Reactions Review PAPsue
advertisement

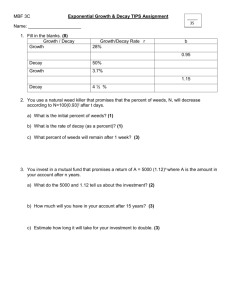
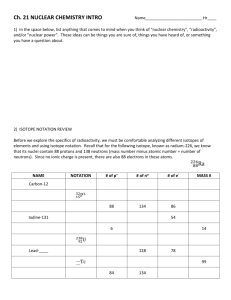
Name _______________________________________________ Period _______________ Reactions Review – PAP Directions: Identify the following as alpha, beta, gamma, or neutron. 1. 1 0 n 2. 0 1 e 3. 4 2 He 4. 0 0 γ 5. Nuclear decay with no mass and no charge 6. An electron 7. Least penetrating nuclear decay 8. Most damaging nuclear decay to the human body 9. Nuclear decay that can be stopped by skin or paper. 10. Nuclear decay that can be stopped by aluminum. Complete the following nuclear equations. 42 11. 19 0 K → 9 13. 4 -1 __________ 12. Be → Li 3 4 4 Pu → 94 9 He + __________ 2 235 231 Be + __________ 14. He + __________ 16. __________ → 92 U → _________ + Th 90 4 6 15. 239 e + → 2 142 Ba + 56 91 36 1 Kr + 3 n 0 Nuclear Decay Series 238 92U ↑ ↑ ↑ 234 90Th 234 91Pa The figure maps the radioactive decay of uranium-238 to lead-206. Use the figure to answer the following questions. 234 92U 218 84Po ↓ 214 82Pb ↑ ↑ ↑ 222 88Rn 226 90Pa ↑ ↑ ↑ 214 206 83Bi 82Pb 214 84Po ↑ ↑ 210 84Po ↓ 230 92Th 17. How many alpha particles are produced as one atom of uranium-238 decays to an atom of lead-206? 18. How many beta particles? 19. Explain why lead-206 is a stable isotope. 210 82Pb ↓ 20. When protactinium-229 goes through two alpha decays, francium-221 is formed. 210 83Bi Stable Iosotope 21. Write the nuclear equation for the decay of Po-210 if it undergoes 2 consecutive alpha decay followed by a beta decay followed by another alpha decay. 22. The decay chain (or series) of uranium-238 is shown in the following figure. What is the final product in this decay series? 23. Using the figure on the previous page, list each type of decay that uranium-238 goes through to become lead-206. 24 Determine whether the following equations represent fission or fusion. 3 He + 3 He → 4 He + 21 H 2 2 2 1 235 1 92U 1H + + 1 1 n 0 1H → → 90 2 H 1 38Sr + + 143 Xe 54 + 310n 0 β +1 Balancing Equations 1. NaCl + H2SO4 2. Sb + Cl2 SbCl3 3. H2 + Cl2 HCl 4. HCl + MnO2 MnCl2 + 5. HCl + Ca(ClO)2 6. CaF2 + H2SO4 HF 7. NaCl + H2O NaOH + KCl + 8. KClO3 9. SnCl2 + 10. HgO 11. NaBr + HgCl2 Na2SO4 + HCl H2O + Cl2 CaCl2 + H2O + + CaSO4 + Cl2 H2 O2 SnCl4 + Hg + O2 Cl2 NaCl + Hg2Cl2 Br2 Cl2 Writing Chemical Equations using formulas and symbols. Balance !!!!! 1. When solid magnesium carbonate is heated, it produces solid magnesium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. 2. Aqueous potassium bromide added to aqueous lithium iodide makes aqueous lithium bromide and aqueous potassium iodide. 3. When aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and calcium chloride are combined, aqueous calcium nitrate and silver chloride (a precipitate) are formed. 4. Aqueous potassium sulfate plus aqueous magnesium chloride makes a precipitate of magnesium sulfate and aqueous potassium chloride. 5. When aqueous solutions of iron (III) nitrate and sodium hydroxide are combined, the result is a precipitate, iron (III) hydroxide and aqueous sodium nitrate. Writing Chemical Equations in words. 6. 2Na3PO4(aq) + 3CaCl2 Ca3(PO4)2 ↓ + 6NaCl(aq) 7. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)