4Electrochemistry
advertisement

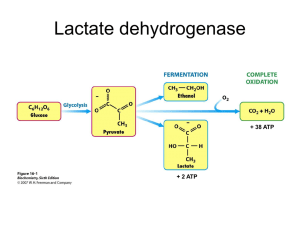
Balance the following reactions using the half reaction method: Identify which species is oxidized, which is reduced, which is the oxidizing agent and which is the reducing agent. Balance in an acidic solution using the half reaction method: For this one balance it for a basic solution . Rebalance this one in an acidic solution, keeping it together instead of using the half reaction method: Here is an example of a reaction where it would be very difficult to try and separate the half reactions. Balance it in an acidic solution The standard reduction potential of a zinc electrode is -0.76 V. Given that the standard potential of the cell where Zn is oxidized and Sn4+is reduced to Sn2+ is +0.91V find the standard potential of the Sn4+/Sn2+ half reaction and write the cell diagram. Calculate the standard free-energy change for the following reaction at 25oC using standard reduction potentials. 2𝐴𝑢3+ (𝑎𝑞 ) + 3𝑀𝑔 (𝑠) 2𝐴𝑢(𝑠) + 3𝑀𝑔2+ (𝑎𝑞) Calculate the pressure of H2 in atm, required to maintain equilibrium with respect to the following reaction at 25oC, Given that [Pb2+]=0.035 and the solution is buffered at pH 1.6 Calculate the reaction quotient Q for the cell reaction, given the measured values of the cell potential. How many grams of aluminum can be deposited by the passage of 105 C through an electrolytic cell? How long does it take to deposit 0.63 g Ni on a decorative drawer handle when 8.7 A are passed through a Ni(NO3)2 solution Chapter Capstone Example Problem: Many important biological reactions involve electron transfer. Because the pH of bodily fluids is close to 7,the “biological standard potential” of an electrode E, E*, is measured at pH=7. a) Calculate the biological standard potential for the reduction of hydrogen ions to hydrogen gas, b) and the reduction of nitrate ions to NO gas. Calculate the biological standard potential E* for the reduction of the biomolecule NAD+ to NADH in aqueous solution. The reduction half reaction under thermodynamic standard conditions is NAD+(aq)+H+(aq)+2e-NADH (aq), with Eo= 0.099V. The pyruvate ion, CH3C(=O)CO2-, is formed during the metabolism of glucose in the body. The ion has a chain of three carbon atoms. The central carbon atom has a double bond to a terminal oxygen atom and one of the end carbon atoms is bonded to two oxygen atoms in a carboxylate group. Draw the Lewis structure of the pyruvate ion and assign a hybridization scheme to each carbon atom. The lactate ion has a similar structure to the pyruvate ion, except that the central carbon is no attached to an –OH group: CH3CH(OH)CO2-. Draw the Lewis structure of the lactate ion and assign a hybrization scheme to the central carbon atom. During exercise the pyruvate ion is converted to lactate ion in the body by coupling to the half reaction for NADH given above. For the half reaction pyruvate+2H++2e-lactate, E*=-0.190 V. Write the cell reaction for the spontaneous reaction that occurs between these two biological couples and calculate E* and Eo for the overall reaction. Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction for the overall reactions in the above reaction. Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25oC for the reaction.