Verbo
advertisement
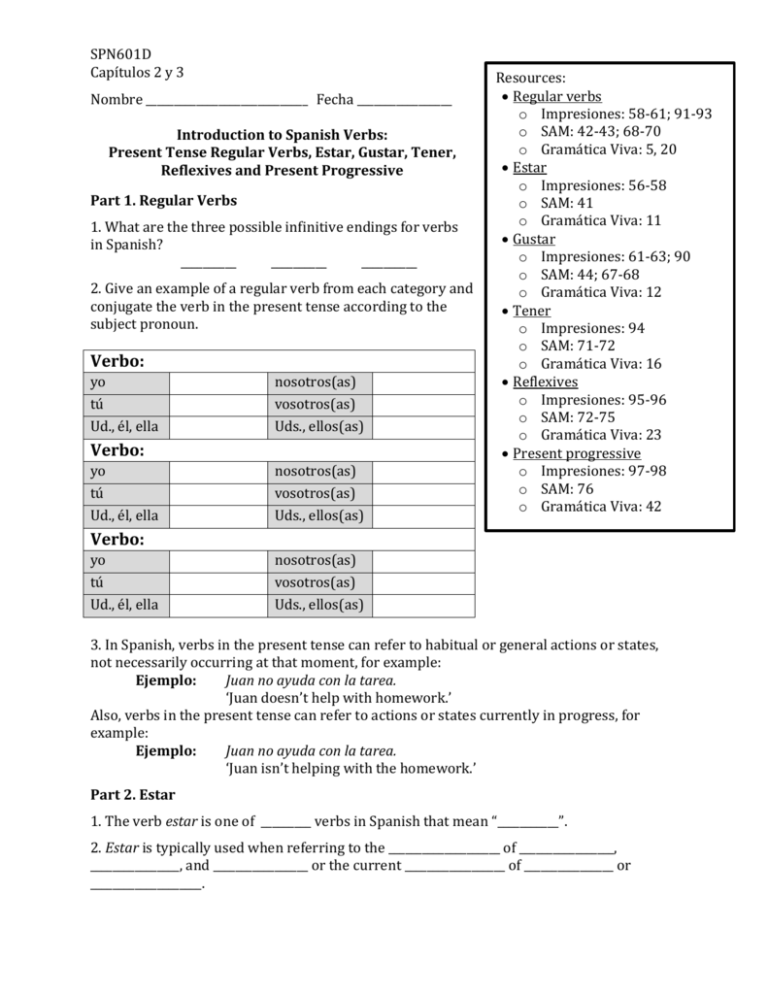
SPN601D Capítulos 2 y 3 Nombre _____________________________ Fecha _________________ Introduction to Spanish Verbs: Present Tense Regular Verbs, Estar, Gustar, Tener, Reflexives and Present Progressive Part 1. Regular Verbs 1. What are the three possible infinitive endings for verbs in Spanish? __________ __________ __________ 2. Give an example of a regular verb from each category and conjugate the verb in the present tense according to the subject pronoun. Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) Resources: Regular verbs o Impresiones: 58-61; 91-93 o SAM: 42-43; 68-70 o Gramática Viva: 5, 20 Estar o Impresiones: 56-58 o SAM: 41 o Gramática Viva: 11 Gustar o Impresiones: 61-63; 90 o SAM: 44; 67-68 o Gramática Viva: 12 Tener o Impresiones: 94 o SAM: 71-72 o Gramática Viva: 16 Reflexives o Impresiones: 95-96 o SAM: 72-75 o Gramática Viva: 23 Present progressive o Impresiones: 97-98 o SAM: 76 o Gramática Viva: 42 Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) 3. In Spanish, verbs in the present tense can refer to habitual or general actions or states, not necessarily occurring at that moment, for example: Ejemplo: Juan no ayuda con la tarea. ‘Juan doesn’t help with homework.’ Also, verbs in the present tense can refer to actions or states currently in progress, for example: Ejemplo: Juan no ayuda con la tarea. ‘Juan isn’t helping with the homework.’ Part 2. Estar 1. The verb estar is one of _________ verbs in Spanish that mean “___________”. 2. Estar is typically used when referring to the ____________________ of _________________, ________________, and _________________ or the current __________________ of ________________ or ____________________. SPN601D Capítulos 2 y 3 3. Forms of estar Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) 4. When used with an adjective, the adjective must agree in ____________________ and _______________________ with the noun it’s describing. 5. How would you write the following in Spanish using the verb estar? a. I am at the library. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Are you at the cafeteria? _________________________________________________________________ c. She is at the stadium. _____________________________________________________________________ d. We (nosotros) are happy (contento). ___________________________________________________ e. You (vosotros) are happy (feliz). ________________________________________________________ f. They (ellas) are angry (enojado). ________________________________________________________ Part 3. Gustar 1. The verb gustar can be used to refer to ________________ and dislikes. 2. With reverse psychological verbs like gustar, the subject (i.e., the stimulus) typically comes __________________ (after/before) the verb, and the object (i.e., the experiencer) comes _____________________ (after/before) the verb, for example: Ejemplo: Indirect object A Juan le gusta la clase de español. Juan (experiencer) likes Spanish class (stimulus). Indirect object pronoun Subject 3. The indirect object is generally omitted but can be used for pragmatic purposes, such as, to introduce the topic of the sentence, clarify an ambiguous indirect object pronoun, or emphasize who likes or dislikes something. 