Genetics Part 2 Study Guide
advertisement

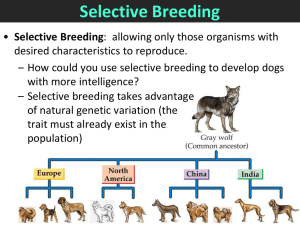
Genetics Part 2 Study Guide Name_________________________________________ Know how to read and interpret a pedigree. 1. What is selective breeding? (page 319) Allowing only those animals with desired traits to produce the next generation of offspring. 2. Why is selective breeding used? (page 319)To take advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation to pass on desired traits to the next generation. 3. Crossing breeding two organisms with very different traits is a process called Hybridization (page 319) 4. What is the ultimate source of gene variability? Mutations in DNA (page 307) 5. What process do breeders use in order to maintain desired traits? Selective breeding (page 320) 6. What is a clone? A member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell. (page 333) 7. How is a clone made? Take the nucleus out of an egg cell, replace it with a nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. Allow fusion and cell division then implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. (figure 13-13 on page 332) 8. What types of cells are used to make a clone? Somatic (body) cell and an Egg cell (figure 13-13 on page 332) 9. What is shown in a karyotype? All of an organisms chromosomes arranged in a pattern (large to small, and paired) (page 341) 10. What is the probability of an offspring being male? 50% (page 342) 11. What is a pedigree used to show? Relationships within a family and the passing on of a trait from generation to generation. (page 342) 12. True or False. A human can survive without an X chromosome. EXPLAIN your answer. FALSE, X chromosomes are vital for life, they carry a lot of necessary genes. (page 350) 13. What sex-chromosomes represent a male? Female? MALE = XY FEMALE = XX (page 341) ESSAY In what ways has selective breeding been useful to humans today and in the past? (page 319) *THIS IS THE ESSAY QUESTION ON THE TEST, YOU NEED TO PREPARE YOUR ANSWER* Genetics Part 2 Study Guide CROSSWORD PUZZLE ANSWER KEY ACROSS 2. Male 3. Selective Breeding 5. Hybridization 6. Twins 7. Fifty Percent 9. Phenotype 11. Inbreeding 13. Heterozygous 14. Mutations Down 1. Karyotype 4. Genotype 8. Homozygous 10. Pedigree 12. Female Name_________________________________________