Weather Unit – Test, Friday Jan. 16th Vocabulary – Put a check mark
advertisement

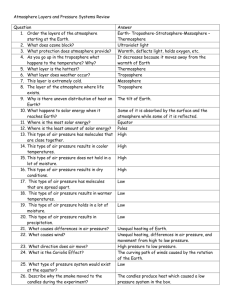
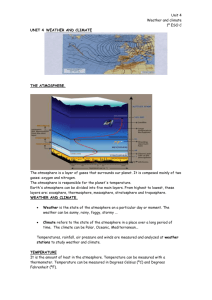
Weather Unit – Test, Friday Jan. 16th Vocabulary – Put a check mark in front of each word that we cover in class Climate – a description of the usual temperature, precipitation, and seasons of an area Polar – cold climates; the area surrounding the Earth’s poles Moderate/Temperate – medium climates Tropical – hot climates; the area surrounding the Earth’s equator Humid – wet Arid – dry Weather – a description of the atmosphere in a particular place at a particular time. Weather is a measure of temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind, and air pressure. Atmosphere – the layers of gases which surround the Earth; Weather occurs in the lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. Air mass – a huge body of air which has similar temperature, pressure, and humidity throughout. Air masses move and create new weather Thermometer – an instrument used to measure temperature Barometer – an instrument used to measure pressure Anemometer – an instrument used to measure wind speed Clouds – water vapor in the Earth’s atmosphere which collects on bits of dust. Clouds are visible because the water vapor condenses or freezes as it rises into the colder heights of the atmosphere Cirrus – wispy, feathery clouds Cumulus – puffy, heaps of clouds Stratus – spread out clouds which cover the whole sky Alto – high in the sky Nimbus – storm cloud Front – the boundary between two air masses; weather changes at fronts Local winds – winds that blow over short distances Global winds – winds that blow steadily in specific directions over long distances Doldrums – the area near the equator which has little to no wind Horse latitudes – calm air at 30◦ N and S latitude Trade winds – winds which blow from the Northeast to the equator in the Northern Hemisphere and southeast to the equator in the Southern Hemisphere Prevailing westerlies – winds which blow west to east across the midlatitudes of the Earth, including the United States Polar easterlies – winds which blow east to west across the polar regions of the Earth Jet stream – a steady wind which blows from west to east about 6 miles above the Earth’s surface Essential questions – What is the difference between climate and weather? How are clouds named? What global winds affect our area? How does air pressure affect the weather?