Ecology Terminology
advertisement

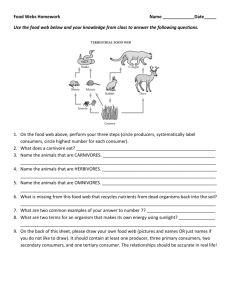
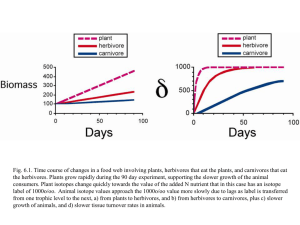
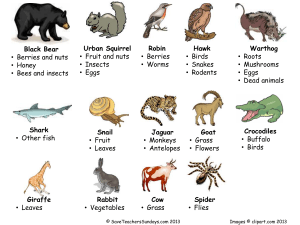
Ecology Terminology Ecology - The study of the interactions between organisms and their environment. Lesson 1 Biosphere – Where organisms live (air, land and water) Biomes – The largest ecological regions distinguished by characteristics of plants and animals. Ecosystems – All of the living and non-living things in a specific area. Ecotones – A transition zone between 2 ecosystems. Habitat – A place where an organism lives. Population – A group of the same species interacting and living in the same area. Community – Different populations living in the same area and how they interact with each other and their surrounding environment. Niche – An organism’s role in the ecosystem. Biotic- Living Abiotic – Non-living Lesson 2 Symbiotic relationships – interaction between species; The species will either interact, help or fight for survival. 1. Mutualism – Both species gain (honey bee – flower) 2. Commensalism – One species benefits and the other is not harmed but doesn’t benefit (chicken – egg) 3. Parasitism – One benefits and the other is harmed (mosquito – human) 4. Predator-Prey – One benefits the other is killed. (hawk – rabbit) A. Producer - a living thing that makes its own food from sunlight, air, and soil. Green plants are producers who make food in their leaves. B. Consumer - is a living thing that cannot make its own food. Consumers get their energy by eating food. All animals are consumers. Carnivores are animals that eat mostly meat. Examples of carnivores: wolves, foxes, lions, tigers, eagles, storks, pelicans, snakes, penguins. Herbivores are animals that eat plants. Examples of herbivores: cows, horses, goats, rabbits, zebras. Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. Examples of omnivores: pigs, grizzly bears, humans raccoons, opossums C. Decomposer - is a living thing that gets energy by breaking down dead plants and animals. Examples - Fungi and bacteria Lesson 3 Adaptations – The ability of an organism to adjust to become more suited to an environment.