introduction of immunology
advertisement

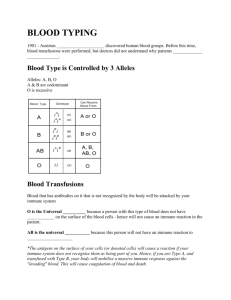
Dr.Fadwah AlGhalib Basic Immunology 2nd yr 2011 (1st Lecture) Introduction of the immune system Objectives: 1-Define what is immunology? What is Immunity? What is Antigen? What is antibody? Homeostasis? 2- Define the terms , "intra" and " extra" cellular pathogens, immune response and inflammation? 3- Describe and classify the cells of the immune system. 4- Classify the elements of the immune system in regarding to : a. the type of the pathogen recognition " specific or non-specific immune response" b. the type of the immunological element involved in the immune response either cellular or humoral (non-cellular). 5- Explain the "main functions" of the immune system. --------------------------------------- Definitions: Immunology: is the study of the immune system System: The whole unit which composed of different elements to perform a specific function. [ e.g: respiratory system, digestive system, immune system..etc...] Immune system: is a collection of cellular elements & non cellular (humoral) elements. They do not interact with self components, but respond ( interact) to non-self components and destroy them. Immune Response: the reaction of an organism's body to foreign materials (antigens), including the production of antibodies Immunity: The ability of the body to defend itself against specific invading agents such as bacteria, toxins, viruses and foreign tissues. Antibody: are proteins that are formed in response to an antigen and that react specifically with that antigen 1 Dr.Fadwah AlGhalib Basic Immunology 2nd yr 2011 Antigens: are substances that can stimulate an immune response, that react specifically by binding to effector molecules (antibodies) and effector cells ( T lymphocytes). Intracellular pathogens: enter inside the human cells and multiply. [ All viruses and some protozoan, some bacteria,] Extracellular pathogens: Exist outside the host cells (human cells). [ large parasites, and many bacteria] they live in tissues & body's fluid.] Where exactly in our body do these pathogens lives and multiply???? Define Homeostasis? Hemeos (the same) stasis (standing): Is the maintained steady-state conditions existing in healthy individuals. What are the functions of the immune system? a. Surveillance (recognition of non-self) the antigen b. Defence: initiating an immune response, The immune system can eliminate threats by isolation, disruption, or ingestion or by combination of the three actions c. Regulation: i--control of the immune responses to maintain hemeostasis, and return the immune system to a state that existed before the antigenic stimulation. ii--To prevent tissue injury that may result from an exaggerated immune Response. d. Immunity (immunological memory): state of resistance (acquired protection) following exposure to a stimulating agent e. Tolerance: induction of a state of unresponsiveness toward certain antigens (mainly self-antigens) 3-What are the cells of the immune system? Agranular Leukocytes and Granular Leukocytes Agranular Leukocytes: Plasma cells Monocytes (are phagocytic cells in circulation) in tissues are Macrophages Dendritic cells ( are phagocytic cells) Lymphocytes (T, B, & NK cells) Granular Leukocytes: Neutrophils , Basophils, Eosinophils 4-What are the types of the immune responses? a. Natural- innate- (non-specific) b. Adaptive- acquired- (specific) 2 Dr.Fadwah AlGhalib Basic Immunology 2nd yr 2011 What are the cellular components for each immune responses? 1) Natural immunity: 1- Cells: I) Phagocytic cells ( internalize pathogen and kill) & others do not. It is classified into 2 types according to their nuclear shapes and number. a- polymorphonuclear phagocytes: includes Neutrophils (short lived cells) and Eosinophils. b- Mononuclear phagocytes: includes Monocytes and macrophages (long lived cells) and dendritic cells. II) Non-phagocytic cells: a- Auxiliary cells such as Mast cells, Basophiles, & platelets b- Tissues cells (some epithelial cells). 2- Soluble molecules:- Complement [is the major humoral non-specific defence mechanism] - 2) Adaptive Immunity: There are two major branches of the adaptive immune responses: a- humoral immunity and b- cell-mediated immunity. a- Humoral immunity: involves the production of antibody molecules in response to an antigen and is mediated by B-lymphocytes Some components of the humoral immunity ( Soluble mediators' of immunity): 1- immunoglobulins ( IgA, IgG, IgM, IgD, IgE) 2- Cytokines ( interferone, interlukines, & colony stimulating factors) 3- Acute phase proteins ( C-reactive proteins) 4- Complement (C1-C9) b- Cell-mediated immunity: includes the LYMPHOCYTES. B CELLS, AND T CELLS. i- B CELLS: differentiate to plasma cells which produces the soluble immunoglobulins. ii- T CELLS: 3 Dr.Fadwah AlGhalib Basic Immunology 2nd yr 2011 There Are Four Main Types Of T-Cells: a- Helper T-cells –. 1) They secrete lymphokines (cytokines) which are hormones that stimulate other cells in the body to resist invading antibodies. 2) They display the protein CD4 on their surface; 3) which assist in both cell mediated immunity (CMI) and Antibody-mediated immunity (AMI). b- Killer T-cells – 1) which kill antigens directly once stimulated by agents released by the helper T-cells. 2) They display the protein CD8 on their surface; c- Suppressor T-cells – are a controversial cell that is believed to dampen or suppress the immune response d- Memory T-cells - which recognise the original invading antigen. When the antigen returns thousands of memory cells are available to initiate a far swifter reaction than occurred during the first invasion. 4