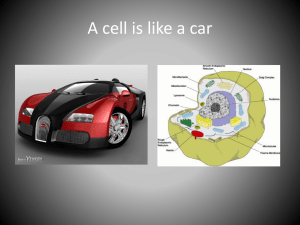
Year 7 Learning List: Cells
advertisement

7A Keyword learning list: Tissues and transplants Key word adaptation Sounds like add app tay shun Meaning The changes in structure that make it better at doing its job. cell sell The smallest independent part of an organism. The building blocks which living things are made from. cell membrane sell mem bray nnn The thin outer layer that holds the cell together and controls what enters and leaves the cell. cell wall sell wall Plant cells have a tough, rigid outer coat that protects and supports the cell and its shape. cytoplasm site O plaz em The jelly-like substance within cells where chemical reactions take place. focus foe kuss Bringing images that look blurry to the eye to the point where details become clear and sharp. magnification mag niff ick ay shun How much bigger a microscope makes an image appear. microscope my crow sko prr An optical device that allows really tiny objects to be magnified and become visible to the naked eye. nucleus new clee us The ‘control centre’ of the cell which also contains the nuclear material or DNA of the cell. Plural: nuclei. organ or gann A large part of a plant or animal that carries out a specific job for the organism. It is made from different cellular tissues that work together. tissue tiss you A large number of identical cells working together to carry out a particular job for the organism. vacuole vack U ole A bag-like structure found in plant cells. It is used to store fluids like water. chloroplast klor O plarst chlorophyll klor O fill neuron new ron root hair cell Circulatory system Digestive system root hare sell Sir q larity sistem Die jess tive sistem Green disc containing chlorophyll, found in plant cells. This is where the plant makes food using photosynthesis. Green substance found inside chloroplasts. It traps light energy from the Sun to power photosynthesis. a cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses A cell specialised to absorb water in plants A system that circulates blood through the body, consisting of the heart and blood vessels A system responsible for the ingestion, digestion, and absorption of food. 7E Keyword learning list: Acids and Alkalis Key word Sounds like Meaning aa sid acid An aqueous solution containing hydrogen ions (H+). Acids have a sour or sharp taste, turn blue litmus red and have a pH below 7. alkali ale ker lie corrosive core row siv hazardous haz ard uss A substance or situation that could cause harm to health, life or the environment. hydrogen ion hy drow jen I on The positively charged particle of hydrogen. If present it makes things acidic. hydroxide ion hy drox ide I on The negatively charged particle of hydrogen and oxygen. If present it makes thing alkaline. irritant ear rit ant A substance that causes irritation to skin and eyes. neutral new trull A substance or solution that is neither acidic nor alkaline. It has a pH of 7. neutralisation new trull I zay shun A chemical reaction where an acid and alkali react to form a neutral salt and water. pH scale P H sk ale The scale used to measure the strength of acidity or alkalinity of a substance. Numbers below 7 are acids. Numbers above 7 are alkalis. salts sol t’s Chemical compounds made when acids react with alkalis. universal indicator U nee ver sull in dee kay tor A mixture of indicators giving a different colour depending on how weak or strong an acid or alkali is. Risk assessment Litmus paper Risk as es meant Assessment of the risks involved in a practical investigation a colouring material (obtained from lichens) that turns red in acid solutions and blue in alkaline solutions; used as a very rough acid-base indicator Lit mos paper The chemical opposite of an acid. An aqueous solution containing hydroxide ions (OH-). Alkalis have a bitter taste, turn red litmus blue and have a pH above 7. Substances that attack and damage metals, stonework and skin on contact. 7I Keyword learning list: : Energy and sustainable living Key word coal Sounds like kole Meaning A carbon based fossil fuel formed from ancient trees buried millions of years ago. When it is burnt it releases energy as heat and light. conserved con sur v‘d Not used, lost or wasted. energy en ur G The word used to describe what makes thing work. fossil fuel foss ill few ell fuel few ell Coal, oil and natural gas – all fuels formed from the remains of dead plants and animals. They all release energy when burnt. They take millions of year to form and are classed as non-renewable. Anything that stores energy that can be converted into heat energy, e.g. fossil fuels, nuclear and biofuels. joule jool The unit for measuring energy. Symbol, J. natural gas nat chur al gass Fossil fuel formed from the remains of dead plants and animals that lived in the sea millions of years ago. non renewable non ree new A bull Any energy resource that will run out and we cannot renew our supplies of it, e.g. oil. oil oy ull Fossil fuel formed from the remains of dead plants and animals that lived in the sea millions of years ago. renewable ree new A bull An energy source that will never run out or can be regrown, e.g. solar power, wood. transfer trans fur To move from