4. Forming the verb gustar: Verbo: a mí a ti a Ud., a él, a ella me gusta(n) a nosotros(as) a vosotros(as) a Uds., a ellos(as) SPN601D Capítulos 2 y 3 When used with a verb, the third person singular form of gustar is used: ___________ When used with a noun, the form of gustar depends on if the noun (the subject) is _________________ or _________________. If there is one noun and it is singular, then use _______________. If the noun is plural or there is more than one noun, then use _______________. 5. How would you write the following sentences in Spanish? a. I like to run. ________________________________________________________________________________ b. I like to run and eat. ______________________________________________________________________ c. I like Spanish. ______________________________________________________________________________ d. I like Spanish and English. _______________________________________________________________ e. I like Math. _________________________________________________________________________________ Part 4. Tener Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) The verb tener is often used in idiomatic expressions. Which of the following expressions deals with obligation and which deals with desire? a) tener que: Tengo que trabajar los viernes1. __________________________ b) tener ganas de: Tenemos ganas de relajarnos2. __________________________ What form of the verb is used with these particular expressions? _________________________ a. Tengo que trabajar los viernes. b. Tenemos ganas de relajarnos. Part 5. Reflexives 1. Reflexive verbs generally refer to actions that you do to or for oneself and appear with a reflexive pronoun. 2. The reflexive pronoun agrees with the ______________________ of the verb. 3. List the reflexive pronouns: _______, ________, ________, ________, 1 2 ‘I have to work on Fridays.’ ‘We feel like relaxing.’ os , ________ SPN601D Capítulos 2 y 3 4. Form the verb bañarse (‘_______________________’) in the present tense: Verbo: yo tú Ud., él, ella nosotros(as) vosotros(as) Uds., ellos(as) 5. In a verb phrase with two (or more) linked verbs, the reflexive pronoun can appear ___________________ the conjugated verb OR ______________________ to the infinitive. Ejemplo 1: I have to shave. ________________________________________________ or ________________________________________________ Ejemplo 2: He likes to have fun. ________________________________________________ Part 6. Present Progressive Only used to refer to activities in which one is engaged at a specific time. Formed using a form of the verb ________________ (to be) along with the present participle of the activity verb. Present participle: Remove the infinitive ending and add ___________ (–ar verbs) or ___________ (–er and –ir verbs). Hablar ___________________ Comer ____________________ Escribir____________________ How would you write the following sentences in Spanish? a. I am talking. ______________________________________________________________________________. b. Are you eating a hamburger? __________________________________________________________. c. She is writing. ____________________________________________________________________________. d. We are reading. __________________________________________________________________________. e. They are washing their hands. (OJO: Careful with accents!) i) __________________________________________________________________________. (or) ii) __________________________________________________________________________. f. They are getting dressed. (OJO: Careful with accents!) i) __________________________________________________________________________. ii) __________________________________________________________________________. (or)