Pregnancy and Isolation
advertisement

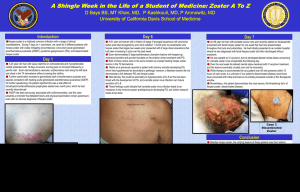
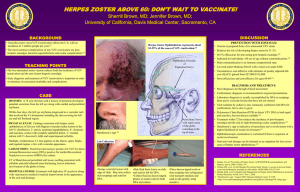
Pregnancy, Isolation and You Pregnant healthcare workers ARE NOT at greater risk of contracting infectious diseases than are other healthcare workers who are not pregnant; however, if a healthcare worker develops an infection such as HIV, Varicella, Hepatitis B, CMV, or Rubella during pregnancy, the infant may be at risk of becoming infected. Because of this risk, pregnant healthcare workers should be especially familiar with and strictly adhere to precautions to minimize the risk of transmission of infectious diseases. Work reassignment is generally not necessary Pregnant women SHOULD NOT work with patients who have Varicella infection without serologically documented immunity to Varicella Zoster Virus. Pregnant healthcare workers who have questions regarding exposure in the hospital should contact Infection Prevention & Control. Department. INFECTION AIDS (acquired immune deficiency Syndrome) INTERVENTION No restriction is necessary Chicken pox If exposed to herpes zoster or varicella, employees with negative or unknown history of chickenpox should notify Employee Health Reassignment is not necessary for infection prevention purposes Cytomegalovirus COMMENTS Transmission does not occur via casual contact or from inanimate objects. Wear protective attire when contact with blood and body substances is anticipated. Restriction from patient contact is based on history of immunity and not on the pregnancy. The risk of getting CMV through casual contact is very small. The virus is usually passed from infected people to others through direct contact with body fluids, such as urine, saliva, or breast milk. CMV is sexually transmitted. It can also be spread through transplanted organs and blood transfusions. Hepatitis B Herpes Simplex Type II Employees who anticipate contact with blood/body fluids are urged to receive Hepatitis B vaccine prior to becoming pregnant No restrictions necessary Greater risk of acquisition is through contaminated needle sticks, blood exposures, or sexual contat. No risk via casual contact Transmission does not occur via casual contact or inanimate objects. Requires sexual contact for transmission.Greatest risk to the infant if at the time of birth if the mother has active genital herpes. If employees are unsure of history of chickenpox, serologic testing is available. Restriction is based on history of immunity and not on pregnancy Herpes Zoster(shingles) Patient care staff who have not had chickenpox should not have contact with patients with chickenpox or herpes zoster Rubella (German Measles) Patient care staff should not Women of childbearing age care for patients with rubella should be immune to rubella. until employee immunity is proven by blood test or documentation of vaccination No restriction necessary Person-to-person transmission does not occur. Greatest risk is from cat feces (emptying litter boxes) or from poorly cooked meat. No restriction necessary Wear a N-95 or approved fit tested mask. If exposed to herpes zoster Restriction from patient or varicella, employees with contact is based on history of negative or unknown history immunity and not on the of chickenpox should notify pregnancy. Employee Health Toxoplasmosis Tuberculosis Varicella-Zoster