omega-3 fatty controlled – acids 4g/d, crossover Placebo study 8 weeks of treatment Conclusion DHA supplementation improves liver steatosis in children with NAFLD DHA supplementation improves liver steatosis and insulin sensitivity in children with NAFLD Preliminary study showed that longterm consumption of olive oil enriched with n-3 PUFA in NAFLD decreased circulating liver enzymes and triglycerides, with significant improvement of adiponectin levels. 25 Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, blood pressure, Fasting lipids Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation has a beneficial effect on liver fat content and other cardiovascular risk factors in women with PCOS, including those with NAFLD. 24 LFT, triglycerides 40 Ultrasound, ALT, HOMA, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha serum levels, Triglycerides Supplementation improved triglycerides and transaminases. ALT, triglycerides, serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels, and fatty liver improved after polyunsaturated fatty acid administration (20 per group) Zhu 2008 Capanni 2009 Tanaka 2008 Vega 2008 Patients with NAFLD and hyper lipidemia Patients with NAFLD Randomized Group A: controlled recommended diet and 2g n-3 PUFA from seal oils 3x/d Group B: recommended diet and 2g placebo 3x/d Open label 134 n-3 PUFA from seal oils is beneficial for patients with NAFLD associated with hyperlipidemia and can improve symptoms scores, ALT, serum lipid levels, and normalize US evidence. 24 weeks of treatment Symptom scores, ALT, (66 in Group AST, GGT, A, 68 in Serum lipid Group B) levels, Ultrasound, Weight, Fasting blood glucose, Renal function, CBC n-3 PUFA 1g/d 56 Supplementation with n-3 PUFA improves biochemical, sonographic and haemodynamic abnormalities in liver steatosis 12 months of treatment Patients with biopsy proven NASH Open label EPA 2700mg/d 23 12 months of treatment Patients with elevated liver fat on MRI Open label 9g/d of fish oil 8 weeks of treatment 22 AST, ALT, GGT, Triglycerides, FG, n-6/n-3, Ultrasound, Liver perfusion by DPI, Food questionnaire, BMI Liver biopsy, ALT, FFA, TNF receptor 1 & 2, ferritin, thioredoxin, HOMA, plasma glucose, insulin, adiponectin, Weight MRI, Lipoproteins, Adiponectin, Triglycerides Beneficial for patients with NASH due to antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties N-3 fatty acids at high doses lower plasma triglyceride levels, but there are no significant decreases in hepatic triglyceride content for the group as a whole. Plasma triglyceride lowering is uniform but liver response is more variable. DHA docosahexaenoic acid; NAFLD non alcoholic fatty liver disease; ALT alanine amino transferase; BMI body mass index; HOMA homeostatic model of assessment; PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acids; BP blood pressure; PCOS poly cystic ovary syndrome; LFT liver function tests; DP diet and PUFA; AHA American heart association; AST aspartate amino transferase; GGT gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; FFA free fatty acids; TNF tumor necrosis factor α; NASH non alcoholic steatohepatitis; MRI magnetic resonance imaging; DPI Doppler perfusion index.