one place to another. For example when a fuel burns, energy stored in the fuel is transferred to the thing being heated. variable vair E A bull A factor which can change or be changed in an experiment. biomass Bi O mass hydroelectric Hi dro e lek trick Plant material, vegetation, or agricultural waste used as a fuel or energy source. Generating electricity by conversion of the energy of running water. geothermal Ge O fer mal solar cells So lar sells power is produced by pumping water into cracks in the Earth's crust and then pumping the heated water or steam back to the surface to drive turbines a cell that converts solar energy into electrical energy 8A Keyword learning list: Food glorious food! Key word Sounds like Meaning ab zorp shun absorption When small, soluble molecules go through pores in the membrane of the small intestine into the blood. by ul bile A bitter-tasting, dark green to yellowish brown fluid that is produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder to aid the digestion of fats and lipids. car bow hy dray’t carbohydrate An organic compound that contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and is the nutrient that is used as the main source of energy. die jess chun digestion The mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller soluble substances that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. fat fat A nutrient that is used as a high energy store. It also helps to keep heat in our bodies and to protect organs from physical shocks. gall blad der gall bladder A small storage organ that sits below the liver and aids fat digestion. large intestine lar dge in tess tyne liver liv er mineral min er al Nutrients, elements or compounds, needed in small quantities for good health, e.g. calcium. oesophagus ooo sof urg us Tube that goes from the mouth to the stomach. Also called the gullet or food pipe. protein pro teen A nutrient that is used for growth and repair of cells. small intestine sm all in tess tyne starch star chh Organ where most digestion happens. The soluble substances produced by digestion are absorbed in the body here. Also called the ileum. Type of insoluble carbohydrate found in plants. stomach stum ack Organ containing strong acid that mixes food up and digests proteins. sugar shug er Type of soluble carbohydrate. Glucose is an example of a sugar. enzyme En zime Biological catalyst to speed up biological reactions The second to last part of the digestive system where water is removed from the indigestible food matter. Biggest internal organ that makes and destroys many substances in the body. vitamin vit urm in Nutrients needed in small quantities for health, e.g. vitamin C. Balanced diet Bal ant sed die et Circulatory system Sir q larity sistem A diet that consists of the right balance of the food groups A system that circulates blood through the body, consisting of the heart and blood vessels 8E Keyword learning list: In the drink Key word Dissolve filtering Sounds like Dis ol v Fil ter ring compound com pow n’d insoluble soluble Solute In sole u ball Sole u ball Sole U t solvent Sole molecule mol E q’all saturated Sat you rated chromatography Krome A tog rap he structure struck chur Meaning Solute to pass into solution. A porous material through which a liquid or gas is passed in order to separate the fluid from suspended particulate matter A substance that can be split up into simpler substances. A chemical that cannot be dissolved A chemical that can be dissolved A substance that is dissolved in another substance (a solvent), forming a solution A substance in which another substance is dissolved in, forming a solution. Two or more atoms joined together. a solution that is unable to dissolve more of a solute. A technique used to separate the components of a chemical mixture by moving the mixture along a stationary material The shape and arrangement of particles or how they are organised. 8I Keyword learning list: Heat Transfers Key word absorb Sounds like ab zorb Meaning When energy is ‘soaked up’ or ‘taken in’. If something absorbs light it soaks it up and does not let it back out. Celcius sell see us A scale of temperature. Unit is ºC. conduction con duck shun The way heat travels through solids. convection current con vek shun curr rent A current created by heat causing changes in the density of a fluid. density den sit E The amount of mass that 1 cm3 of a substance has. Measured in g/cm3. emit E mitt To give out energy. Infra Red radiation in frar red ray D A shun A ‘colour’ of light beyond red. We can feel this as heat but we cannot see it. It can travel through transparent things and a vacuum (space). temperature tem purr at chur How hot something is, measured in ºC. thermal conductor thur mal con duck tor Another word for a heat conductor. thermal expansion thur mal ex pan shun How an object gets bigger as it gets hotter. thermal insulator thur mal in sue lay tor A material that does not let heat energy flow through it easily. thermometer thur mom eat er A device for displaying how much heat energy a substance contains. joules expand contract jewls X pand Kon tracked The unit of energy or work done To increase the size or volume To decrease in size or volume